Answer the following questions:
1) Energy surrounds us in all aspects of life. Do you believe that the ability to harness it and use it for constructive ends as economically as possible is the challenge before mankind? Why?
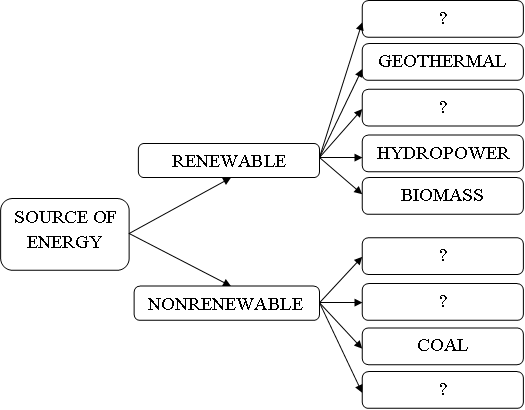
2) What sources of energy do you know? What is the difference between renewable and nonrenewable energy? Fill in the table below.
3) How do you understand the notion “alternative energy”? Are alternative sources more expensive but more environmentally friendly than conventional oil, gas, or coal?
4) Do you think it is important to develop alternative energy facilities? Why?
5) Can you imagine that alternative energy will replace traditional sources of energy soon? Give your reasons.
A) Match the energy source with its description:
| | Source of energy
| | Description
|
| 1.
| Wind energy
| A
| Of the renewable energy sources that generate electricity, this energy source is the most often used. Mechanical energy is derived by directing, harnessing, or channeling moving water. The amount of available energy in moving water is determined by its flow or fall.
|
| 2.
| Geothermal Energy
| B
| This energy is the solar radiation that reaches the earth. Solar Energy incorporated the use of photovoltaic (solar cell) technologies. It can be used directly as heating and cooling system, as lighting device, as electricity generator or in a variety of other industrial purposes.
|
| 3.
| Hydropower Energy
| C
| It is energy in the nucleus (core) of an atom. There is enormous energy in the bonds that hold atoms together. It can be released from atoms in two ways: nuclear fusion and nuclear fission.
|
| 4.
| Biomass Energy
| D
| It is energy generated from heat stored in the earth, or the collection of absorbed heat derived from underground.
|
| 5.
| Solar Energy
| E
| It is nonrenewable energy and the second source of energy in the world.
|
| 6.
| Petroleum Energy
| F
| It was formed from the remains of animals and plants that lived millions of years ago in a marine (water) environment before the dinosaurs. Over the years, the remains were covered by layers of mud. Heat and pressure from these layers helped the remains turn into what we today call crude oil.
|
| 7.
| Natural gas energy
| G
| Through the use of wind turbines mounted on a tower at 100 feet, wind power is captured and converted into useful form, such as electricity. This technology or wind turbine can be used as stand-alone applications for water pumping or communications. It can be also connected to the power grid or combined with solar energy systems. A plant with numerous wind turbines is required for large scale demands of energy.
|
| 8.
| Coal energy
| H
| It is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock composed mostly of carbon and hydrocarbons. It takes millions of years to create. It is one of the largest worldwide sources of carbon dioxide emissions. It is extracted from the ground by mining, either underground or in open pits.
|
|
| Nuclear energy
| I
| It is organic material made from plants and animals. It contains stored energy from the sun. Plants absorb the sun's energy in a process called photosynthesis. Some examples of it are wood, crops, manure, and some garbage.
|
http://ru.scribd.com/doc/22902319/World-Oil-Gas-Consumption





