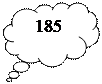ENGLISH AS THE WORLD LANGUAGE
A language achieves a genuinely global status when it develops a special role that is recognized in every country. This role will be most obvious in countries where large numbers of the people speak it as a first language – in the case of English, this would mean the USA, Canada, Britain, Ireland, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, several Caribbean countries, and a scattering of other territories. However, no language has ever been spoken by mother-tongue majority in more than a dozen or so countries, so mother-tongue use by itself cannot give a language world status. To achieve such a status, a language has to be taken up by other countries around the globe. They must decide to give it a special place within their communities, even though they may have few (or no) mother-tongue speakers. There are two main ways in which this can be done. First, the language can be made the official (or semi-official) language of a country, to be used as a medium of communication in such domains as government, the law courts, the media, and the educational system. Second, the language can be made a priority in a country’s foreign-language teaching. It becomes the language which children are most likely to be taught at school, and the one most available to adults who – for whatever reason – never learned it, or learned it badly, in their early educational years. Over 100 countries treat English as just a foreign language; but in most of these, it is now recognized as the chief foreign language to be taught in schools. Those who have learned English as a first language are now estimated to be round 400 million. 400 million use English as a second language and there are 600 million who use English as a foreign language. What can account for it? An obvious factor is the need for a Lingua Franca – a concept probably as old as language itself. But the prospect that a Lingua Franca might be needed for the whole world is something which has emerged strongly only in the 20th century, and since the 1950s in particular. Recall that the chief international forum for political communication – the United Nations – dates only from 1945, and then it had only 51 member states. By 1960 this had risen to over 80 members. But the independence movements which began at that time led to a massive increase in the number of new nations during the next decade, and this process has continued steadily into the 1990s. There are now 185 members of the UN – nearly three times as many as there were 50 years ago. The need for a Lingua Franca is obvious, and the pressure to find a single Lingua Franca is a consequence, the alternative being expensive and often impracticable multi-way translation facilities. But why English? There is, of course, nothing intrinsically wonderful about the English language that it should have spread in this way. Its pronunciation is not simpler than that of many other languages; its grammar is no simpler – what it lacks in morphology (in cases and genders) it certainly makes up for in syntax (in word-order patterns) – and its spelling certainly isn’t simpler. A language becomes a world language for one reasons only – the power of the people who speak it. But power means different things: it can mean political (military) power, technological power, economic power, cultural power. Political power, firstly, in the form of the colonialism that brought English around the world from the 16th century, so that by the 19th century, the language was one ‘on which the sun never sets’. Secondly, technological power, in the sense of the industrial revolution of the 17th and 18th centuries, was very significant at the English-language event. The 19th century saw the growth in the economic power of the United States and Great Britain.
Закончите предложения в соответствии с содержанием текста. 1. A language achieves a genuinely global status when _______. a) it develops a special role that is recognized in every country b) large number of people speak English as a second language c) no language has ever been spoken by mother-tongue majority in more than a dozen or so countries d) the USA, Canada, Britain, Ireland, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, several Caribbean countries speak English e) the language is made official (or semi-official) language of a country 2. The language is made a priority __________. a) in a country’s foreign-language teaching b) in such domains as the law courts and poetry c) in linguistics, morphological structure and clause structure 3. Those who have learned English as a first language are now estimated _______. a) to be round 400 million b) to be round 600 million c) to be round 1 billion 4. A language becomes a world language because of __________. a) the power of the people who speak it b) the need for a Lingua Franca c) its pronunciation, grammar, spelling 5. The power of the people who speak English means _________. a) political power b) technological power c) economic power d) cultural power e) all the above mentioned
6. Выразите свое согласие/несогласие со следующими утверждениями, используя ту или иную речевые модели. Исправьте неверные утверждения. Models: a) I strongly agree with this statement.
|

 4. Найдите в тексте и объясните, что значат числа, приведенные ниже.
4. Найдите в тексте и объясните, что значат числа, приведенные ниже.