Key provisions2.1 Basic terms and definitions Uncertainty of measurement - a parameter related to the measurement result, which characterizes the scattering of the values that could reasonably be assigned to the measurand. The following types of uncertainty: standard, enhanced, and the total standard uncertainty. The standard uncertainty (H): uncertainty of measurement results, expressed as standard deviation (SD), it is the primary quantitative expression of measurement uncertainty The overall standard uncertainty (H c): standard uncertainty of measurement results obtained through the values of other quantities, equal to the positive square root of the sum of terms, and the members are or Variances covariances of these other quantities weighted according to how the measurement result varies with these quantities, it is the primary quantitative expression of uncertainty of measurement in which the result is determined by the values of other variables Expanded uncertainty (H p) value that defines an interval around the measurement result within which, as you might expect, there is a big part of the distribution of values that reasonably could be attributed to the measurand. There are two types of calculations the standard uncertainty: - Calculation of the type A - by statistical analysis of measurement results; - Calculation of the type B - using other methods. Estimation of uncertainty of measurement results by the type A and type B made both by direct and indirect methods for measurement. 2.2 Assessment of uncertainty of the results of measurement of physical quantities with direct measurements of ejection fraction: Uncertainties of measurement results by type A. The initial data for calculating the H and A are the statistical number of measured input variables: x i (where i = 1, 2,..., n). Standard uncertainty of a single measurement q-th input variable H Aq is determined by:
Standard uncertainty of H A (x) measurements of a number of input values
The overall standard uncertainty (H c A) in the case where direct measurement is determined by:
Evaluation of measurement uncertainty of the outcome of type B. Standard uncertainty of the measurement result by type in: ,
where l = 1, 2, 3.... L, a - basic error, ξ - Factors affecting the measurement. Here - Standard uncertainty caused by the change in the basic error of SI; - Standard uncertainty affecting the measurement of PV. For analog SIT uncertainty is calculated in accordance with the formula:
where - Standard uncertainty caused by the change in temperature T 0; - Standard uncertainty caused by shunting the output impedance of the object input resistance of the ITA. For digital SIT should also take into account the uncertainty arising in the quantization of the analog signal. The standard uncertainty of H ab (x), defined by the formulas, depending on the distribution function of the basic error (Appendix A): - For the rectangular (uniform) distribution function:
where a - basic error determined by the accuracy class of instrument. To estimate the uncertainty of T H 0 V, due to the temperature deviation from the normal rules of T = 20 ˚ C is assumed that the limit of additional error caused by deviation of the device ambient temperature (T okr.sr). Within the normal operating temperature of no more than the limit basic error for every 10 ˚ C temperature change is:
Uncertainty is given by: ,
where Since the value of load resistance and input impedance are known about and are, within certain limits [R min; R max], [R vhmin; R vhmax], assuming all the values of resistors within the marked boundaries equally, their uncertainty can be estimated as:
Fordirectmeasurementsofthetotalstandarduncertaintyoftype B isequaltothestandarduncertaintyoftype B:
The resulting standard uncertainty is determined by the formula:
2.3 Evaluation of uncertainty of the results of indirect measurements of ejection fraction: In general, the measured value of Y is defined by: Y = ƒ;(x 1,…, xm)
Initial data for calculation of the type A HA is a statistical number of measured input variables:{ xq } (where q = 1,..., m).Standard uncertainty of type A indirect measurements of ejection fraction is defined by the expressions:
The overall standard uncertainty (NcA) in the case of uncorrelated estimates of indirect measurements of ejection fraction is given by:
where Evaluation of the total standard uncertainty of indirect measurements of type B (Nvc) in the case of uncorrelated estimates x 1,…, хm calculated by the formula:
where The resulting standard uncertainty is determined through the NSA and NSV by the formula:
Expanded uncertainty of Hp with a given probability p and the known distribution law is determined as follows:
where k — coverage factor. In accordance with the recommendations of DSTU [2] and the assumption of normality of the distribution of values of the measured quantity take k
where
|

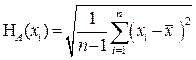 (1)
(1)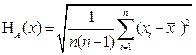 (2)
(2)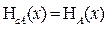 (3)
(3)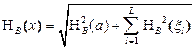 (4)
(4)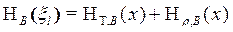 (5)
(5)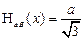 (6)
(6)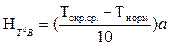 (7)
(7) (8)
(8)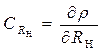 ,
, 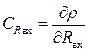 - Sensitivity coefficients
- Sensitivity coefficients 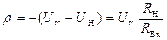 ; H R H - The uncertainty of the load resistance; H R input - the uncertainty of input resistance.
; H R H - The uncertainty of the load resistance; H R input - the uncertainty of input resistance.
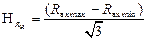
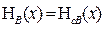
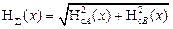
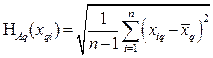
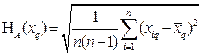

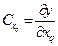 — sensitivityfactor.
— sensitivityfactor.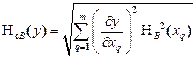 ,
,
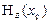 — standard uncertainty of measurement results q- ththe input variable.
— standard uncertainty of measurement results q- ththe input variable.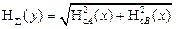
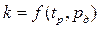
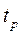 — Student coefficcient,
— Student coefficcient, — confidence probability.
— confidence probability.


