Figure 2.1London School of Commerce MODULE TITLE/ Business and Managerial Economics SEMESTER: Semester One SEMESTER:February - May 2010 Student Name: Student Number:
1.
Demand Deficient Unemployment
This type of unemployment occurs when there is not enough demand in the economy to sustain full employments. If the general demand for products decreases, a firm would sell and supply less, and so reduce production, and if the firm is producing less, which lead to low demand for workers. Firm may reduce their workforce and stop employing new workers. In a case where there is prolonged period in fall in demand, a firm may become bankrupt, of which leads to mass redundancy. Factors that may affect demand deficient unemployment causing it to be worsened can stem from: the economy moving into recession – this would fuel further rise in unemployment, of which affects consumer confidence and spending. Householders may turn to saving instead of spending that can lead to further decrease in the demand of the firm’s products, and further reduce economic growth and continuous rise in unemployment. When an economy moves into recession, unemployment among the young are among the highest, the firm may cut some of its old staff by laying off these staff, but will not higher any new staff. Furthermore, the increase in interest rates, would increase the borrowing cost of business contribute reduction in the number of people the a firm employees.
Real-Wage Unemployment
Under this type of unemployment, the assumption is that labour market is perfectly, that is market equilibrium wage is set by the forces of demand and supply of labour. However, if wages rise above the market equilibrium wage, will lead to the cause of unemployment. In this case unemployment reflects the disequilibrium in the labour market. Factors that may affect this type of unemployment, arises from legislation that ensures everyone a minimum wage, for examples 60% of the national wage average. This is seen by economics as wages above the market clearing equilibrium and as such would increase unemployment. Economics argue against legislation and trade union to artificially increase real wage. If real wage were allowed to fall inline with the market level, there would be no unemployment within the economy.
Frictional Unemployment
This is occurs when people moves between jobs, for example graduates changing jobs for the next best alternative, this is common form of unemployment, of which would-be worker may be encourage to stay out of work because of high state benefits. In addition, this can also be explained as a supply-side economics approach to solve unemployment. Where government policies attempts to advance productivity and efficiency and reduce unemployment. Under this approach, the remedies put forward to reduce unemployment includes: providing better information about job, reduction of benefits, reduce the power of trade unions with the labour market, increase flexibility within the labour market, and the provision of education and training. The factor that can worsen frictional unemployment would come from government decision to close job centers in an attempt to save money, as this would reduce the availability of information pertaining to jobs, that the unemployed required getting them employed. In crease in the income tax by 2% would impacted on the amount of net earning available for workers, and worker may not be motivate to seek employment, especially in circumstances where the state benefit is high, and would be more or equally to what the would-be employee would get after tax.
Structural Unemployment
This form of unemployment occurs when because of mismatch of skills in the labour market, of which is caused by: occupational immobility – occurs where there is difficulties in learning new skills require for a new industry because of change in technology; geography immobility – the inability of workers to get jobs regionally; change in technology – the development of machine tense industry that reduce the demand for labour; and structural changes – a decline in one industry, because of the lack of competition, and leaves a lot of people who use to work in that industry unemployed. The factors that can worsen this type of unemployment would come from: the introduction of robots in manufacturing, and the development of the single market in Europe that leads to a movement of capital to the ‘centre of gravity’ in Europe.
Technological Unemployment
This is unemployment caused by the introduction and application of new technology that eliminates by changing the nature and of works available. Those who would have previously have worked would no longer have the applicable skill to do so with the new technology. This type of unemployment would be worsened, if the introduction of robots in manufacturing process was being implemented in manufacturing industries.
Seasonal Unemployment
This unemployment is expected based on given time of year. For example certain industry experience seasonal unemployment because of the off-season. This is adjusted in government statistics as seasonal adjustments. Factors that would worsen this type of unemployment would come from more people force to take their annual holidays when the schools are on holiday, because there is not business demand would fall because school is out.
2.
a)
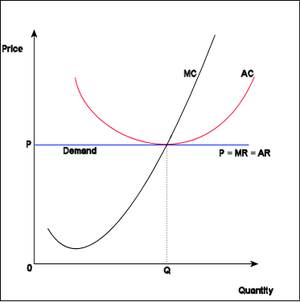
Figure 2.1
This image was copied from http://centralecon.wikia.com/wiki/Perfect_Competition
A firm is break even when total sales revenues equals to its total cost. This is the point at which average variable cost AC intersect with marginal revenue MR. At the break even point, the company will not make any profit or loss. The shut down price is when a firm average variable cost curve is above the marginal revenue curve. When this occurs, is an indication that the firm will leave the market. At the point of the firm leaving the market, the supply would decrease, that would lead to the increase in the profit of the firms that staff in the market.
b)
|