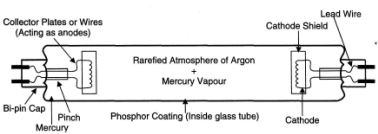
The most obvious example of this type is the popular fluorescent tube. It is classified as a MCF lamp (M - mercury, C - low pressure, F - fluorescent coating) (Refer Figure 22.3). The inside wall of the glass tube is coated with a fluorescent phosphor, which emits white or coloured light.
The coating is meant to absorb ultraviolet rays and convert them into visible light Variations of fluorescent material create different hues of white light. The most commonly known are given in Table 22.5. Fluorescent tubes are available in lengths from 150mm to 2400mm with power ratings from 4 Watts to 125 watts. The tube ends are usually fitted with bi-pin lamp caps or miniature bi-pin caps for the smaller tubes. Typical luminous efficiency for a fluorescent tube is approximately 70 lumens per watt with an average operating life of 5000 hours. It is capable of giving a glare-free, cool daylight effect.
| Material
| Colour
|
| Calcium Tungstate
| Blue
|
| Magnesium Tungstate
| Blue-white
|
| Zinc Beryllium Silicate
| Yellow-white
|
| Cadmium Borate
| Pink
|
| Zinc Silicate
| Green
|





