End Sub. Note: Here you created the firstTaskas normal, but you used the ContinueWith() method to have the runtime execute the subsequent calls in order.
Note: Here you created the first Task as normal, but you used the ContinueWith() method to have the runtime execute the subsequent calls in order.
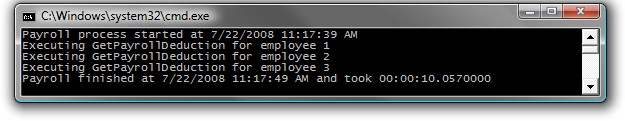
3. Build and run the application. 4. You should observe that the tasks execute in order – employee 1 first, followed by employee 2, and finally employee 3.
Figure 11 Output from running tasks in parallel and using ContinueWith to ensure their order and wait conditions
Next Step: Exercise 3: Use the Generic Task Class to Create and Run Tasks that Return a Value
Exercise 3: Use the Generic Task Class to Create and Run Tasks that Return a Value As you can see, Tasks are useful for launching a unit of functionality in a parallel environment; they also provide a mechanism for returning values as a result of executing the unit. To demonstrate this, you are going to create a new instance of a Task<decimal>; and then use the static Task.Factory. StartNew() method to execute the GetPayrollDeduction() method in a manner that allows you to capture its return value.
Task 1 – Capturing a Task’s Return Value 1. Open Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 from Start | All Programs | Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 | Microsoft Visual Studio 2010. 2. Open the solution file ParallelExtLab.sln located under Source\Ex03-UseTaskResult\begin. (choosing the folder that matches the language of your preference) Optionally, you can continue working with the solution you created in the previous exercise. 3. Replace the current method calls from Main(), with a call to Ex3Task1_TaskReturnValue(). C# static void Main(string[] args) { ... // Methods to call
|