READING
1 Read the text about Japanese quality gurus and answer the questions:
1. What is Dr Kaoru Ishikawa famous for? 2. What are the advantages of cause-and-effect diagrammatic representation? 3. How does Pareto effect operate in quality improvement? 4. Kaoru Ishikawa argued that 95% of organization problems can be solved with the help of 7 tools. What are they? 5. Who does the idea of robust product design belong to? 6. What three stages should off-line quality control be divided into according to Taguchi? 7. What is the name of Shigeo Shingoassociated with? 8. What is the effect of SMED system? 9. How does Poka -Yoke system operate? 10.Why is it reasonable to differentiate between errors and defects?
2.1. Dr Kaoru Ishikawa (1915-1989) made many contributions to quality, the most noteworthy being his total quality viewpoint, company wide quality control, his emphasis on the human side of quality, the Ishikawa diagram and the assembly and use of the “seven basic tools of quality”:
• Pareto analysis which are the big problems? • Cause and effect diagrams what causes the problems? • Stratification how is the data made up? • Check sheets how often it occurs or is done? • Histograms what do overall variations look like? • Scatter charts what are the relationships between factors? • Process control charts which variations to control and how? He believed these seven tools should be known widely, if not by everyone, in an organisation and used to analyse problems and develop improvements. Used together they form a powerful kit. One of the most widely known of these is the Ishikawa (or fishbone or cause-and-effect) diagram. Like other tools, it assists groups in quality improvements.
 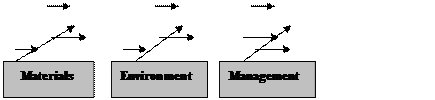
Fig. 2.4. Ishikawa’s fishbone diagram The diagram systematically represents and analyses the real causes behind a problem or effect. It organises the major and minor contributing causes leading to one effect (or problem), defines the problem, identifies possible and probable causes by narrowing down the possible ones. It also helps groups to be systematic in the generation of ideas and to check that it has stated the direction of causation correctly. The diagrammatic format helps when presenting results to others.
Quality and reliability are pushed back to the design stage where they really belong, and he broke down off-line quality into three stages: • System design • Parameter design • Tolerance design “Taguchi methodology” is fundamentally a prototyping method that enables the designer to identify the optimal settings to produce a robust product that can survive manufacturing time after time, piece after piece, and provide what the customer wants.
|

 2. THE JAPANESE WHO DEVELOPED NEW QUALITY CONCEPTS
2. THE JAPANESE WHO DEVELOPED NEW QUALITY CONCEPTS
 2.2. Dr Genichi Taguchi (1924) believed it is preferable to design product that is robust or insensitive to variation in the manufacturing process, rather than attempt to control all the many variations during actual manufacture. To put this idea into practice, he took the already established knowledge on experimental design and made it more usable and practical for quality professionals. His message was concerned with the routine optimisation of product and process prior to manufacture rather than quality through inspection.
2.2. Dr Genichi Taguchi (1924) believed it is preferable to design product that is robust or insensitive to variation in the manufacturing process, rather than attempt to control all the many variations during actual manufacture. To put this idea into practice, he took the already established knowledge on experimental design and made it more usable and practical for quality professionals. His message was concerned with the routine optimisation of product and process prior to manufacture rather than quality through inspection.



