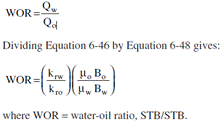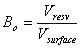Theoretical QuestionsProduction Technology Note: You will not get exactly these questions during the Final Exam. However, if you answer these questions while preparing for the exam, then you can consider yourself prepared for the “theoretical questions” part of the Exam. 1. What kind of data is included in Diagnostic Plot? 2. What is a primary recovery method? 3. What is a secondary recovery method? 4. What is a natural flow? 5. Types of Artificial Methods? 6. Reservoir drive mechanisms? 7. What kind of parameters are used to estimate STOIIP? 8. What does IPR describe? 9. What kind of information is required to construct IPR plot? 10. What does VLP describe? 11. What kind of information is required to construct VLP plot? 12. What happens if IPR and VLP curves do not intersect? 13. How does viscosity, pressure difference, cross section area and length of a system affect permeability? 14. What is Productivity Index? 15. What’s the difference between Steady State Flow and Semi Steady State Flow? 16. What is a skin factor and what does mean positive/negative skin factor? 17. Perforation objectives? 18. How is shaped charge performance is gauged? 19. What is geosteering during Horizontal well construction and what type of data is required? 20. What is a smart well? 21. What are the benefits of horizontal wells? • Large volume of the reservoir can be drained by each horizontal well. • Higher productions from thin pay zones. • Horizontal wells minimize water and gas zoning problems. • In high permeability reservoirs, where near-wellbore gas velocities are high in vertical wells, horizontal wells can be used to reduce near-wellbore velocities and turbulence. • In secondary and enhanced oil recovery applications, long horizontal injection wells provide higher injectivity rates. • The length of the horizontal well can provide contact with multiple fractures and greatly improve productivity. 22. Where pressure losses occur? 23. d) Some horizontal and multi lateral wells
24.
25.
26. What is a dew point pressure and bubble point pressure?
27. What is Oil FVF? 28. What are the advantages of Hydraulic pumps?
29. What are the disadvantages of Hydraulic pumps? 30. What’s the principle of gas lift method?
31. Gas lift advantages? 32. Gas lift disadvantages? 33. Gas lift design parameters? 34. Gas lift valves? 35. If water cut increases how does VLP curve change? 36. What is the difference between continuous and intermittent gas lift methods? 37. ESP downhole equipment and their properties? 38. ESP surface equipment and their properties? 39. ESP advantages? 40. ESP disadvantages? 41. ESP motors? 42. PCP principle? 43. PCP advantages? 44. PCP disadvantages? 45. The principle of sucker pump? 46. Sucker pump failure reasons? 47. What is dynamometer used for in Rod Pumps? 48. Rod pumping advantages? 49. Rod pumping disadvantages? 50. Rod pump rate is dependent on what parameters? 51. What is formation damage? 52. What does Skin Total include? 53. Hawkings equation of Formation Damage? 54. Sources of Formation Damage? 55. Formation damage due to fluid loss? 56. Relative permeability principle? 57. What does happen to relative permeability to oil and to water, if water saturation increases? 58. What is a capillary pressure? 59. What’s the purpose of well stimulation? 60. What stimulation techniques are available and their objective? 61. Minimum matrix stimulation candidate well selection criteria? 62. The stimulation cycle? 63. Potential formation damage caused by Matrix Stimulation? 64. Matrix stimulation – laboratory testing? 65. Matrix stimulation – bullhead or treatment via coiled tubing? 66. What kind of information can be obtained from Well Testing? 67. What kind of information can be obtained from Production Logging? 68. Minimum requirements for a propped hydraulic fracturing well candidate? 69. Key fracture design issues? 70. What is production system optimization? 71. What are the bottom hole completion techniques and what's the difference among them? 72. What are the flow conduit between the reservoir and surface and what's the difference among them?
|


 What is Absolute Open Flow?
What is Absolute Open Flow?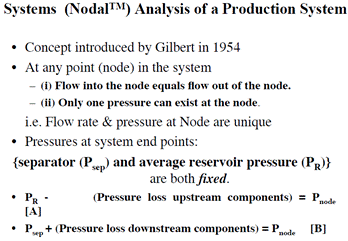 What is the purpose of Nodal Analysis?
What is the purpose of Nodal Analysis?
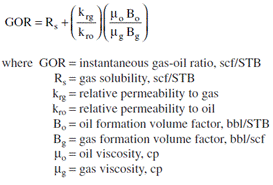 What is GOR, WOR, GLR?
What is GOR, WOR, GLR?