Basic economic theory of risk. Expected utility function, risk premium and risk aversion measures.
Origins of Expected Utility Theory:The concept of probability was developed in the 17th century by Pascal, Fermat. This led immediately to the first mathematically formulated theory about the choice between risky alternatives, namely the expected value (or mean value). The expected value of a lottery A having outcomes x, with the probability p, is given by
For that reason, it makes no sense compute the expected value in terms of monetary units. Instead, we have to use units which reflect the usefulness of a given wealth. This concept leads o the utility theory. The determination of the value of an item must not be based on the price, but rather on the utility (“moral value”) it yields. In other words, every level of wealth corresponds to a certain numerical value for the person’s utility. A utility function u assigns to every wealth level (in monetary units) the corresponding utility. Utility Function: A preference relation that is complete, reflexive, transitive and continuous can be represented by a continuous utility function. Continuity means that small changes to a consumption bundle cause only small changes to the preference level.
x’> x” U(x’) > U(x”) x’< x” U(x’) < U(x”) x’~ x” U(x’) = U(x”).
A utility function In order to maximize expected value of utility Expected Utility Theory (EUT) was introduced. EUT was first introduced in 18th century by Bernoulli, but has only been accepted in the middle of the 20th century. It is used in economics to explain choice under uncertainty.
EUT implies that rational individuals act as though they were maximizing expected utility, and allows for the fact that many individuals are risk averse, meaning that the individuals would refuse a fair gamble (a fair gamble has an expected value zero). In the presence of risky outcomes, a decision maker could use the expected criterion as a rule: higher expected value investments are simply the preferred ones. Risk aversion implies that their utility functions are concave and show diminishing marginal wealth utility. The risk attitude is directly related to the curvature of the utility function: risk neutral individuals have linear utility functions, while risk seeking individuals have convex (выпуклая) utility functions and risk averse individuals have concave (вогнутая) utility function. The degree of risk aversion can be measured by the curvature of the utility function. We call a person risk-averse if he prefers the expected value of every lottery over the lottery itself. We call a person risk-seeking if he prefers every lottery over its expected value.
|



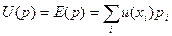 - EUT, where u – utility, x – outcomes, p – probability.
- EUT, where u – utility, x – outcomes, p – probability.


