Quantized text №1
Methods of study of the morphology of microorganisms. Types of microscopy, purpose, principles of application. Micro-organisms can be seen with an optical microscope instrument (Greek micros - small, scopeo - look). Depending on the purpose of using various types of microscopy: light, dark field, phase - contrast, fluorescent, electronic. light microscopy Light microscope consists of a mechanical and optical parts (Figure 1. 1). The mechanical part is represented by a leg (or foot), tubusoderzhatelem, tubes, sample stage. At the bottom of tubusoderzhatelya are macro and microscrews for coarse and fine feed tube. The upper part is provided with a screw fastening tubusoderzhatelya revolver lens. The optical part of the microscope consists of a lens, an eyepiece and lighting apparatus. Lenses are divided into dry and immersion (immersion). Dry the lens - is an object between the front lens is considered a drug and is air. Of - the difference in the refractive indices of the slide and the air of the light beam misses the eye of the observer. In the study of microorganisms is mainly used immersion ("dip") lens with a small focal length and a higher resolution (magnification 60x-100x). When the immersion microscope lens system is immersed in oil (cedar, vaseline, peach, "immersiol" et al.) Whose refractive index close to the refractive index of the glass. In this case, the rays of light passing through the glass slide, do not change their direction and do not disperse and fall into the lens. This achieves the best possible illumination of the object, since the rays are not refracted and fall into the lens. The resolution of the immersion lens of about 0.2 microns. The maximum increase in modern optical microscopes reaches 3000h-2000s. In conventional light microscopy observed object examined in transmitted light. Because microbes, like other biological objects, low contrast, then, for better visibility paint them.
1 PICTURE
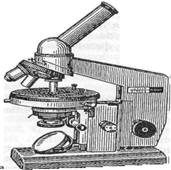
1 Microscopes and - a general view of the microscope "Biolam"; b - Microscope MBR-1: 1 microscope base; 2, the stage; 3 screws for moving the stage; 4-terminal, the pressing drug; 5-condenser; 6 bracket condenser; 7 screw firming condenser in the sleeve; 8-handle moving the condenser; 9-handle iris condenser; 10 mirror; 11 tubusoderzhatel; 12 makrometricheskogo handle screws; 13-handle micrometer; 14 nosepiece; 15 lenses; 16-inclined tube; 17 screw for fixing the tube; 18 eyepiece. Rules for working with a microscope. Working with the light microscope includes the installation of proper illumination and field of view of the preparation and microscopy of various lenses. The lighting can be natural or artificial, which use special light sources - fixtures of different brands. Lighting installed under the supervision of the lens 8x-9x. Microscopy preparations with immersion objective should strictly adhere to a particular order: 1) on the stained preparation apply a drop of immersion oil, place it on the stage, reinforcing clamps; 2) turn the gun to the level of immersion lens 90s or 100x; 3) using makrovinta carefully lower tube microscope before immersion lens in a drop of oil on the slide. Immerse immersion objective under the control eyes, watching from the side. Once the lens touches the oil, looking through the eyepiece, carefully lower the tube microscope until the difference in the field of view of the contours of the drug. Take care not to crush the glass preparation, which entails damage to the front of the lens! Then, using a micrometer screw to adjust the exact image of the object; After microscopy raise tube microscope, and then remove the drug; front lens gently wipe with a soft cloth (you must remove the oil immersion objective), sometimes wetting it with alcohol, diluted with water 1: 1 and transferred to a small revolver lens 8x. Since the microscope - an optical device, in working with it must comply with a series of rules. For protection against dust microscope must be stored under cover. From time to time should be checked for cleanliness and condition of the optics and wipe it, but only from the outside. To clean the optics use a hair brush or soft cloth moistened with ethyl alcohol, diluted with water, but in any case, do not use gasoline or xylene to avoid pasting lenses. Mechanical moving parts rubbed xylene or benzene, and then oiled. dark-field microscopy The method of microscopic examination of objects that do not absorb light, poor visibility in the method of a light field. With dark-field microscopy objects illuminated by oblique rays or side beam of light, which is achieved using a special condenser. In this case, the lens of the microscope get only the rays scattered objects in the field of view so the viewer sees these objects glowing brightly on a dark background. Dark-field microscope used for in vivo study of treponemes, Leptospira, Borrelia flagellar apparatus of bacteria. Phase contrast microscopy The method of investigation transparent, unstained, does not absorb light objects, based on the image contrast enhancement. Transparent objects (including live bacteria) are different from the environment for the refractive index does not absorb light but changes its phase. These changes are not captured by the eye. When a phase-contrast light microscopy, the object is not absorbed, passes through the so-called phase-ring disposed on one of the lens elements. Phase shifts the phase of the ring of the transmitted light by a quarter wavelength and reduces its intensity. Passage of direct, not absorbed by the object light through the phase ring is provided an annular diaphragm condenser. Rays, even slightly deflected (scattered) in the product does not fall within the phase ring and do not undergo a phase shift. As a result, the phase difference between the deflected and undeflected rays increases, giving a contrast image of the structure of the drug. Phase - contrast microscopy is used for in vivo study of bacteria, fungi, protozoa, plant and animal cells. electron microscopy Method morphological analysis with the electron flux. The role of optical lenses operate electric and magnetic fields. Use as a source of radiation flux of electrons increases the resolution of the microscope, measured in nanometers. This allows us to study the structure of the objects at the subcellular and macromolecular level. Used to study the anatomy of submicroscopic viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa. Using electron microscopy, in conjunction with immunological methods resulted in the development of immuno - electron microscopy. Along with the devices "transmission" type used scanning electron microscopes to ensure a relief image of the object surface. The advantage of scanning electron microscopy is that it provides three-dimensional image of the object. fluorescent microscopy Microscopy method that allows to observe the primary and secondary luminescence microorganisms. Luminescence (lat. (Lumen-light) - a special kind of light, which is excited by short-wavelength part of the visible light or ultraviolet rays. Fluorescent microscopy to apply any special fluorescent microscopes, or attachment to a conventional "biological" microscopes. It helps to conduct an expedited identification of microorganisms. Primary (on site) luminescence characteristic of a number of biologically active substances (aromatic amino acids, porphyrins, chlorophyll, vitamins a and B2, tetracyclines, etc..). secondary (or induced) luminescence arises from the processing of the object glowing dyes - fluorochromes (acridine orange, FITC, ethidium bromide, and others.). Among the various types of fluorescent microscopy, the most common direct flyuorohromirovanie - fluorochrome staining and immunofluorescence (IFA). immunofluorescence (method Koons) - a combination of microscopic method to immune. We are offering you the job, which can be one, two, three, and a greater number of correct answers. Press the keys with the numbers of all the correct answers. 1.Osobennosti {fluorescent, phase contrast, dark field, light microscopy, electron} 1) Use of fluorescent dyes 2) The use of UV light as a light source 3) Study of unpainted moving microorganisms (spirochetes), visible in the side light on a dark field 4) The oil system by equalizing the refractive indices of light increases the level of the desired increase in the microscope 5) The use of diaphragms to convert phase fluctuations in the amplitude of the light beam, which can be more clearly examine unstained microorganisms Set the correct sequence 2 stages of immersion microscopy □ -.povernut tube until the immersion of the object in a drop of oil □ - set the focus using the indicative makrovinta □ - rotate the gun to the level of immersion lens X90 □ - make the final focus of the drug microscrews turning it within one revolution □ -.na ready colored smear cause a drop of immersion oil and place the specimen on the stage
|