Florence Nightingale
The English nurse Florence Nightingale (1820-1910) was the founder of modern nursing and made outstanding contributions to knowledge of public health. Florence Nightingale was born in Florence, Italy, on May 12, 1820, of wealthy parents. Her father was heir to a Derbyshire estate. Her mother, from solid merchant stock, dedicated herself to the pursuit of social pleasure within the circumscribed life then proper for women of high station. Though Florence was tempted by prospects of a brilliant social life and marriage, she had a stronger strain that demanded independence, dominance in some field of activity, and obedience to God by selfless service to society. In 1844 Nightingale decided to work in hospitals. Her family furiously resisted her plan, on the ostensible ground that nurses were not "ladies" but menial drudges, usually of questionable morals. Nevertheless, she managed to do some private nursing and then to spend a few months at Kaiserworth, a German school and hospital. In 1853 she became superintendent of the London charity-supported Institution for Sick Gentlewomen in Distressed Circumstances. This opportunity allowed her to achieve effective independence from her family and also to try out novel techniques of institutional organization and management, conducted in a scientific, nonsectarian spirit.
Nightingale saw that her first task was to convert the military doctors to accept her and her nurses. Her discretion and diplomacy, combined with the influx of new sick and wounded, soon brought this about. She also had a large fund of private money, much of it raised by the London Times, with which she could cut through the clogged supply system. By the end of 1854 some order and cleanliness had been created, not only through her efforts but also through the revelations and improvements made by a governmental sanitary commission. The death rate among patients fell by two-thirds. But with improvement came new problems, with the defensiveness and hostility of the officials responsible for conditions now exposed and with the sectarian squabbling among the nurses, which Nightingale called the "Protestant Howl" and the "Roman Catholic Storm." Florence Nightingale left Scutari in the summer of 1856, soon after the hostilities ended. By now she was idolized by the troops and the public as the "Lady with the Lamp" and the "Nightingale in the East." But this popular image is essentially false. Although she did active nursing in the wards, her real work lay outside the expression of tenderness and compassion. It began with her deliberate refusal to respond to public adulation and with her use of her influence in high places, even to the Queen and Prince Albert, to fight for effective reform of the entire system of military hospitals and medical care. Nightingale planned tactics from behind the scenes. In Notes on Matters Affecting the Health, Efficiency and Hospital Administration of the British Army (1857) she used the experiences of the war as a body of data to prove the necessity of a new system. Within 5 years this effort led to the reconstruction of the administrative structure of the War Office. Nightingale's Notes on Hospitals (1859) detailed the proper arrangements for civilian institutions. In the next year she presided over the founding of the Nightingale School for the training of nurses at St. Thomas's Hospital in London. After 1858 she was recognized as the leading expert on military and civilian sanitation in India, in which capacity she advocated irrigation as the solution to the problem of famine. Nightingale's personality is well documented. Her whole life she rebelled against the idle, sheltered existence of her family. She achieved a dominant position in a masculine world, driving and directing her male allies with the same ruthless force she applied to herself. She frequently complained of women's selfishness, and she ironically had no sympathy with the growing feminist movement. But she also developed a conception of spiritual motherhood and saw herself as the mother of the men of the British army - "my children" - whom she had saved. Florence Nightingale never really recovered from the physical strain of the Crimea. After 1861 she was house-bound and bedridden. She died on Aug. 13, 1910. Florence Nightingale's diligence made her a symbol for all nursing and for any kind of dedicated service. LESSON 5 TEXT FOR INDIVIDUAL WORK A Day in the Life of a Student Nurse
LESSON 5
|

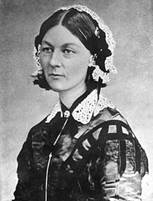
 In October 1854 Nightingale organized a party of 38 nurses, mostly from various religious orders, for service in the Crimean War. They arrived at Constantinople in November. Conditions at the British base hospital at Scutari were appalling and grew steadily worse as the flow of sick and wounded soldiers from the Crimea rapidly increased. The medical services of the British army were both insufficient and inefficient: a supply system of infinite and archaic complexity actually cut off deliveries to the patients; the Barrack Hospital, where Nightingale and her nurses were quartered, sat over a massive cesspool which poisoned the water and even the fabric of the building itself. However, the attitude still prevailed that the common soldier was an uncivilized, drunken brute on whom all comforts and refinements would be wasted.
In October 1854 Nightingale organized a party of 38 nurses, mostly from various religious orders, for service in the Crimean War. They arrived at Constantinople in November. Conditions at the British base hospital at Scutari were appalling and grew steadily worse as the flow of sick and wounded soldiers from the Crimea rapidly increased. The medical services of the British army were both insufficient and inefficient: a supply system of infinite and archaic complexity actually cut off deliveries to the patients; the Barrack Hospital, where Nightingale and her nurses were quartered, sat over a massive cesspool which poisoned the water and even the fabric of the building itself. However, the attitude still prevailed that the common soldier was an uncivilized, drunken brute on whom all comforts and refinements would be wasted. Do you remember when you received your written acceptance to nursing school and officially become a student nurse? It was one of the most exciting and proudest moments of your life, wasn’t it? You became completely submerged in a new life style. For me, I would no longer be working at the dry cleaners, creating stress over wrinkled clothes and plastic wrap. Nursing school is exhausting, nerve racking and a lot of material to comprehend. A typical day in the student nurses’ existence might go like this: After going through the activities of waking up and preparing for school, I begin to assemble my materials for theory class, skills lab and check my separate bag for clinical nursing practice. I have a bag for each of the three components so as to not forget any essential work materials. I run down the steps of my brick condominium in my size thirteen orthopedic long white shoes and survey the brick façade. It is so orderly in architecture in contrast with the chaotic journey that I have embarked on to become a Registered Nurse. I realize then that I have forgotten my essential student nurse badge, so I run back up the steps to get it from the table in the foyer. Additionally, I have forgotten to write down the tasks needed to be accomplished today, so I grab the stack of post-it notes in the bold orange color. Seated in my car, I write out the day’s plan and the grocery list. Then I position my flash cards on the dash board so that I can glance at them during my free time of sitting in traffic or at a red light. There are so many flash cards in the car that I have a plethora of nursing information. I place the post-it note near the steering wheel so I can remind myself to get the groceries and perform the tasks. Wow, it’s a warm day so I open the car window to let some ventilation in. Oh no, the post-it note takes on a life of its own and flies out the window! Now I am clueless as to what I have to buy at the store. I never realized how dependent I was on my post-it notes until they disappeared. I continue through the grueling academic day at nursing school and feeling exhausted, I stop at the store on the way home. In the glow of being immersed in nursing school, I am still wearing my “student nurse badge” with the stethoscope hanging around my neck. I walk up and down the aisles of the grocery store without my list and try to focus on needed items. I fill the cart and find myself in the check-out aisle behind a man who is coughing. Without thinking, I grab my stethoscope and place it on his back to listen to his lung sounds. This frightens him so I use my best nursing student “soothing voice” while unloading my cart onto the grocery conveyor belt. The confusion is seen in the eyes of the coughing man and the sweet girl who is the checker as to what is happening in the grocery aisle. The people behind me are glad they are not coughing and just hope I would speed up the check-out line. Without the post-it note plan I do not have all the necessary groceries, but I am too tired and embarrassed to return to the store. As I drive up to my condominium, I question myself, “am I one brick short of a full load?”
Do you remember when you received your written acceptance to nursing school and officially become a student nurse? It was one of the most exciting and proudest moments of your life, wasn’t it? You became completely submerged in a new life style. For me, I would no longer be working at the dry cleaners, creating stress over wrinkled clothes and plastic wrap. Nursing school is exhausting, nerve racking and a lot of material to comprehend. A typical day in the student nurses’ existence might go like this: After going through the activities of waking up and preparing for school, I begin to assemble my materials for theory class, skills lab and check my separate bag for clinical nursing practice. I have a bag for each of the three components so as to not forget any essential work materials. I run down the steps of my brick condominium in my size thirteen orthopedic long white shoes and survey the brick façade. It is so orderly in architecture in contrast with the chaotic journey that I have embarked on to become a Registered Nurse. I realize then that I have forgotten my essential student nurse badge, so I run back up the steps to get it from the table in the foyer. Additionally, I have forgotten to write down the tasks needed to be accomplished today, so I grab the stack of post-it notes in the bold orange color. Seated in my car, I write out the day’s plan and the grocery list. Then I position my flash cards on the dash board so that I can glance at them during my free time of sitting in traffic or at a red light. There are so many flash cards in the car that I have a plethora of nursing information. I place the post-it note near the steering wheel so I can remind myself to get the groceries and perform the tasks. Wow, it’s a warm day so I open the car window to let some ventilation in. Oh no, the post-it note takes on a life of its own and flies out the window! Now I am clueless as to what I have to buy at the store. I never realized how dependent I was on my post-it notes until they disappeared. I continue through the grueling academic day at nursing school and feeling exhausted, I stop at the store on the way home. In the glow of being immersed in nursing school, I am still wearing my “student nurse badge” with the stethoscope hanging around my neck. I walk up and down the aisles of the grocery store without my list and try to focus on needed items. I fill the cart and find myself in the check-out aisle behind a man who is coughing. Without thinking, I grab my stethoscope and place it on his back to listen to his lung sounds. This frightens him so I use my best nursing student “soothing voice” while unloading my cart onto the grocery conveyor belt. The confusion is seen in the eyes of the coughing man and the sweet girl who is the checker as to what is happening in the grocery aisle. The people behind me are glad they are not coughing and just hope I would speed up the check-out line. Without the post-it note plan I do not have all the necessary groceries, but I am too tired and embarrassed to return to the store. As I drive up to my condominium, I question myself, “am I one brick short of a full load?”


