Why are the Oceans Salty?
As water flows in rivers, it picks up small amounts of mineral salts from the rocks and soil of the river beds. This very-slightly salty water flows into the oceans and seas. The water in the oceans only leaves by evaporating (and the freezing of polar ice), but the salt remains dissolved in the ocean - it does not evaporate. So the remaining water gets saltier and saltier as time passes. The salinity (salt content) of ocean water varies. The oceans and seas contain roughly 5 x The oceans are about 3.5% salt (by weight). Salinity is generally reported in terms of parts per thousand (abbreviated ‰), the number of pounds of salt per 1,000 pounds of water; the average ocean salinity is 35 ‰. The saltiest water is in the Red Sea and in the Persian Gulf, which have a salinity of about 40 ‰ (due to very high evaporation rates and low fresh water influx). The least salty seas are in the polar regions, where both melting polar ice and a lot of rain dilute the salinity. 1. 2. vanish 3. melted 4. salt content 5. approximately 6. entry 7. weaken
Task 5. Read the text and complete the sentences after it choosing the best answer:
|

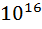 tons of salts. One cubic foot of average sea water contains 2.2 pounds of salt.
tons of salts. One cubic foot of average sea water contains 2.2 pounds of salt. watercourse
watercourse


