Read the text without a dictionaryWhy did the Byzantine art result in the greatest architecture of history?
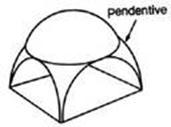
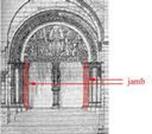
Gradually Byzantine Empire inherited the artistry of the Greek world, though it could escape neither the color nor mysticism of the East. All this Byzantium exploitedto the glory of the Church which was intent both in its liturgy and its architecture upon showing that the teaching of Jesus had been transmuted into an institution which was imperial, powerful, hierarchial and divine. In Orthodoxy the Church is an image of the universe, an image of the transfigured world which is blessed by Christ (main dome) who was foretold by the prophets (drum), and preached by Evangelists (pendentives) and the many saints (arches, windows, jambs), who came down to earth for our salvation (vaults and walls with Biblical subjects), created the Church on the blood of martyrs and saints (pillars), gives Himself to the faithful in the sacrament of the Eucharist (sanctuary apse), takes special care of the Church and His chosen ones (walls) and is the Judge at the Second Coming (west wall). Give the explanation to the following:
1. dome - …. 2. drum - …. 3. pendentives - …. 4. arches - …. 5. windows - …. 6. jambs - … 7. vaults - …. 8. walls - …. 9. pillars - … 10. sanctuary apse - …
Correspond the given definitions with the notions from the exercise above:
1. the curved inside end of a building, especially the east end of a church; 2. a post that forms the side of a door or window; 3. hanging from something; 4. a tall upright round post used as a support for a roof or bridge; 5. a roof or ceiling that consists of several arches that are joined together, especially in a church; 6. a round roof on a building; 7. something that looks like a drum; 8. a curved structure above a door, a window etc; 9. an upright flat structure made of stone or brick, that divides one area from another or surrounds an area; 10. a space or an area of glass in the wall that lets in light.
b. c.
g.
Notes:
|


 a.
a.




 d. e. f.
d. e. f.


