The Vector, Parametric, Canonical, and General Equations of a Straight Line
The position of a straight line in space is determined by a point equation of such a line in space. z
0 y x To this end, we take an arbitrary point
It is seen from the figure, that If the point М belongs to the straight line, then the vectors Consequently, these vectors meet the collinearity condition
where t is a parameter. Let us write the collinearity condition in the form
equation (*) is the vector equation of the given line. Suppose given the coordinates of the point M0(x0,y0,z0) and the direction vector
the direction vector is
Let us represent equation (*) in the form
Equating the respective coefficients of the unit vectors on the right- and left- sides, we obtain parametric equations of the straight line:
Eliminating the parameter t, we obtain the canonical equations of a straight line:
Example. Write the canonical equations of the straight line passing through the point
Equating each fraction to a parameter t, we obtain the parametric equations of the line:
The general equation of a straight line in space. Since a straight line in space is represented as the intersection of two planes, the general equation of a straight line in space has the form of a system
where the first and the second equations are the equations of the corresponding planes. It is always possible to transform the general equation of a straight line into a canonical equation and vice versa. Since the direction of
i.e., the canonical equation is
The angle between straight lines in space. The parallelism and perpendicularity conditions for straight lines. Let us find the angle between intersecting right lines given by their canonical equations
The angle between these two lines is equal to the angle between their direction vectors
i.e.,
The parallelism and perpendicularity conditions for right lines coincide with the collinearity and perpendicularity conditions of their direction vectors If straight lines are perpendicular, then
If straight lines are parallel, then the vector
The equation of the straight line passing through two given points. Suppose given two points
M2 M1
0 y
x
|

 on this line and a vector
on this line and a vector  parallel to the line. Let us write an
parallel to the line. Let us write an


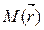
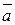
 on the line, join М0 and М to the origin, and find the coordinates of the radius-vectors
on the line, join М0 and М to the origin, and find the coordinates of the radius-vectors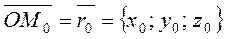 ,
, .
. .
.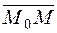 and
and  are collinear.
are collinear. ,
,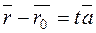 ; (*)
; (*) . Let us write the left-hand side of equation (*) in the vector form
. Let us write the left-hand side of equation (*) in the vector form
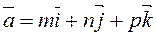 .
.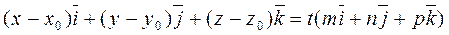 .
.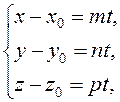 or
or 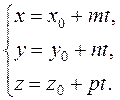 (27)
(27)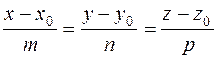 . (28)
. (28) parallel to the vector
parallel to the vector  . We compose the canonical equation by formula (28):
. We compose the canonical equation by formula (28):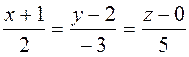 .
.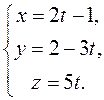
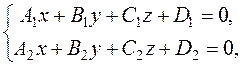
 is perpendicular to those of the vectors
is perpendicular to those of the vectors  and
and 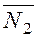 , it follows that
, it follows that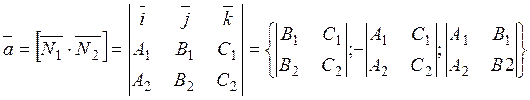 ,
,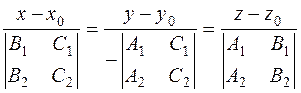 .
.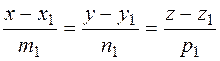 ;
;  .
. ;
;  ,
,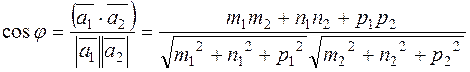 .
. and
and 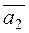 .
. , i.e.,
, i.e., 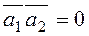 , and the perpendicularity condition is
, and the perpendicularity condition is .
.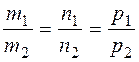 .
.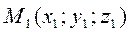 and
and  in space.
in space. z
z


