Solution1. Determine the arithmetic mean of the peak voltage is determined by:
Determine the average value of rms voltage
Calculation of uncertainty of type A Ka
2. We define the standard uncertainty of measurement of a single peak (PP) voltage H A (Um)
Also calculate the standard uncertainty of a single measurement root mean square value (RMS) voltage HA (U)
3. We define the standard measurement uncertainty and the number of CT RMS H A (Um) иH A (U):
4. We define the total standard uncertainty NcA (Ka) in the case of uncorrelated estimates of indirect measurements
где
Calculation of uncertainties of the B type Ka В
To calculate the standard uncertainty of type B - HB (Ka), it is necessary to take into account influencing factors: 1) The technical characteristics of the device (the limit of the basic relative error limit of the additional error of the device, the resistive component of the input resistance of the device), 2) The scheme of measurement (the output voltage source with internal resistance, the limit of the measurement device), 3) the measurement conditions (ambient temperature, humidity, pressure, etc.). Also, to calculate the standard uncertainty is necessary to consider the rectangular distribution function. 5. We define the standard uncertainty for each voltage
where а –boundaries of the basic allowable error derived from the class of instrument accuracy. As in the example z accuracy class is denoted simply by the number 4.0 - this means that the normalized limit reduced error and prev = 4%. The above error is the ratio of the absolute error in the normal miruyuschemu value:
As a fiducial value (), the limit of measurement used by the voltmeter.Wedefinetheabsoluteerror:
6. Next, take into account the uncertainty caused by the temperature deviation from the normal Тнорм=20˚С.
7. We define the measurement uncertainty introduced by the amendment (ρ;):
where the coefficients of sensitivity The calculation for the first point in the series in italics in Table.1 Um:
The calculation for the first point in the series in italics in Table 1 U:
Since the value of load resistance and input impedance are known about and within certain limits [Rmin; Rmax], [Rvhmin; Rvhmax], assuming all the values of resistors within the marked boundaries equally, we estimate their uncertainty as:
8. We define the total standard uncertainty::
9. We define the total standard uncertainty Ncv for indirect measurements:
10. We define the resulting standard uncertainty:
11. Expanded uncertainty of Hp with a given probability p and the known distribution law (Appendix A) is determined as follows:
Нр= k ∙Нå = 0,18
where k - coefficient of coverage. In accordance with the recommendations of DSTU and the assumption of normality of the distribution of values of the measured quantity take k. When Po = 0,95, k = 2,228 (Annex B). 12. The result of measurements of the amplitude of the Ca is obtained from the formula:
All the results set up the table 3 Table 3 - ExampleSolution
|







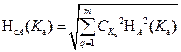
 и
и  sensitivity coefficient.
sensitivity coefficient. ;
; ;
;

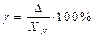 .
.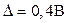 , т.е.
, т.е.  .
. .
. В
В ,
, ,
,  .
. В/Ом;
В/Ом; В/Ом.
В/Ом. В/Ом;
В/Ом; В/Ом.
В/Ом.

 ;
; .
. ,
, .
.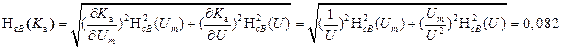 .
.

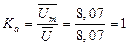
 = 8,07 В
= 8,07 В
 = 8,07 В
= 8,07 В

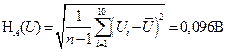



 = 0,04В
= 0,04В
 В
В
 В
В
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , k ∙= 2,228,Р д = 0,95, Нр= 0,18
, k ∙= 2,228,Р д = 0,95, Нр= 0,18



