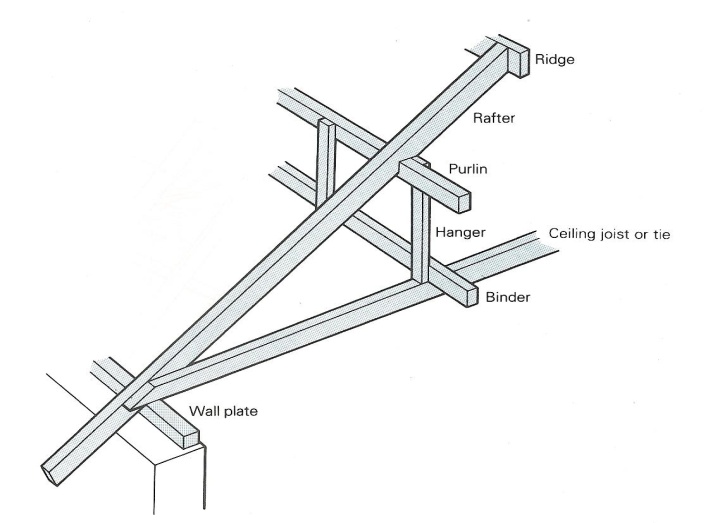
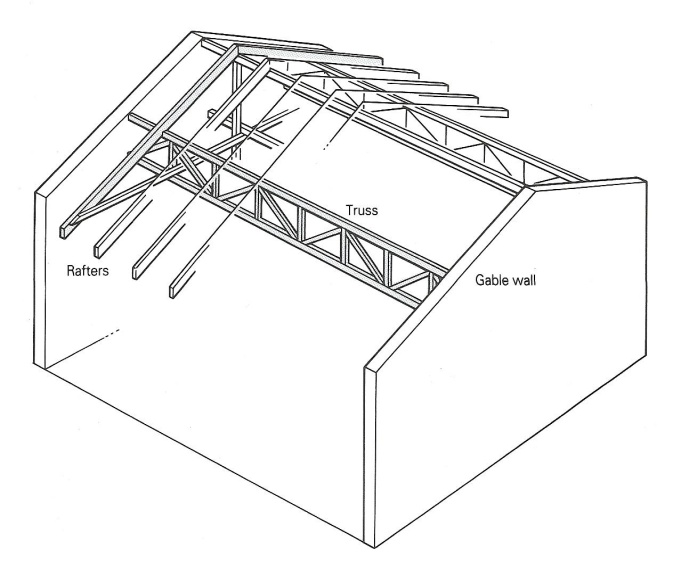
IFFERENT METHODS of PITCHED ROOF CONSTRUCTIONPitched roofs can be built in different ways depending on the loads and sizes. This list describes some common types of pitched roof that use different methods of construction.
21 Topics for projects and presentations: 1. Metal roofing. 2. Defects of roofing. 3. Solar roofs. 4. Roof gardens. 5. Roof garden vs. green roof.
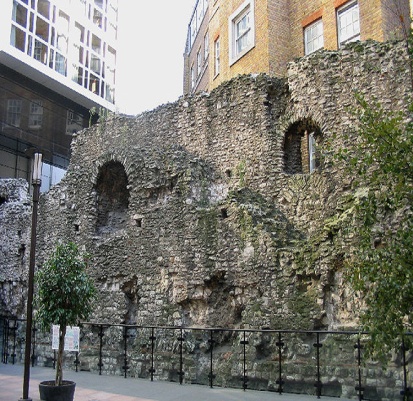
“Traditional buildings have thick exterior walls. Modern buildings have thin walls.” Matthew Frederick (architect)
10.1 Types of Walls 1 Explain how the following words are connected with “walls”: internal, external, load-bearing, non-load-bearing, cladding, separation, sound insulation.
2 Match information to the pictures:
L t1UKDXHTtVBSKC5JzEtJzMnPS7VVqkwtVrK34+UCAAAA//8DAFBLAwQUAAYACAAAACEAUNS3c8IA AADcAAAADwAAAGRycy9kb3ducmV2LnhtbESPwarCMBRE94L/EK7g7pnqokg1iopCcfHAPj/g0lyb 0uamNFHr3xvhgcthZs4w6+1gW/Gg3teOFcxnCQji0umaKwXXv9PPEoQPyBpbx6TgRR62m/FojZl2 T77QowiViBD2GSowIXSZlL40ZNHPXEccvZvrLYYo+0rqHp8Rblu5SJJUWqw5Lhjs6GCobIq7VZAf z3kj03PR3K57sytcHX6PB6Wmk2G3AhFoCN/wfzvXChbzFD5n4hGQmzcAAAD//wMAUEsBAi0AFAAG AAgAAAAhAPD3irv9AAAA4gEAABMAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAFtDb250ZW50X1R5cGVzXS54bWxQ SwECLQAUAAYACAAAACEAMd1fYdIAAACPAQAACwAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAuAQAAX3JlbHMvLnJlbHNQ SwECLQAUAAYACAAAACEAMy8FnkEAAAA5AAAAEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAApAgAAZHJzL3NoYXBleG1s LnhtbFBLAQItABQABgAIAAAAIQBQ1LdzwgAAANwAAAAPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAJgCAABkcnMvZG93 bnJldi54bWxQSwUGAAAAAAQABAD1AAAAhwMAAAAA ">
• Write a paraphrase. • Say whether you agree or not, and why.
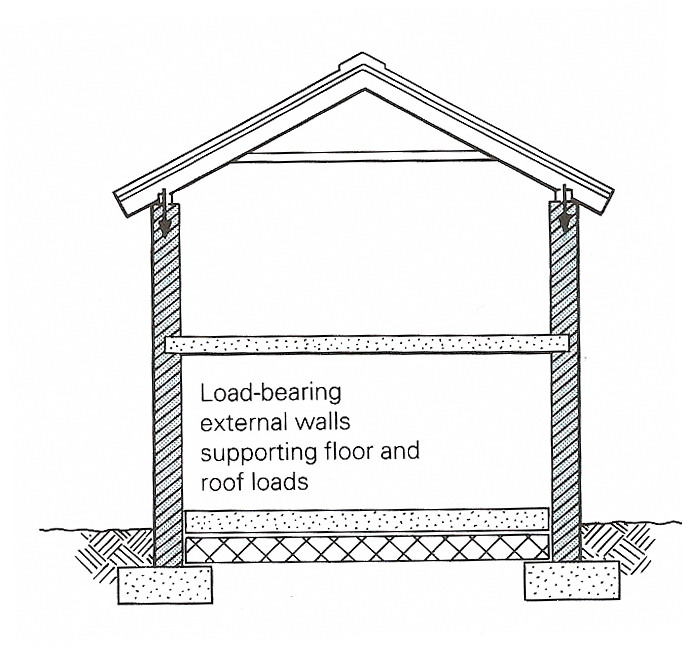
4 a) Transcribe the following words: areas, characteristics, strength, thermal, durability, domestic, corrugated, insulation, reasonable, majority. b) In what context do you think the following words and phrases will appear in the text? •enclose and separate•external and internal •weather resistance •thermal properties •fire-resistance•load-bearing/ non-load-bearing •domestic •cladding sheets •separation •sound insulation c) Read the text and check your answers: WALLS Walls are constructed to enclose areas and to separate the spaces inside and outside a building. This unit describes the main characteristics of external and internal walls. External walls should have the following characteristics: 1) strength to resist being crushed by the loads from floors and roofs; 2) stability to resist other forces such as wind pressure and roof loads; 3) weather resistance to keep out wind and rain; 4) thermal properties to keep the interior cool in hot weather and retain warmth in cool weather; 5) durability; 6) fire-resistance to provide security and stability in the event of fire; 7) openings for daylight and ventilation; 8) good construction and use of materials. External walls can be divided into the load-bearing external walls and non-load-bearing external walls. Load-bearing external walls (Figure. 10.2) are normally used for domestic buildings or other small structures that are one or two storeys high. The weight of the roof and any upper floors is supported by load-bearing masonry of brick, block or stone construction.
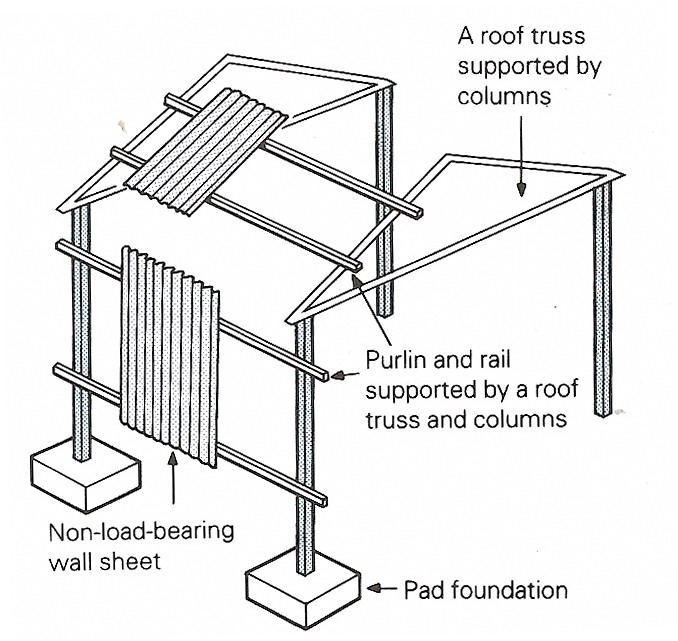
Figure 10.2 Load-bearing external walls Non-load-bearing external walls (Figure.10.3) are often built from corrugated sheet cladding that is attached to a framework of timber or steel rails and column. The cladding sheets do not support the structure of the building. Support is provided by the framework. The cladding sheets must be wind-resistant.
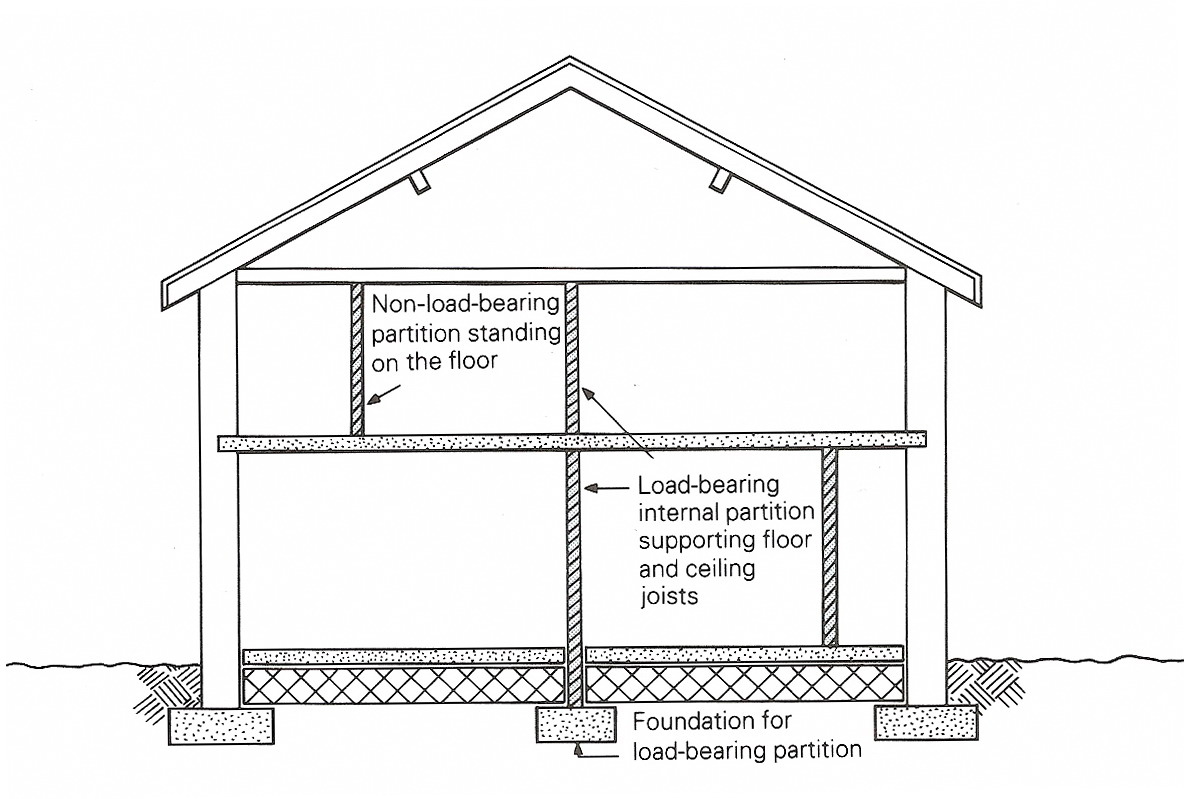
Figure 10.3 Non-load-bearing external walls Internal walls should have the following characteristics: 1) positions that provide separation between rooms; 2) sound insulation that provides a reasonable level of noise control between adjoining rooms; 3) stability to resist normal impact and to support fixtures and fitting; 4) fire-resistance to prevent the rapid spread of fire to adjoining rooms. Internal walls can be divided into the load-bearing internal walls and non-load-bearing internal walls (Figure 10.4).
Figure 10.4 Load-bearing and non-load-bearing internal walls Internal walls are load-bearing if additional support is needed for the roof or floors. These walls will need to be strong and stable. They usually stand on concrete foundation. Non-load-bearing internal walls divide the internal space in buildings and stand independently of the main structure. The majority of internal walls are in this category.
4 Read the text again and answer the questions that follow (1-7): 1. What characteristics of external walls can you offer? 2. How can you classify external walls? 3. What is the function of load-bearing external walls? 4. What is the role of sheet cladding in non-load-bearing external walls? 5. What are the characteristics of internal walls? 6. What have you learnt about internal load-bearing walls? 7. What types of walls divide the internal space in buildings? Follow-up 6 a) Find in the text the synonyms for the following words: principle features, to withstand, not allow to, thermic qualities, to hold warm temperature, small buildings, brickwork, plating, is ensured, acceptable rate of sound control, to obviate fast spreading, adjacent space, extra bearer/ bearing.
|