Past Perfect
To form the Past Perfect Tense we use had with the past participle form of the verb. Most past participles end in - ed (painted, arrived, visited, etc.). Irregular verbs have special past participles that must be memorized. (told, said, spoken, eaten, etc.) We use Past Perfect Tense: · to say that something had already happened before another action or specific time in the past (often with adverbs like already, until, already... by, before, after,just; if either before or after is used Past Simple may be used instead Past Perfect) Example: When Linda arrived her husband had left. · the action which occurs previously in time is expressed in the past perfect tense, and the action which occurs later is expressed in the past tense Example: After I had cooked (cooked) the dinner I watched TV. · in reported speech after verbs like told,asked, said, wanted, wondered, explained Example: Your parents wanted to know what you had doneyesterday. · to show regret about the past Example: I wish we had stayed at another hotel. · in third conditional, also called conditional type 3 (if + past perfect in the 'if' clause,perfect conditional in the main clause). This is a structure we use to talk about unreal conditions in the past. Example: If the children had been good their mother would have taken them to the zoo. · with conjunctions like no sooner... thanor hardly/barely... when Example: Hardly had he finished working, when his girlfriend arrived. · a state that started in the past, and continued up to some time in the past Example: He had worked there for two years before he got fired.
Exercise 1.Put the verbs in brackets into the correct form:
Exercise 2.Translate into English:
Exercise 3.Rewrite the sentences using the words in brackets and the Past Perfect as in the example:
Exercise 4.Make up the sentences using the Past Perfect Tense:
TEST 4 (Past Simple / Past Perfect) 1. Underline the correct answer:
2. Put the verbs in brackets into the Past Perfect or Past Simple:
3. Put the verbs into the correct tense (simple past or past perfect simple): 1. When he (wake up) 2. We (go) 3. He (hear) 4. When she (start) 5. Jane (already / type) 6. By the time he (arrive) 7. Before that day we (never / think) 8. I (know) 9. They (not / know) 10. It (be)
4. Put the verbs into the correct tense (simple past or pas perfect simple): 1. It (be) 2. I (switch) 3. Then I (begin) 4. But the notes (be) 5. I (turn) 6. And where (find / I) 7. I (leave) 8. Now that I (find) 9. First I (know / not) 10. I (complete / almost) 11. After I (reboot) 12. So I (have)
|








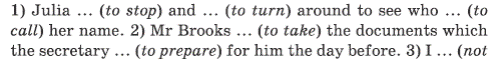

 , his mother (already / prepare)
, his mother (already / prepare) 


