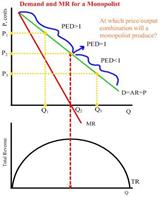
Monopoly demandAssumptions: Patents, economies of scale, or resource ownership secure the monopolist's status. No unit of government regulates the firm. The firm is a single-price monopolist; it charges the same price for all units of output. Because the pure monopolist is the industry, its demand curve is the market demand curve. And because market demand is not perfectly elastic, the monopolist's demand curve is downsloping (Qd increases as P decreases). The three implications of the downward-sloping demand curve are: Marginal revenue is less than price: The monopolist's downwoard sloping demand curve means that it can increase sales only by charging a lower price. MR is less than price for every level of output except the first. This is because the lower price applies not only to the extra unit sold but also to all prior units of output. Thus, the MR decreases because the monopoly has sacrificed this price for greater output. Each additional unit of output sold increases total revenue by an amount equal to its own price minus the sum of the price cuts that apply to all prior units of output. Hence, MRDARP is not one line in pure monopoly markets; rather, D=AR=P is a downsloping curve and MR is another downsloping curve that starts at the same point as D but decreases faster (steeper). Because MR is the change in TR, MR is positive when TR is increasing. When TR is at its maximum, MR = 0; when TR is decreasing, MR is negative. The monopolist is a price maker: Firms with downward-sloping demand curves are price makers. All imperfect competitors (pure monopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition) have downward-sloping demand curves. Firms can influence total supply through own output decisions; by changing market supply, firms can influence product price. For pure monopoly: ONE firm controls total output and price, because it is the sole producer of said product. Monopolists face downsloping demand curve in which EACH output is associated with some UNIQUE price. Monopolists are indirectly determining price they will charge when deciding on quantity of output, becauase each quatity decided equals a different price, the degree of this is steeper in this type of market structure due to the nature of extending the price line up from the mc=mr point. Monopolists can make the price through their control of output (↑ output = ↓ price; ↓ output =↑ price)
|