Multiplication.
a1 . a2 =(a1 +b1i)(a2 +b2i)= a1a2+b2ia1+b1a2i+b1b2i2= =(a1a2-b1b2)+i(a1b2 +b1a2), т.к. i2=- 1.
Multiplication of complex numbers is performed as usual multiplication of algebraic expressions; after the multiplication the real and imaginary parts are grouped separately. The numbers a =a +bi, a =a –bi are called complex conjugates or simply conjugates. The product of two conjugates is a nonnegative real number a2+bia-abi-i2b2=a2+b2. 4) Division. Definition. The quotient complex number b such that Suppose,
Due to equality of real and imaginary parts,
Solve the resulting system of linear equations
and find the real numbers c and d
The denominator of both expressions is the product of two conjugates, so let us multiply both the numerator and the denominator of
Rule. In order to find the quotient of two complex numbers, it is enough to multiply both the numerator and the denominator by the conjugate of the denominator, and then separate the real and imaginary parts. Examples. 1. Divide
2. Solve the equation х2- 2 х +10=0 and check Viete's theorem for the complex zeros
The magnitude and argument of a complex number. Plot the complex number a=a+bi on the
r b j 0 a x It is easy to see that r2=a2+b2 and
Trigonometric form of a complex number, de Moivre's formula Use the above figure to express the real and imaginary parts a,b of the complex number in terms of the magnitude and argument ρ, j. a=r. cos j, b=r .sin j. Hence a=r( cos j+i sin j) This is the trigonometric form of a complex number. Each complex number has a unique trigonometric form because it has a unique magnitude and argument. Example. α=
Therefore,
1. Multiplication. Consider complex numbers a1 =r1 ( cos j1 +i sin j1) and a2 =r2 ( cos j2 +i sin j2). The product equals a1·a2 = r1 ( cos j1 +i sin j1). r2 ( cos j2 +i sin j2)= =r1·r2 [( cos j1 cos j2 -sin j1 sin j2)+i( sin j1 cos j2 + cos j1 sin j2); a1·a2 = r1·r2 [ cos (j1+j2)+i sin (j1+j2)]. Therefore, in order to multiply two complex numbers, it is necessary to multiply their magnitudes and add the arguments. 2. Division. Multiply both the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator
Therefore, in order to divide two complex numbers, it is necessary to divide their magnitudes and subtract the arguments. A power of a complex number. If a1=a2=a3=…=an=a, then an = r ·r ·r·…·r[cos(j+j +j+…+j)+i(sin(j+j +j+…+j)]= =rn[cosnj+isinnj] or ak =rk[coskj+isinkj] -de Moivre's formula. Roots of a complex number. Write down de Moivre's formula for
where k may be any of n integers 0,1,2,…, n- 1. Example. Solve the equation x 3+1=0. 1 -st method: (x +1)(x 2- x +1)=0, x 1=-1, 2 -nd method: x 3=-1,
k= 1, k=2, =
|

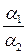 of two complex numbers is a
of two complex numbers is a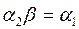 .
.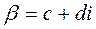 , then by the definition
, then by the definition ;
; .
.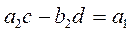 ;
;  .
.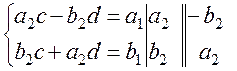 ,
,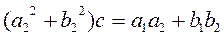 ,
,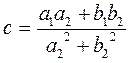 ,
, 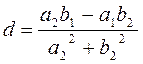 .
.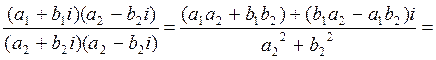
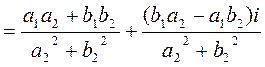 - as expected, the result equals b.
- as expected, the result equals b.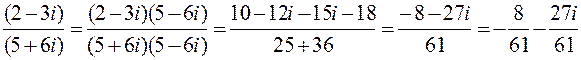 .
. ;
;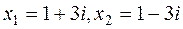 ; x 1 +x 2=2; x 1 .x 2=12+32=10.
; x 1 +x 2=2; x 1 .x 2=12+32=10. plane.
plane. у
у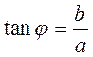 ; the numbers ρ and j are called the absolute value (or magnitude) and the argument of a complex number respectively.
; the numbers ρ and j are called the absolute value (or magnitude) and the argument of a complex number respectively.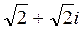 .
.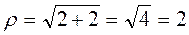 ;
;  .
. .
.
 using the fact the sine and cosine are periodic functions with the period T=2p:
using the fact the sine and cosine are periodic functions with the period T=2p: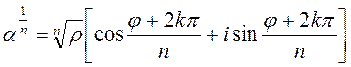 ,
, ;
;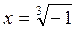 , -1=cosp+ i sinp, which is a trigonometric form of a number.
, -1=cosp+ i sinp, which is a trigonometric form of a number.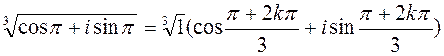 . Using the formula, k=0,
. Using the formula, k=0, 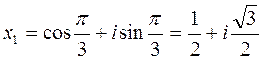 ,
,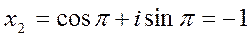 ,
,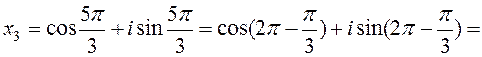
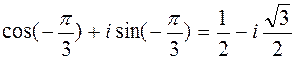 .
.


