End Sub. 7. Build and run the application.
7. Build and run the application. 8. You should observe the main application waits until all individual Tasks are completed before continuing.
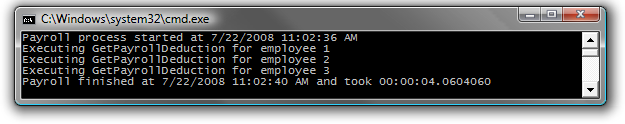
Figure 9 Output from running tasks in parallel with the WaitAll() method
Task 3 – Using the IsCompleted Property There will be times when you want to check on the completion status of a Task before doing other work (for instance, you may have another task to run that is dependent on the first task completing first), but you may not want to utilize the Wait() method because Wait() blocks execution on the thread you’ve launched your Task from. For these situations, the Task class exposes an IsCompleted property. This enables you to check whether Task objects have completed their work before you continue with other processing. 1. Replace the current method calls from Main(), with a call to Ex2Task3_TaskIsCompleted(). C# static void Main(string[] args) { ... // Methods to call
|