Coursework Cover Sheet
If you are handing coursework in late you must submit an Extenuating Circumstances or your work will be penalised according to the late submission regulations.
Word count: 1598 The economic situation in the country is very closely linked with the majority of political and economic decisions of the government. The economy of any country can not develop and grow without defining its development objectives. Under the economic objective, economists understand the basic direction of economic development, which is revealed with the help of the tasks. Over the entire period of development of society as the most important objectives underlying the economic policies put forward quite a number of purposes. Usually, different governments have different objectives but most of them are quite similar and aimed at economic growth, well-being and welfare of the state as a whole. However, it is important to understand that it is impossible to achieve all of them at once. Therefore, they select some targets to achieve and stick to them and gradually improve through implementing a mixture of policies in order to minimize the loss.
The objective of macroeconomic policies is setting in order to maximize the level of national income, providing economic growth, to raise the standard of living and general development in the economy. There are several main government macroeconomics objectives, which have the most serious impact on the state economy: Uuml; Full employment or low unemployment. It is assumed that everyone who is able and willing to have a job, find it, and there are no people who did not find himself a suitable employment. It also needs to understand that there will be a certain amount of frictional, seasonal and structural unemployment. ü Price stability. This is the one more important economics goal, which strongly influences not only companies, but also ordinary citizens’ lives. In order to maintain a stable price level, the government must monitor the money supply to match the level of the produced goods. Moreover, when prices remain largely stable, there is usually neither rapid inflation nor deflation. ü Sustainability. Economic growth is usually measured by the rate of change in real GDP, which allows an increase in living standards without structural and environmental difficulties. For example, a crisis in 2008-2009 destabilized the most of the EU economics. Nowadays it is impossible to say about growth or decline of the UK economy because the inflation rate is equal to 0%.
Uuml; Balance of payments in equilibrium. Itrecords all flows of money into, and out of, the state over a given time period. It is split into two: the Current Accountand theCapital and Financial Accounts. The most important factor here is the balance of exports and imports. Each state, which participate in the international division of labor, and engage in international economic relations, should not "live on credit" at the expense of other states. It is necessary that the number of goods sold at the prices coincided with the amount of goods purchased from other countries in the long-run (Anderton, 2008).
There are also a number of secondary objectives which are held to lead to the maximization of income over the long run period:
ü Increasing Productivity. First of all, this goal means that the government had to use the best resources from all available, and use the most advanced technology and the corresponding level of the labor force.
ü Improving the quality and cost effectiveness of public services in order to maintain people’s welfare.
ü Securing an efficient market in financial services and banking is one of the goals which will help to keep stability (Businesscasestudies.co.uk, 2015).
ü Economic freedom. This objective presupposes freedom of choice for all market players in the field of activity, occupation, income opportunities.
ü Equitable distribution of income. Realization of this goal requires the organization of distribution, in which each participant in production could earn an income corresponding to the quality and quantity of labor expended them.
ü Economic support. As an economic purpose, the provision assumes that all citizens of the state should have the products necessary to maintain their lives at a satisfactory level, regardless of their labor contribution, but essentially belonging to the state (S-cool.co.uk, 2010).
In order to determine the general direction of development of the national economy, the state puts forward a particular target or multiple targets. An important condition is compatibility of goal setting because the named goals can conflict with each other. There are several examples of the most common conflicts between macroeconomics objectives:
ü Low unemployment (or full employment) and low inflation.If a government tries to reduce unemployment through reflationary measures, such as lower interest rates or increased public spending, then the resulting reduction in unemployment will push wages, and then prices will arise and provoke the inflation (Businesscasestudies.co.uk, 2015).
ü Economic efficiency and full employment. The state is not able to reach any of them, or one will be achieved at the expense of another. Cost-effectiveness involves the use of the best resources supplied by the factors of production while the achievement of full employment requires the employment of all who want to work. However, not all members of the production will be high enough and equally qualified.
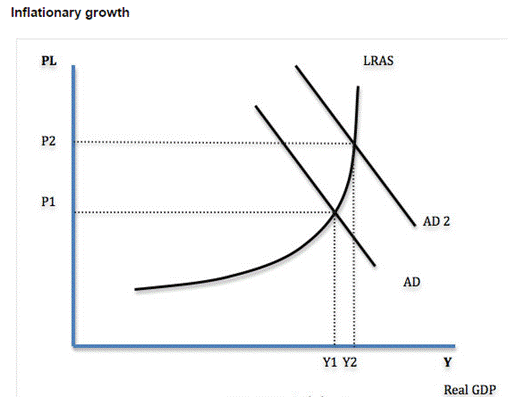
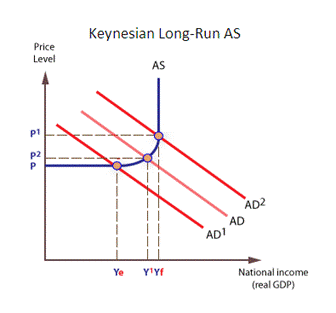
ü Economic Growth and Inflation. T he steps taken to keep inflation low, like relatively high-interest rates, can often restrict growth via reduced consumer spending and investment. From the opposite point of view, when the economy expands it is more likely that inflationary pressures will increase. This is very clearly seen on a Keynesian model of the long-run supply curve. After reaching of full employment demand policies are not working, but also only increasing prices and rate of inflation (Pettinger, 2013). ü Economic growth and balance of payments. High economic growth may increase inflation and make exports less competitive and moreover, as consumer spending rises there will be a rise in import spending that will tend to cause a deficit in the current account
ü Economic growth and budget deficit. The government can reduce the budget deficit, but it will require higher taxes and lower spending. However, this tightening of fiscal policy will lead to a drop in demand and lead to lower economic growth. If a cut of spending in general lead to higher unemployment, the government will need to pay more for benefits and get lower tax revenues, so the deficit may experience only a slight decrease (Pettinger, 2013).
In order to support economic development and various changes within the state, government influences the economy through its economic policies. There are two main tools used by the state to achieve its macroeconomic objectives: Fiscal policy and monetary policy. The first one, fiscal policy, is based on the demand control through inflation control. When aggregate demand in the economy is high, the rise in prices shows that the economy is spending too much. In this case, the government will reduce the budget spending is cut and the investment costs, such as the construction of roads and hospital equipment. On the other hand, the government collects money in the form of taxes and spends money through its development expenditure such as building roads, bridge, defense, transports and so on (Anderton, 2008).
Another instrument of controlling is monetary policy. It is related with a change in interest rates by the Central bank. Decisions to increase or decrease the interest rate received on the basis of projections because the effect of the changes will be evident only after several years. This means that monetary policy works only in the long term. A higher interest rate will result in fewer investments, wealth effect, and also affect the exchange rate. Moreover, there is less ability for businesses to expand as they have to pay more interest to the bank for their loans and they have less profit left. There is absolutely the same situation with general consumers because demand will also fall as they will not be getting cheap loans to pay for the buying new houses and luxury items (Dineshbakshi.com, 2015). It is important to add, that besides the interest rate, there are few more policy instruments, such as credits quantity of money which are under the government and central bank control too.
One more type is supply-side policies, which includes all those policies which aim at improving the efficient supply of goods and services. For example, efficiency may be increased throughIncreasing competition in all industries by removing entry barriers or Imparting training and improving the education level of the workforce resulting in higher skills.
To draw the conclusion, it is safe to say that in order to determine the general direction of development of the national economy, the state has set itself several goals. Mainly they are aimed at improving the welfare of citizens, economic stability, productivity growth and overall economic growth. Unfortunately, not all goals can be achieved; moreover, most of them have to sacrifice for the sake of others. Often this is due to the maintenance of stability and economic growth of the economy, which can not be maintained a priority simultaneously. However, the government has several important policies, which obtain the optimum policy mix of the two to achieve macroeconomic goals. Moreover, it helps to regulate and mitigate major conflicts between macroeconomics objectives.
Bibliography: 1. S-cool.co.uk, (2010). The Main Macroeconomic Objectives | S-cool, the revision website. Available at: http://www.s-cool.co.uk/a-level/economics/macroeconomic-objectives/revise-it/the-main-macroeconomic-objectives [Accessed 4 May 2015]. 2. Anderton, A. (2008). Economics. Fifth edition. Harlow: Longman. 3. Businesscasestudies.co.uk, (2015). Government aims and objectives - Steering the economy - HM Treasury | HM Treasury case studies and information | Business Case Studies. Available at: http://businesscasestudies.co.uk/hm-treasury/steering-the-economy/government-aims-and-objectives.html#axzz3Z5cwvx46 [Accessed 4 May 2015]. 4. Pettinger, T. (2013). Macro Economic Objectives + Conflicts | Economics Help. Economicshelp.org. Available at: http://www.economicshelp.org/blog/419/economics/conflicts-between-policy-objectives/ [Accessed 4 May 2015]. 5. Ons.gov.uk, (2015). Office for National Statistics (ONS) - ONS. Available at: http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/index.html [Accessed 4 May 2015]. 6. Dineshbakshi.com, (2015). Government macroeconomic objectives and policies. Available at: http://dineshbakshi.com/igcse-business-studies/external-environment/revision-notes/60-government-macro-economic-objectives [Accessed 4 May 2015].
|