РЕГИОНЫ РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ 2 страница
40. A: B: AI: R < -1
The best answer is A. Plug in a number for R. For example R = -2. Column A = 9 while column B = 5 and therefore column A is greater.
41.
A: The area of the triangle CBD B: The dotted area AI: AD = DE
The best answer is C. Focus on the triangle ABC and CBD. Both have the same base yet ABC has double the height, thus its area is doubled. The area of the dotted area is the area of ABC minus the area of CBD and therefore the dotted area is equal to the area of the triangle CBD.
42. A: The sum of the numbers in group X B: The sum of the numbers in group Z AI: Group X has 11 numbers with an average of 44. Group Z has 24 numbers with an average of 24.
The best answer is B. The sum is simply the amount of numbers multiplied by the average. The sum of the numbers in group X is 11 x 44 = 484 and the sum of the numbers in group Z is 24 x 24 = 576, which is greater.
43. A: 3Q of 15 in percent terms B: 25Q AI: Q is a natural positive number.
The best answer is B. 3Q out of 15 in percent terms is equal to
44. A: X B: -1 AI:
The best answer is A. The expression given to us can be easily simplified.
Compare the powers of both sides: 2X – 2 = 8X + 2.5 è 6X = -4.5 è X = -3/4 and therefore X is greater.
45. A: Y B: 14 AI: X and Y are two consecutive numbers. X2 – Y2 = 27
The best answer is B. Simplify the expression: X2 – Y2 = (X – Y)(X + Y) = 1(X + X – 1) = 2X – 1. 2X – 1 = 27 è 2X = 28 è X = 14 and Y = 13 and therefore column B is greater.
46. A: The sum of the digits X + Y B: The double digit number XY AI: XY is a positive double digit number
The best answer is B. Plug in some numbers. Say XY = 54 è X + Y = 9. Take a smaller number: XY = 11 è X + Y = 2. No matter which number you choose, the sum of the two digits cannot surpass the number itself and so the answer is B.
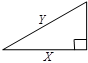
A: The area of the triangle:
B: The area of the triangle:
AI: Z < Y
The best answer is B. The height in the triangle of column A is The height in the triangle of column B is We know that Z<Y and so the height of the triangle in column B is greater and so is the area of the triangle since the bases are the same length (X).
48. A: X B: 3 AI: Y is a positive integer greater than 1.
The best answer is A. Simplify the expression:
In we want Y to be a positive integer we must eliminate the fraction-power and therefore X must be dividable by 4 and 2. Every number that is dividable by 4 is greater than 3 and so column A is greater.
49. A: X + Y + Z + W B: 8 AI: AI: (X + Y)(Z + W) = 21 X, Y, Z and W are positive integers.
The best answer is A. There is only one combination of numbers that will result in 21 and it’s 3 and 7. (X + Y) = 3 and (Z + W) = 7 or vise-versa. The expression in column A is equal to 3 + 7 = 10 and so column A is greater.
50. A: B:
The best answer is B. Column A = Column B =
1. A: Y – X B: X – Y AI: Y < X
The best answer is B. These kinds of questions are best solved by plugging in some numbers. For example: X=2 and Y=1. Column A = -1 while column B = 1 and therefore the answer is B.
2. A: XYZ B: X + Y + Z AI: X, Y and Z are negative integers.
The best answer is D. Try two sets of numbers: (-1, -1, -1) and (-4, -4, -5). The first set will give: A = -1 and B = -3 à column A is greater. The second set will give: A= -80 and B = -13 à column B is greater. When you get two different answers, mark D since the answer cannot be determined.
3. A: X – 1 B: 1 – X AI: -1 > X
The best answer is B. Replace X with any number smaller than -1, for example X = -2. Column A = -3 and column B = 3 and therefore the answer is B.
4. A: B: X + Y AI: X and Y are negative integers.
The best answer is A. Plug in numbers for X and Y, for example: X=-1 and Y=-2. Column A = -1/3 and column B = -3 and so column A is greater.
5. A: X/Y B: Y/X AI: 0 < X < 1 -1 < Y < 0
The best answer is D. Plug in numbers for X and Y. For example: X = ½ and Y = -1/2. Column A = -1 and column B = -1. It seems like the answer is C. Plug in different numbers: X = ½ and Y = -1/4. Column A = -2 and column B = -1/2 and so the answer cannot be determined.
6. A: 1 – K B: AI: 0 < K < 1
The best answer is B. Replace K with a number in the specified range: K = 1/2. Column A = 1 – ½ = ½. Column B = 1/(1 – ½) = 2. And so column B is greater.
7. A: B: AI: X > 1
The best answer is A. Column A can be written as X3/2. Column B can be written as X1/2. Since X > 1, column A is greater because it makes X bigger while column B makes X smaller.
8. A: A3 B: A2 AI: A is a positive integer
The best answer is D. Take two cases: A = 1 and A = 2. In the first case, column A and B are equal while in the second case column A is greater and therefore the answer cannot be determined.
9. A: 3Y B: 9Y2 AI: 0 < Y < 1/3
The best answer is A. Plug in a number, for example Y = ¼. Column A = 3/4 = 12/16. Column B = 9/16 and therefore A is greater.
10. A: A – (-7) B: B – (-3) AI: 0 < B < A
The best answer is A. Column A = A + 7 and column B = B + 3. Since A is greater column A must also be greater than column B. 11. A: X – (- 9) B: Y – (12) AI: 0 < Y < X
The best answer is D. Plug in two sets of numbers: (2, 1) and (10, 1) In the first set of numbers, A = 11 and B = 13 and so B is greater. In the second set of numbers, A = 19 and B = 13 and so A is greater. The answer cannot be determined and so the mark is D.
12. A: X – (-6) B: Y – (-4) AI: Y < X< 0
The best answer is A. Plug in numbers for X and Y, for example: X= -1 and Y= -2. Column A = 5 and column B = 2 and so column A is greater.
13. A: B: AI: 0 > Y > X
The best answer is B. Plug in numbers for X and Y, for example: X = -2 and Y = -1. Column A =
14. A: B: AI: 0 < Y < X
The best answer is B. Plug in numbers for X and Y, for example: X= 2 and Y= 1. Column A = -1/2 and column B = 1 and so column B is greater.
15. A: X – (Y + Z) B: X – Y + Z AI: X < Y < 0 < Z
The best answer is B. The easiest way is to plug in some numbers. X = -2, Y = -1 and Z = 5. Column A = -2 – (4) = -6. Column B = -2 + 1 + 5 = 4 and so this column is greater.
B. Fractions
16. A: 1/3 + 1/5 B: ½ + ¼
The best answer A. Column A = Column B =
17. A: 3/7 + 2/5 B: 2/3 + 1/5
The best answer is B. Column A = Column B =
18. A: B: AI:
The best answer is C. Take the expression in column B: divide both the numerator and the denominator by 3X to get:
19. A: B: The best answer is B. The power of 1/3 in column A is 6 while in column B its 5 and we know that dealing with fractions, the smallest the power the largest the expression and so column B is greater.
20. A: B: AI: X2Y3 > 0 XY < 0.
The best answer is A. From X2Y3 > 0, we know that Y is positive and using the data that XY < 0 we can conclude that X is negative. The expression in column A is positive. The expression in column B is negative and so column A is greater.
C. Absolute value
21. A: B: AI: X < 0 < Y < 1
The best answer is A. Plug in numbers that fit, for example: X= -1 and Y= ½. Column A = 1.5 and column B = ½ and so column A is greater.
22. A: B: AI: Y < -2
The best answer is C. The easiest way is to plug some numbers. For example: Y = -4. Column A = 11 and column B = 11 and so both columns are equal.
23. A: B: AI: Y < -7
The best answer is C. The easiest way is to plug some numbers. For example: Y = -8. Column A = 15 and column B = 1 and so column A is greater.
24. A: B: AI: Y < X < 0
The best answer is B. The easiest way is to plug in numbers. For example: X= -1 and Y= -2. Column A = 6 and column B = 9 and so column B is greater.
25. A: B: R + 5 AI: R < 0
The best answer is D. Take R = -5, both columns end up zero. Take R = -10, column A is greater and so the answer cannot be determined.
26. A: B: S + 3 AI: S < -3
The best answer is A. Take a representative number, for example S = -5. Column A = 2 and column B = -2 and therefore column A is greater.
27. A: B: Z – 17 AI: Z >17
The best answer is C. Both expressions will always be positive and so the absolute value has no meaning. Both columns are equal.
28. A: B: 12 AI: Y2 = 12 X2 = 3
The best answer is B. From the additional data we can conclude that: The expression in column A =
29. A: 1 B: X AI:
The best answer is A. Simplify the expression: Plug in X = 1, we can see that the inequality is wrong and so X must be smaller than 1. Therefore column A is greater than column B.
30. A: -2 B: Y AI:
The best answer is D. Simplify the expression: Only Y smaller than -1 will validate this inequality and therefore -2 is one of them. Y can be -2 or even -8 and so the answer is not distinct.
31. A: Y B: 0 AI:
The best answer is B. X is bigger than an absolute value and therefore X is positive. XY is negative and therefore Y must be negative. Column B is greater than column A since 0 is bigger than any negative number.
32. A: B: -X2 AI: X < 0
The best answer is C. The easiest way if you don’t see the answer right away is to plug in numbers. Take X= -2, column A = -4 and so is column B.
33. A: 1 B: a AI:
The best answer is A. b is positive since it is larger than an absolute value. a can’t be positive, because then the left hand side would be larger than the right hand side. a can’t be zero because then both sides would be equal è the only option left is that a must be negative and so column A is greater.
34. A: 0 B: T AI:
The best answer is D. From the additional data we can conclude that T is greater or equal to zero and therefore we cannot determine which column is greater.
35. A: X3 B: X2 AI:
The best answer is B. Since The expression in column A is negative while the expression in column B is positive and thus greater.
D. Powers and simplifications
36. A: (Y – 2)2 B: 2 – Y AI: 0 < Y < 1
The best answer is A. (Y – 2)2? 2 – Y -(Y – 2)(2 – Y)? 2 – Y 2 – Y? 1 2 – Y is greater than Y in the specified range and so the answer is A.
37. A: B: AI: X > 0
The best answer is C. 1 by any power is 1 and therefore the columns must equal to one another.
38. A: (W + 1)2 B: (W + 2)2
The best answer is D. Simplify the expressions: W2 + 2W + 1? W2 + 4W + 4 subtract common items from both sides. 0? 2W + 3 We don’t know if W is positive or not and therefore the answer cannot be determined.
39. A: W – Z B: X – Y AI: X < W Z < Y
The best answer is A. Add Y – W to both columns to get: A = Y – Z and B = X – W. These are easier to compare, Y > Z and so column A is greater.
40. A: B: AI: X is a positive and odd number.
The best answer is A. Column A = (+)(+) since (-5) is powered by an even power. Column B = (-)(+) and so column A is greater than column B.
41. A: (-5)X B: (-5)X+1 AI: X is a positive and even integer
The best answer is A. Column A = (-5)X and column B = (-5)X(-5). Plug in X = 2 to get: A = 25 and B = -125 and so column A is definitely greater.
42. A: 0 B: Z AI: X < Y ZX < ZY
The best answer is B. If Z was negative the inequality ZX < ZY would be opposite and therefore we can conclude that Z is positive and thus greater than zero. Column B is greater than column A.
43. A: 0 B: P2 – 1 AI: 3P+2 = 81
The best answer is C. 3P+2 = 81 = 33 è P + 2 = 3 è P = 1. Column A = 0. Column B = 1 – 1. Both columns are equal and so the answer is C.
44. A: 5 B: Y AI: 2Y-1 = 32
The best answer is B. 32 = 25 = 2Y – 1 è 5 = Y – 1 è Y = 6. Column A = 5. Column B = 6. Column B is greater than column A and so the answer is B.
45. A: 3 B: Q AI: 33(Q+3) = 1
The best answer is A. Any number by the power of zero is 1 and therefore we want that Q + 3 =0 and so Q = -3. Column A = 3 and column B = -3 and the answer is A.
46. A: B:
The best answer is C. Simplify each of the expressions. Column A = Column B = We can see that both columns are equal.
47. A: B: AI: X < -2
The best answer is Simplify each of the expressions. A = 5X+2. B = 52X. Plug in X = -4 for example. A = 5-2 = 1/25. B = 5-8 = 1/(58), which is a lot smaller than column A and so the answer is A.
48. A: B: AI: 1 < X < 2
The best answer is B. 32X ? 32+X 2X? 2+X X? 2 2 is greater than X and therefore column B is greater.
49. A: B:
The best answer is C. Take the expression in column B and simplify it:
We can see that the columns are equal.
50. A: 36 B: 63
The best answer is A. I think the easiest way here is to write the expressions in the following form: A = 33 x 33 B = (2 x 3)3 = 23 x 33, we can see that the expression in column A is greater.
51. A: 56 B: 57 - 51
The best answer is B. Divide both sides by 56: 1? 5 – 5-5 5-5? 4 4 is much greater than 5-5 and therefore the answer is B.
52. A: (A + 4)2 B: (A – 4)2 AI: 1 < A < 4
The best answer is A. (A + 4)2? (A – 4)2 A2 + 8A + 16? A2 – 8A + 16 subtract A2 + 16 from both sides. 8A? -8A 16A? 0 A is positive and so column A (16A) is greater.
53. A: 8X – 3Y B: 6X + 5Y AI: X > 2 Y = 0.5
The best answer is A. First replace Y with 0.5: 8X – 1.5? 6X + 2.5 Add 1.5 – 6X to both sides. 2X? 4. Since X is greater than 2, column A is greater than column B.
54. A: X B: -1 AI:
The best answer is A. Simplify the expression in the additional data: è 6X = -2 è X = -1/3, which is larger than -1 and therefore column A is greater.
55. A: 13 + 2X B: 3.5X + 7 AI: X > 5
The best answer is B. 13 + 2X? 3.5X + 7 subtract (7 + 2X) from both sides. 6? 1.5X. The expression in column B can be 9 and up and therefore column B is greater.
56. A: 7 – 3Y B: 2Y – 13 AI:
The best answer is A. 7 – 3Y? 2Y – 13 Add 3Y + 13 to both sides. 20? 5Y Column B can be 15 at most and therefore column A is greater.
57. A: B: AI:
The best answer is C. From the extra data we know that a = 1/b. Simplify the expression in column A:
We can see that both columns are equal.
58. A: Y B: ¼ AI: XY = 2 X3Y3Z3 = X4Y5Z3
The best answer is A. Take X3Y3Z3 = X4Y5Z3 and divide both sides by Z3: X3Y3= X4Y5 è Replace XY with 2: 23 = 24Y è Y = ½ and therefore column A is greater.
|




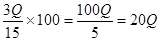 , which is smaller than 25Q since Q is defined positive.
, which is smaller than 25Q since Q is defined positive.

 47.
47.
 .
. .
.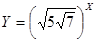
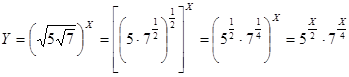


 .
. and therefore column B is greater than column A.
and therefore column B is greater than column A.

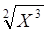



 and column B =
and column B =  and so the answer is B.
and so the answer is B.
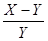
 .
.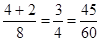 and so this column is greater.
and so this column is greater.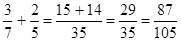 .
. and so this column is greater.
and so this column is greater.


 and so both columns are equal and the answer is C.
and so both columns are equal and the answer is C.
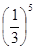

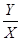


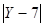
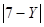

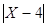
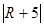


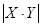
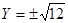 and
and  .
. and therefore column B is greater.
and therefore column B is greater.
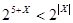 è
è  .
.
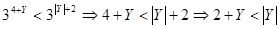 .
.
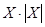







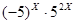
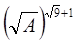

 .
. .
.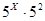





 .
.
 .
.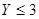
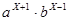


 .
.



