Appendix 12. Reading Chemical FormulasБуквы латинского алфавита, обозначающие названия элементов, читаются так же, как буквы латинского алфавита, например: O [ou], Al [¢ei ¢el], Hg [¢eitò ¢dgʤi:] HCl [¢eitò ¢si: ¢el] CO2 [¢si: ¢ou ¢tu:] 2KCl [¢tu: ¢molikju:lz əv ¢kei ¢si: ¢el] Знак + читается: plus, and или together with Знак = читается: give или form (здесь знак = означает равенство) Знак ® читается: give, pass over to или lead to
¢fo:m ənd α: ¢fɔ:md frɔm ¢tu: ¢mɔlikju:lz əv ¢en ¢eitò ¢θri:]
¢si: ¢el ¢tu:]
¢ɔksiʤən ¢aiən ¢plΛs ¢haidriʤən ¢aiən]
Знак “ - “ или “: ” обозначает одну связь, не читается
Знак “=” или “::” обозначает две связи, не читается
O [¢si: ¢θri: ¢eitò ¢tu:] [¢si: ¢tu: ¢ou ¢tu: ¢ou¢eitò ¢tu:]
Appendix 13. Thermal Expansion, Temperature temperature (n.) A property of an object that indicates in which direction heat energy will flow if the object is placed in thermal contact with another object. Heat energy flows from places of higher temperature to places of lower temperature. Zeroth law of thermodynamics (n.) If two bodies X and Y are each separately in thermal equilibrium with another body Z, then they are in thermal equilibrium with one another. In the most common case the body Z is a thermometer. temperature scale (n.) A sequence of values which represent temperature. Such a sequence is usually obtained by choosing two fixed points (identified by specified properties of stated substances) between which there are subdivisions made on a chosen basis. The Celsius scale has 99 divisions between the melting point of pure water and the boiling point of pure water. Celsius scale (n.) A temperature scale for which the ice point is at 0° and the steam point is at 100°. One Celsius degree is defined as 1/100 of the temperature interval between the ice point and the steam point. Centigrade scale (n.) The name formerly used for the Celsius scale. The name is not now used in SI units but is often used by meteorologists. Fahrenheit scale (n.) A temperature scale for which the ice point is at 32° F and the steam point at 212°F. Originally the zero was obtained in a freezing mixture and another point was fixed at 96° for blood temperature. Reaumur scale (n.) A temperature scale in which the ice point is at 0° and the steam point at 80°. i deal gas scale (n.) A scale in which changes of temperature are measured either by changes of pressure, or changes of volume, for gases operating at pressure low enough for the gases to behave as ideal gases. thermodynamic scale (n.) A temperature scale which does not depend upon the working properties of any substance. The ideal gas scale is identical with this scale. absolute scale (n.) A thermodynamic temperature scale in which the lower fixed point is absolute zero of temperature and the interval is identic with that on the Celsius scale. The temperature on the absolute scale is obtained by adding to θ,the Celsius temperature, 1/ a where a is the coefficient of expansion of a gas at constant pressure. This gives a scale on which the ice point is 273∙15°; i.e. °A = °C + 273∙15. The absolute scale was often called the Kelvin scale and temperatures measured in fixed points (n.pl.) Those points on a temperature scale which are fixed and which can be referred to a given property of a substance. The two main fixed points are the ice point and the steam point. ice point (n.) That fixed point on a temperature scale at which pure solid water (ice) and pure liquid water are in equilibrium at 101 325 N m-2 (760 mm Hg). It may be more simply described as the melting point of pure ice at standard pressure (101 325 N m-2 or 760 mm Hg). steam point (n.) That fixed point on a temperature scale at which pure water boils at standard pressure (101 325 N m-2; 760 mm Hg). This is 100° on the Celsius scale. zinc point (n.) A fixed point on an international temperature scale, fixed at the temperature at which zinc changes from liquid to solid (the freezing point of zinc) at standard pressure (101 325 N m-2). This corresponds to 419∙58 °C. international temperature scale (n.) A practical scale which is as near as possible
Below 630°C platinum resistance thermometer; up to 1064 °C a thermocouple or special platinum resistance thermometer; above 1064 °C a radiation pyrometer. KEYS:
|

 - [eitòtu:ou]
- [eitòtu:ou]
 Знак читается: forms или is formed from, либо reversibly
Знак читается: forms или is formed from, либо reversibly [¢si: ¢ou ¢tu: ¢plΛs ¢si: ¢ei ¢ou ¢giv ¢si: ¢ei ¢si: ¢ou ¢θri:]
[¢si: ¢ou ¢tu: ¢plΛs ¢si: ¢ei ¢ou ¢giv ¢si: ¢ei ¢si: ¢ou ¢θri:]


 [¢en ¢tu: ¢plΛs ¢θri: ¢molikju:lz əv ¢eitò ¢tu:
[¢en ¢tu: ¢plΛs ¢θri: ¢molikju:lz əv ¢eitò ¢tu: [¢si: ¢tu: ¢eitò ¢fɔ: ¢plΛs ¢si: ¢el ¢tu: ¢giv ¢si: ¢tu: ¢eitò ¢fɔ:
[¢si: ¢tu: ¢eitò ¢fɔ: ¢plΛs ¢si: ¢el ¢tu: ¢giv ¢si: ¢tu: ¢eitò ¢fɔ: [¢fɔ: ¢mɔlikju:lz əv ¢eitò ¢si: ¢el ¢plΛs ¢ou ¢tu: ¢giv ¢tu: ¢mɔlikju:lz əv ¢si: ¢el ¢tu: ənd ¢tu: ¢mɔlikju:lz əv ¢eitò ¢tu: ¢ou]
[¢fɔ: ¢mɔlikju:lz əv ¢eitò ¢si: ¢el ¢plΛs ¢ou ¢tu: ¢giv ¢tu: ¢mɔlikju:lz əv ¢si: ¢el ¢tu: ənd ¢tu: ¢mɔlikju:lz əv ¢eitò ¢tu: ¢ou]

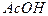
 [¢ei ¢si: ¢ou ¢eitò ¢fɔ:mz ənd iz ¢fɔ:md frəd ¢ei ¢si:
[¢ei ¢si: ¢ou ¢eitò ¢fɔ:mz ənd iz ¢fɔ:md frəd ¢ei ¢si: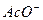 - acyloxy ion (acetate anion)
- acyloxy ion (acetate anion) - hydrogen ion [¢haidriʤən ¢aiən] или univalent positive hydrogen ion или protone
- hydrogen ion [¢haidriʤən ¢aiən] или univalent positive hydrogen ion или protone - negative chlorine ion или negative univalent chlorine ion или chloride
- negative chlorine ion или negative univalent chlorine ion или chloride Cl
Cl или Cl - C - Cl [¢si: ¢si: ¢el¢fɔ:]
или Cl - C - Cl [¢si: ¢si: ¢el¢fɔ:] или O=C=O [¢si: ¢ou ¢tu]
или O=C=O [¢si: ¢ou ¢tu]
 H O
H O




