MonopolyThe monopoly occurs when the output of an entire industry is produced and sold by a single firm. That is the monopolist firm. Because a monopolist firm is the sole producer of the product sold on the market, But as it is assumed that the monopolist firm faces a negatively sloped demand curve (the price and the demand are inversely related), there is a trade-off between the price it charges and the quantity it sells. Sells can be increased only if price is reduced (and vice versa). The marginal revenue of the monopolist firm is less than the price because the price must be lowered to sell an extra unit. Unlike the competitive firm, the quantity or the price behaviour of the monopolist firm Over the range in which the demand curve is elastic, total revenue rises as more units are sold; marginal revenue must therefore be positive. Over the range in which the demand curve is inelastic, total revenue falls as more units are sold; marginal revenue must therefore be negative. The price elasticity of the demand determines the range in which the monopolistic firm can raise its supply without lowering its price. The price elasticity of the demand is the sensibility of the demand to the variations of the price on the market. It is given by:
is the first derivative of the demand when the charged price is modified by the monopolistic firm. The monopolistic market is explained throughout entry barriers in that if a monopolistic firm’s profits are to persist in the long run, the entry of new firms into the industry must be prevented by effective entry barriers which may be either natural or created. Natural barriers most commonly arise as a result of economies of scale. When the long-run average cost curve is negatively sloped over a large range of output, big firms have significantly lower average total costs than small firms. For example, the natural monopoly occurs when the industry’s demand conditions allow only one firm, at most, to cover its costs while producing at its minimum efficient scale (that is the level of production at the minimum point of the long-run average cost curve of the firm which allows it to just cover its costs). Another type of natural barrier is set-up cost. If a firm could be catapulted fully grown into the market, it might be able to compete effectively with the existing monopolist. However, the cost to the new firm of entering the market, developing its products, and establishing such things as its brand image and its dealer network may be so large that entry would be unprofitable. In general, the firms which have technological advantages over new firms can establish barriers to entry. These created barriers are also called economic barriers and depend on the strategic anticompetitive behaviours of big firms dominating industry structuresThere are also barriers which are created by government action. Patent laws, for instance, may prevent entry by conferring on the patent holder the sole legal right to produce a particular commodity for a specific period of time. A firm may also be granted a charter or a franchise that prohibits competition by law. Regulation and licensing of firms, often in service industries, can restrict entry and reduce the competitiveness of markets. Because profits attract entry and entry erodes profits that the firms try to establish technological and economic barriers in order to protect themselves from the competition.
|

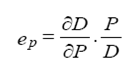 where
where


