Introduction
In this experiment you will observe some spontaneous and non-spontaneous oxidation-reduction reactions, and see how the spontaneous reactions generate an electric current, whereas the non-spontaneous reactions are caused by an electrical current. There is also a quantitative part of the experiment in which you can determine the value of the Faraday (the charge of one mole of electrons), based on the weight loss of a lead anode in an electrolytic reaction caused by a known current for a measured period of time.
A Galvanic Cell
The reaction you study in this part is:
Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu
That reaction is spontaneous, so it can act as an energy source. If the two reactants contact each other directly, the only energy given off is heat. If they are not allowed to contact one another directly, but are made part of an electrical cell, so that they can transfer electrons through a wire, the energy given off does electrical work.
Experimental Procedure
SAFTEY PRECAUTIONS: Wear your safety goggles.
WASTE DISPOSAL: All waste from this experiment should be poured into the inorganic waste containers in the fume hood.
1. Observing the direct reaction: Put about 2 or 3 mL of the copper (II) sulfate solution into a test tube; put in a thermometer and measure and record the temperature. Leave the thermometer in the solution, and put some powdered zinc metal (enough to be about one-fourth of the solution volume) into the solution; stir gently with the thermometer. Record all evidence of reaction.
2. Now set up a galvanic cell (‘battery’) using the same spontaneous oxidation-reduction reaction of Zn with Cu2+. Separate the two half-reactions so that the electrons must be transferred by traveling through the wires attached to the electrodes. Attach the wires to a voltmeter, or to a little electric fan, or other device as evidence that your battery is producing electric current. (See Figure 1)
In this part of the experiment, you observed the same product-favored reaction in two different set-ups. What happened to the energy released by the reaction in each case?
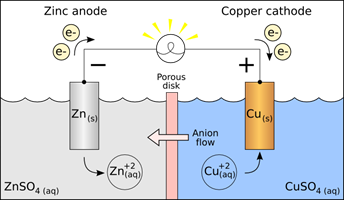
Figure 1.
| CHEMISTRY LAB (EQUIPMENT)
|
| Suggest the Ukrainian translation of the lab equipment and glassware below.
|

| 
| 
| 
|
| beaker
| bottle
| Bunsen burner
| burette
|

| 
| 
|

|
| crucible
| Erlenmeyer flask
| evaporating dish
| Florence flask
|

| 
| 
| 
|
| graduated cylinder
| funnel
| clay triangle
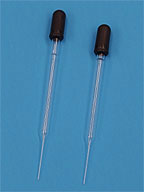
| dropper
|

| 
| 
| 
|
| forceps (tweezers)
| spatula
| mortar and pestle
| ring clamp & stand
|

|

| 
| 
|
| stirring rod
| stopper
| test tube
| test tube holder
|

|

| 
| 
|
| test tube rack
| test tube brush
| goggles
| filtering flask
|

| 
| 
| 
|
| separatory funnel
| thermometer
| tongs
| volumetric flask
|

| 
| 
| 
|
| watch glasses
| wire gauze
| utility clamp
| plastic and rubber policemen
|
|
| Piece of equipment
| Definition and usage
| Translation
|
| 1.
|
| used to hold and heat liquids. Multipurpose and essential in the lab.
|
|
| 2.
|
| can be used for storage, for mixing and for displaying.
|
|
| 3.
|
| are used for heating and exposing items to flame. They have many more uses than a hot plate, but do not replace a hot plate.
|
|
| 4.
|
| is used in titrations to measure precisely how much liquid is used.
|
|
| 5.
|
| are used to heat small quantities to very high temperatures.
|
|
| 6.
|
| is used to heat and store liquids. The advantage of it is that the bottom is wider than the top so it will heat quicker because of the greater surface area exposed to the heat.
|
|
| 7.
|
| is used to heat and evaporate liquids.
|
|
| 8.
|
| is used for heating substances that need to be heated evenly. The bulbed bottom allows the heat to distribute through the liquid more evenly. It is mostly used in distillation experiments.
|
|
| 9.
|
| is a piece of laboratory glassware, cylindrical in shape and graduated, used to accurately measure out volumes of liquid reagents for use in reactions.
|
|
| 10.
|
| is a piece of equipment that is used in the lab but is not confined to the lab. It can be used to target liquids into any container so they will not be lost or spilled.
|
|
| 11.
|
| is used to hold crucibles when they are being heated. They usually sit on a ring stand
|
|
| 12.
|
| is used for moving small amounts of liquid from place to place.
|
|
| 13.
|
| are used for plucking or handling small objects.
|
|
| 14.
|
| is used for moving small amounts of solid from place to place
|
|
| 15.
|
| are used to crush solids into powders for experiments, usually to better dissolve the solids
|
|
| 16.
|
| are used to hold items being heated.
|
|
| 17.
|
| is used to stir things. They are usually made of glass.
|
|
| 18.
|
| is used to plug flasks and test tubes
|
|
| 19.
|
| is used to hold, mix, or heat small quantities of solid or liquid chemicals, especially for qualitative experiments and assays
|
|
| 20.
|
| is used to hold test tubes when they are hot and untouchable
|
|
| 21.
|
| is used to hold test tubes while reactions happen in them or while they are not needed
|
|
| 22.
|
| is used to easily clean the inside of a test tube.
|
|
| 23.
|
| are a protective eyewear
|
|
| 24.
|
| is used for receiving a filtering liquid and that is usually of heavy-walled glass and is often provided with a side tube to connect with a suction pump
|
|
| 25.
|
| is used in liquid-liquid extractions to separate (partition) the components of a mixture into two immiscible solvent phases of different densities
|
|
| 26.
|
| is used to take temperature of solids, liquids, and gases. They are usually in oC, but can also be in oF
|
|
| 27.
|
| are used to hold many different things such as flasks, crucibles, and evaporating dishes when they are hot.
|
|
| 28.
|
| is used to measure one specific volume. They are mostly used in mixing solutions where a one liter or one half a liter is needed.
|
|
| 29.
|
| are used to hold solids when being weighed or transported. They should never be heated.
|
|
| 30.
|
| is to be placed under the container holding the liquid, that is being heated by the Bunsen burner, so that the container doesn't have direct contact with the flame.
|
|
| 31.
|
| is used to hold laboratory glassware, can be tightened to hold something securely.
|
|
| 32.
|
| is used to transfer residues of precipitates or solids from the inside or beakers, flasks or other glass surfaces.
|
|





































