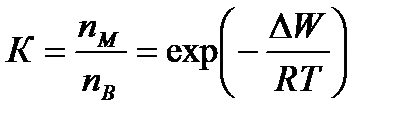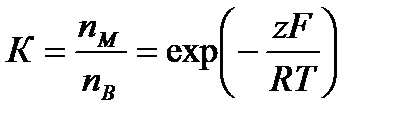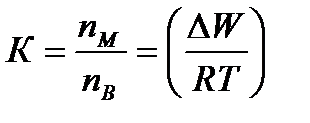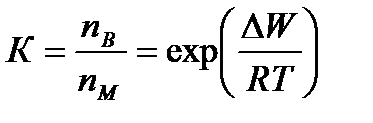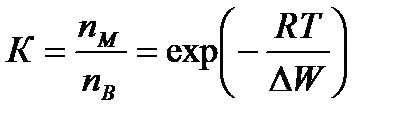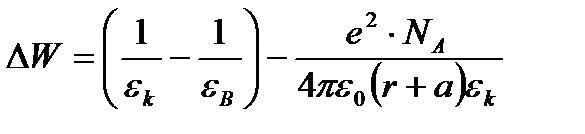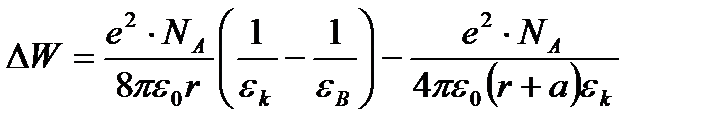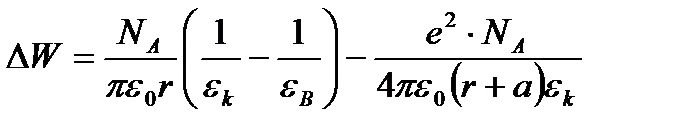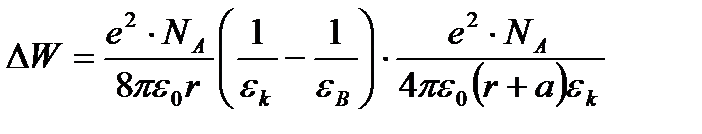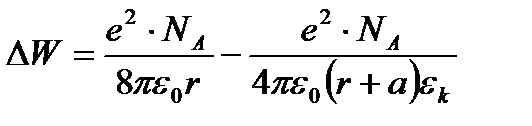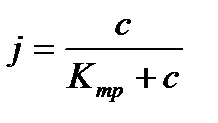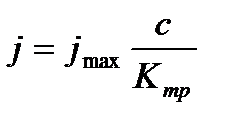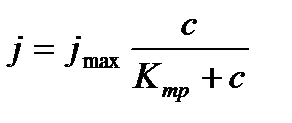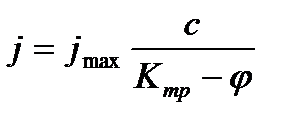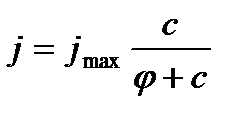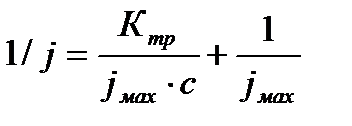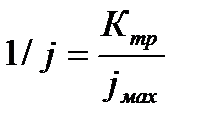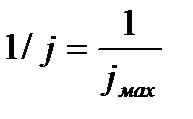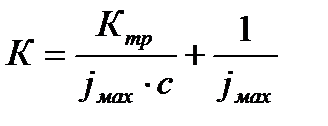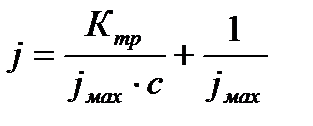Overall assessment of the knowledge. A teacher analyses competencies: knowledge, self-education on the theme, analyses mistakes that were done by students at the passing of testsA teacher analyses competencies: knowledge, self-education on the theme, analyses mistakes that were done by students at the passing of tests. At the end of the lesson corresponding points are put. Test 1. Not only separate molecules can be passed through the membrane but also solid bodies can be. This kind of transport is called: А) endocytosis; В) exocytosis; С) phagocytosis; Д) pinocytosis; Е) secondary active. 2. Not only separate molecules can be passed through the membrane but also solutions can be. This kind of transport is called: А) endocytosis; В) exocytosis; С) phagocytosis; Д) pinocytosis; Е) secondary active. 3. Types of membrane lipids: А) phospholipids, glycolipids, steroids; В) carbohydrates, proteins, glycolipids; С) amino acids, carbohydrates, steroids; Д) phospholipids, proteins; Е) neurons, amino acids. 4. Types of biological membranes: А) neurons, cellular; В) cellular, intracellular, basal; С) nervous fibers, basal; Д) neurons, proteins; Е) cholesterol, proteins. 5. Permeability of a membrane for potassium ions in rest: А) significantly more than the permeability for sodium ions; В) significantly less than the permeability for sodium ions; С) approximately equals to the permeability for sodium ions; Д) infinite; Е) zero. 6. Lipid molecules of which shape being in bilayer are more inclined to form pores? А) cylindrical; В) conical; С) inverted; Д) linear; Е) cubic. 7. Transport of substances with the participation of carriers differs from simple diffusion by: A) greater solubility; B) greater velocities of carrying; C) lower velocities of carrying; D) lower solubility in water; E) lower solubility in lipids. 8. Active transport provides the carrying of substance: A) by the potential gradient; B) by the concentration gradient; C) against the concentration gradient; D) by the pressure gradient; E) against the pressure gradient. 9. Biological membranes are barrier structures that sharply limiting … between cytoplasm and environment: A) active transport; B) simple diffusion; C) filtration; D) osmosis; E) lateral diffusion. 10. At the resting state cytoplasmic membrane is maximally permeable for ions of: A) К B) Na C) Cl D) Ca E) Mg 11. Ability of ionic channels to selectively pass through the ions of one type is called: A) selectivity; B) conductivity; C) transport activity; D) diffusion; E) filtration. 12. Ionic channels are the complex of … that penetrate the membrane: A) organoids; B) lipids; C) proteins; D) lysosomes; E) micelles. 13. Functions of membranes (3 answers): А) create a shock wave; Б) implements the transport of substances; В) mechanical support of a cell; Г) electrical isolators; Д) transport of hematocrit. 14. Functions of membrane proteins: А) provide the transport of hydrophilic substances through the membrane; Б) implement superfluidity; В) implement the transmission of pulse wave; Г) serve as the source of electromagnetic wave; Д) increase the pressure. 15. Membrane proteins: A) enhance the strength of lipid carcass; B) implement superfluidity; C) implement the transmission of pulse wave; D) serve as the source of electromagnetic wave; E) increase the pressure. 16. Biological membranes combine the properties of: А) crystal and liquid; Б) only crystals; В) only liquid; Г) gases; Д) gases and liquid. 17. Boltzmann formula for the distribution coefficient in liquid mediums: A) B) C) D) E) 18. At the transition of monovalent ion from the environment to a channel the changing of free energy is: A) B) C) D) E) 19. The flow of a substance transported by carriers: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 20. Linwear-Burk equation: А. В. С. D. E.
Theme №2: Research methods of the electrical activity of different organs. Electrical activity of the heart, central nervous system, muscles.
Purpose: 1. Learning the methods of registering the biopotentials in heart, brain and muscles. 2. To form the making of diagnosis to a patient by the results of registering the biopotentials. Number of forming competencies:self-education. Tasks on the theme: 1. To explain the significance of the registering of different organs biopotentials for analysis of processes that occur in biological system. Methods of the control of formed on SIW competencies: ü Testing on a computer. ü Answering to the additional questions. Form of performance:Learning the theme using the literature. A teacher suggests 20 multiple choice questions for the checking of learning the material. Criteria of performance: To learn the theme and write the summary. Deadline:a student has to perform and hand over the works strictly according to the timetable. Criteria of the assessment: A teacher analyses competencies: knowledge, self-education on the theme, analyses mistakes that were done by students at the passing of tests. At the end of the lesson corresponding points are put
|