The work of the external and internal forces in tension (compression). Strain energy
In tension (compression) the external forces make the work in tension in consequence of displacement points where they are put (Fig. 2.10 a) Evaluate the statically applied external force work i.e. the force which increases from zero up to its final value with a small velocity in the process of deformation.
а) б)
Fig. 2.10.
An elemental work dW of the external force F under the displacement
But there is the relation (Hook’s law) between
Substituting the value into the formula (2.22) we get
The total force work is found integrating this expression in the limits from zero to the final displacement value
Thus,
Fig. 2.11.
Grafically the force work F is expressed (taking into account the metric scales) by the OCB diagram area drawn in the Notice that the force work F1 (constant by the value) under the displacement
Under the deformation both the external forces and the internal forces (elastic forces) do work. The elemental internal force work (for the element dz) is evaluated by the formula (Fig. 2.11):
where N is the internal force (a normal force); ∆ (dz) is the element elongation. But, according to Hook’s law we have
Integrating both formula parts (2.26) we get the total internal force work for the whole bar length
If N, E and A are constant, then
where
The value equal to the internal forces work but having the opposite sign is called the strain energy. It represents the energy which is stored by the body under its deformation. Thus, the strain energy in tension (compression) for the constant section under the action of the constant normal forces at all sections is determined by the formula
The strain energy set up on a unit volume of the material is called the specific potential energy:
or
Under the general state of stress the specific potential energy is equal to the sum of three items:
Using the general form of Hook’s law we get
It is easy to receive the formula of the plane stress from the formula (2.32) as the special case of one of the principal stresses being equal to zero.
|


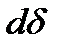 is equal to
is equal to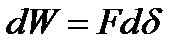 . (2.22)
. (2.22) and F
and F

 :
: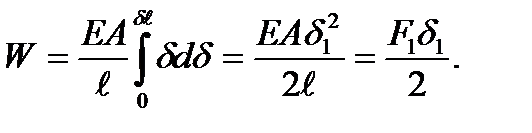
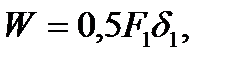 (2.23)
(2.23) i.e. the work of the external statically applied force is equal to half the product of the final force value and the final value of the corresponding displacement.
i.e. the work of the external statically applied force is equal to half the product of the final force value and the final value of the corresponding displacement. coordinates (according to the scale Fig. 2.10 b).
coordinates (according to the scale Fig. 2.10 b). is equal to
is equal to (2.24)
(2.24) (2.25)
(2.25)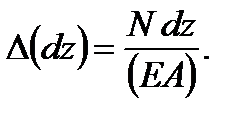 Hence,
Hence, (2.26)
(2.26) :
: . (2.27)
. (2.27) (2.28)
(2.28) is the bar elongation.
is the bar elongation. (2.29)
(2.29) (2.30)
(2.30) as
as  or
or  (2.31)
(2.31)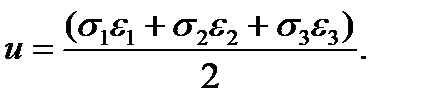 (2.32)
(2.32) (2.33)
(2.33)


