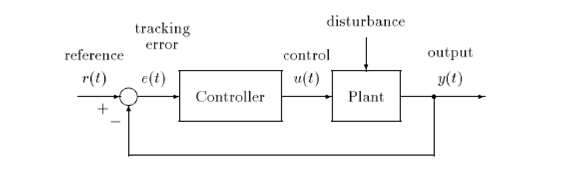
Text 1. Control System
A control system is a mechanism which makes certain physical variables of a system, called a plant, behave in a prescribed manner, despite the presence of uncertainties and disturbances. The plant or system to be controlled is a dynamic system, such as an aircraft, chemical process, machine tool, electric motor or robot, and the control objective is to make the system output y(t) follow a reference input r(t) as closely as possible despite the disturbances affecting the system. Automatic control is achieved by employing feedback. In a unity feedback or closed loop system (see Figure 1), control action is taken by applying the input u{t) to the plant, and this is based on the difference, at each instant of time t, between the actual value of the plant output to be controlled y(t) and the prescribed reference or desired output r(t).
Figure 1. Unity feedback control system
The controller is designed to drive this difference, the tracking error e(t) to zero. Such control systems are also called regulators or servomechanisms. (from S.P.Bhattacharyya, H. Chapellat, L.H.Keel. Robust Control. The Parametric Approach)
7. Answers the following questions:
1. What is a control system? 2. Give examples of the plant? 3. What is the control objective? 4. How is automatic control achieved? 5. How is control action taken in a closed loop system? 6. What is the function of the controller? Make a list of terms from Text 1 referring to control and memorize them. Read and translate Text 2
|