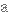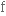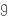What is an LDA? Abomasal displacements cause economic loss in dairy herds through treatment costs, premature culling
Abomasal displacements cause economic loss in dairy herds through treatment costs, premature culling, and production loss. The condition is seen mainly in dairy cows in the first at 3 to 4 weeks after calving and its incidence can be reduced by good management of animals in the weeks before and after parturition. displacement – смещение cause – быть причиной loss – убытки treatment – лечение costs – затраты premature – преждевременный culling – выбраковка production loss – снижение продуктивности condition – патология after – после calving – отёл incidence – число случаев, частота заболеваний reduce – сократить by – за счет management – уход before – перед parturition
Up to 90% of LDAs occur within the first 4 weeks after calving. Affected animals go off feed and become depressed. Producers will frequently notice a drop in appetite and reduced milk production. Symptoms often resemble ketosis with ketones in blood, milk, breath and urine. Animals with right displacement can show more severe signs including colic, elevated heart rate, scant faeces and diarrhoea; if a torsion occurs, animals can go downhill very rapidly showing signs of severe shock with cold extremities and extreme dullness. The veterinary surgeon will listen over the abdomen with a stethoscope for the presence of a pinging noise that sounds like a tap dripping into a steel bucket. The pinging noise is indicative of a gas-filled organ, which is almost certain to be a displaced abomasum. This is the typical area for a left displaced abomasums clinical signs – клинические признаки, симптомы up to – вплоть до occur – происходить within – в течение affected – пораженный go off – переставать feed – кормить, есть producer – производитель frequently – часто resemble – напоминать ketosis – кетоз (избыточное образование кетоновых тел) ketones – кетоны blood – кровь breath urine – моча show – проявлять, обнаруживаться severe – серьезный, тяжелый colic – колики elevated – повышенный heart rate scant – скудный faeces – фекалии diarrhea – диарея torsion go downhill – ухудшаться (о здоровье), идти под откос rapidly – быстро extremity dullness – вялость, притупленность surgeon abdomen – брюхо, брюшная полость stethoscope presence – наличие, присутствие pinging noise – отрывистый звук, звук удара со звуком tap – водопроводный кран drip – капать steel – сталь bucket – ведро filled – наполненный
What is an LDA?
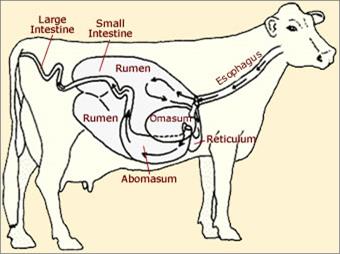
The abomasum is the fourth stomach of the cow. It is the equivalent of our stomach in that it contains all the stomach acids. It is very mobile but normally balances underneath the rumen which holds it in place due to its vast size. large intestine – толстая кишка small intestine – тонкая кишка esophagus – пищевод rumen reticulum omasum abomasum
I imagine the abomasum to be like an inflated balloon in a tub of water. If you use the palm of your hand to hold it to the bottom it is easy due to the large surface area of your hand. If you try and keep it on the bottom with your fingertip it is likely to roll out on one side or the other and float to the surface. The same happens with the rumen. As long as the cow is eating and the rumen is full, the abomasum is held in place. If the rumen is smaller than it should be, the abomasum takes the opportunity to roll out from underneath it and “float” upwards. Whether it becomes an LDA or an RDA depends on which way it rolls (left or right). It usually displaces to (cow’s stomach, viewed from the right side) the left. If it displaces to the right, it can cause more serious complications. Cows with displaced abomasum are typically recently calved cows with a sudden milk drop and decreased appetite. They may have a concurrent problem e.g. retained afterbirth, mastitis, lameness or they may have had milk fever. left displaced abomasums – смещенный влево сычуг dairy – молочный recently – в недавнее время stomach – желудок cow – корова contain – содержать acid – кислота mobile balance – балансировать, находиться по центру underneath hold (held, held) – удерживать due to – благодаря vast – большой happen – происходить like – подобно inflated – надутый tub – ванна palm – ладонь bottom – дно surface area – площадь поверхности fingertip likely – вероятно roll out – выкатываться side – сторона float – плавать (держаться на поверхности) surface – поверхность the same – то же самое as long as – до тех пор, пока eat (ate, eaten) – есть, кушать full – наполненный should – должен take the opportunity – воспользоваться возможностью upwards – вверх whether – ли become (became, become) – становиться depend on – зависеть от which – который cause – вызвать, стать причиной serious – серьезный complication – осложнение calved – отелившийся calf – теленок milk drop – снижение удоев decreased – сниженный appetite – аппетит concurrent – сопутствующий e.g. (for example) – например afterbirth mastitis lameness – хромота milk fever – молочная лихорадка, послеродовой мастит
|








 – роды, отёл
– роды, отёл Clinical Signs
Clinical Signs



 Left displaced abomasums (LDA) have become a regular problem on UK dairy farms recently.
Left displaced abomasums (LDA) have become a regular problem on UK dairy farms recently.






 – рубец (первый отдел желудка)
– рубец (первый отдел желудка)










 What happens when it displaces?
What happens when it displaces?