Death and Legacy
Austen lived the last eight years of her life in Chawton. Her personal life continued to be limited to family and close friends, and she prized herself on being a warm and loving aunt as much as being a successful novelist. A sudden illness, possibly Addison's disease, made her stop work on the novel Sandition, and she died in 1817. After her death, during the nineteenth-century romantic period, Austen was often looked upon with begrudging admiration, as her elevation of intelligence over feeling contradicted the romantic temperament. Toward the end of the nineteenth century, however, Austen's reputation rose considerably, and she gradually gained an enthusiastic cult of admirers that were known as the "Janeites." In America, Austen was little known before 1900, but by mid-century she was receiving more critical attention there than in England. In the last decades of the twentieth century, Austen and her works received considerable attention from the general public: Most of her novels were adapted into films, modern novelists wrote sequels to Pride and Prejudice and endings to Sandition, and a mystery series was even developed with Jane Austen herself as the heroine.
P&P 1. Darcy at the Meryton assembly: discovered to be Proud; according to Mrs. Bennet, he is "high and conceited" (Pride). 2. Caroline Bingley and Louisa Hurst Proud and conceited. 3. Mrs. Bennet: Darcy "ate up with Pride ". 4. Charlotte Lucas and Elizabeth on Pride. 5. Mary Bennet on Pride vs. Vanity. 6. Young Lucas on Pride. 7. Caroline Bingley on Elizabeth's Pride and impertinence. 8. Bingley's Pride in his carelessness. 9. Darcy on Pride vs. Vanity. 10. Darcy: Elizabeth's defect is "wilfully to misunderstand everybody" (Prejudice). 11. Mr. Collins: Lady Catherine not Proud. 12. Mr. Collins's Pride. 13. Elizabeth (to Wickham) on Darcy's Pride. 14. Wickham on Darcy's Pride. 15. Wickham: Georgiana Darcy Proud. 16. Wickham on Darcy's Pride, re Lady Catherine. 17. The ball at Netherfield: Elizabeth "resolved against any sort of conversation with" Darcy, because of Wickham. (Prejudice). 18. The ball at Netherfield: Elizabeth says to Charlotte Lucas that it "would be the greatest misfortune... to find a man [Darcy] agreeable whom one is determined to hate" (Prejudice). 19. The ball at Netherfield: Darcy hopes he never allows himself to be blinded by Prejudice 20. Mr. Collins's Pride hurt; his angry Pride. 21. Elizabeth on Georgiana Darcy's supposed Pride. 22. Elizabeth thinks that Darcy despises Gracechurch Steet (in a commercial, rather than a "gentlemanly" part of London) (Pride). 23. Mrs. Gardiner recollects Darcy as Proud. 24. Elizabeth on Darcy's Pride and caprice as the cause of his interference. 25. Elizabeth thinks Darcy's Pride superficial. 26. Elizabeth acts "as if intending to exasperate herself as much as possible against Mr. Darcy" (Prejudice). 27. Darcy avows his Pride to Elizabeth. 28. Darcy: Elizabeth rejects him only because his honesty has hurt Elizabeth's Pride. 29. Elizabeth: Darcy's shameless avowal of his abominable Pride. 30. Elizabeth's strong Prejudice against any explanation of Darcy's. 31. Elizabeth: Darcy's Pride and insolence. 32. Elizabeth: Darcy's Pride not so bad after all. 33. Elizabeth feels herself to have been "blind, partial, Prejudiced, absurd"; realizes her false Pride. 34. Elizabeth says to Jane that she "meant to be uncommonly clever in taking so decided a dislike to him [Darcy] without any reason" (Prejudice). 35. Elizabeth to Jane: The misfortunes consequent to her former Prejudices. 36. Wickham on Darcy's Pride again. 37. Darcy's housekeeper's Pride in him and Georgiana. 38. Mrs. Gardiner attributes his housekeeper's praise of him to "family Prejudice ". 39. Darcy's housekeeper never saw anything of his being Proud. 40. Darcy's Pride tested on introduction to the Gardiners. 41. Mrs. Gardiner seconds the housekeeper's opinion (Darcy not Proud). 42. Elizabeth observes Georgiana Darcy not Proud. 43. Inhabitants of Lambton attribute Pride to Darcy 44. Elizabeth uses Darcy's Pride to diagnose Love. 45. Georgiana Darcy's manners can create the appearance of Pride and reserve. 46. Elizabeth to Mrs. Gardiner on Wickham's false report of Georgiana Darcy being Proud, reserved, and disagreeable. 47. Elizabeth reflects on her change in feelings since she Proudly spurned Darcy. 48. Mrs. Bennet's Pride in Lydia's marriage. 49. Darcy's avowal to the Gardiners of mistaken Pride. 50. Elizabeth thinks Darcy's Pride will keep him away, on account of Wickham. 51. Elizabeth Proud of Darcy for his actions with regard to Lydia's marriage. 52. Mr. Bennet "Proud"; of Wickham as son-in-law. 53. Kitty Bennet: Darcy a "tall, proud man". 54. Mrs. Bennet's idea of Darcy's Pride. 55. Elizabeth knows that knowledge of Darcy's interference would Prejudice Jane against him. 56. Elizabeth tells Darcy how all her former Prejudices had been gradually removed. 57. The chastened Darcy on his former Pride and conceit. 58. Mr. Bennet tells Elizabeth: "We all know [Darcy] to be a Proud, unpleasant sort of man". 59. Elizabeth denies to Mr. Bennet that Darcy has any improper Pride. 60. Mrs. Bennet's delighted Pride in the marriage of "her two most deserving daughters".
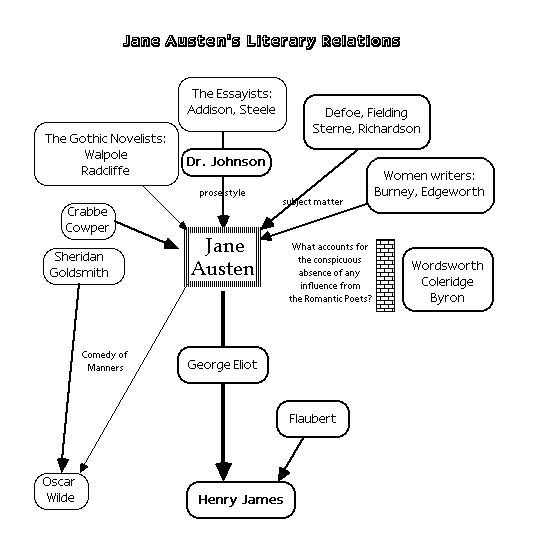
Two of the many authors who said they thought very highly of Jane Austen's writings were Henry James and J. K. Rowling.
|