Systems of Linear EquationsConsider system of m linear equations with n unknowns:
(2)
Definition. The numbers Definition. A system of equations (2) is said to be consistent if it has at least one solution, and it is said to be inconsistent if it has no solutions. Definition. A system is called determined if it has a unique solution, and it is called undetermined if it has many solutions. For example, the system of equations
Consider the following system of n linear equations with n unknowns
It is required to find a solution
Cramer’s Rule
To solve system (3), we multiply the first equation by А 11, the second by А 21, etc., the last equation is multiplied by Аn 1. Then, we sum the equations and collect similar terms:
Consider the n th-order determinant composed of the coefficients of system (3):
The coefficient of х 1 is the sum of the products of the element of the first column and their algebraic complements. According to property 9, it equals determinant (4). The coefficients of the unknowns The right-hand side is the product of the free terms and the algebraic complements of the elements of the first column; consequently, it equals the determinant (4) in which the first column is replaced by the column of free terms:
Expressions for the other unknowns are obtained in a similar way: we multiply system (3) by the algebraic complements of the n corresponding columns
where Example. Solve the system of equations
Let us evaluate the principal determinant of the system:
To obtain zeros in the first row, we leave the third column unchanged; multiply it by –2 and add to the first column; then multiply it by 3 and add to the second column. Let us calculate the auxiliary determinants. х 1 is derived from by replacing the first column by the free terms:
By Cramer's rule (5) we obtain
1. In (5), the principal determinant must be different from zero. In this case, system (3) has a unique solution. 2. If 3. If
|

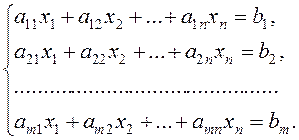
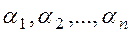 are called a solution of system (2) if substituting them into the equations, we obtain true equalities.
are called a solution of system (2) if substituting them into the equations, we obtain true equalities.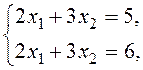 has no solutions, i.e., it is inconsistent, because its left-hand sides are equal, while the right-hand sides are different.
has no solutions, i.e., it is inconsistent, because its left-hand sides are equal, while the right-hand sides are different.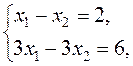 is consistent, but undetermined, because it has infinitely many solutions. Reducing the second equation by 3, we obtain two identical equations.
is consistent, but undetermined, because it has infinitely many solutions. Reducing the second equation by 3, we obtain two identical equations.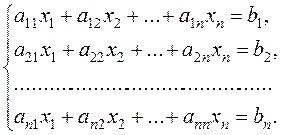 (3)
(3)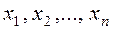 of system (3), expressed in terms of the coefficients
of system (3), expressed in terms of the coefficients 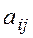 and the free terms
and the free terms 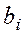 , where
, where 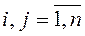 (from 1 to n).
(from 1 to n).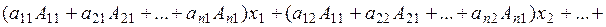
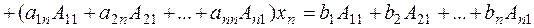
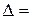
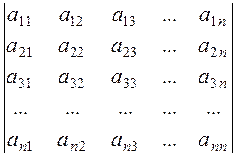 . (4)
. (4)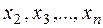 are the products of the elements of the second, third, …, n th columns by the algebraic complements of the elements of the first column; consequently, they equal zero by property 10.
are the products of the elements of the second, third, …, n th columns by the algebraic complements of the elements of the first column; consequently, they equal zero by property 10.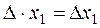 ,
, 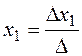 .
.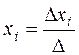 ,
, 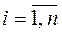 , (5)
, (5) is the principal determinant of the system and the
is the principal determinant of the system and the 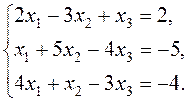
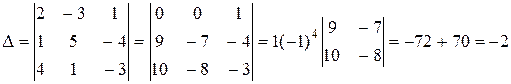 .
.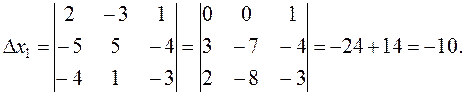
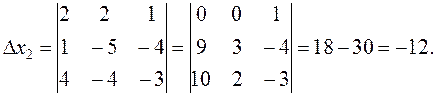
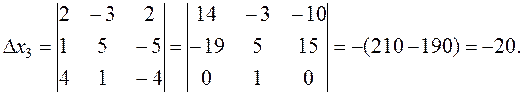
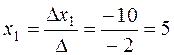 ;
; 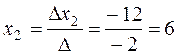 ;
; 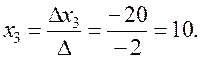
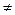 0), then the system has no solutions at school, we would say that division by zero is not allowed.
0), then the system has no solutions at school, we would say that division by zero is not allowed.


