Economic Data and Econometric Analysis. Four types of Economic Data. Role of Econometrics. Main Application of Econometrics.
E is the same as economic statistics. Main object of E should be to promote studies that aim at a unification of the theoretical-quantative and empirical-quantative approach to economic problems. Economic data are commonly numerical time-series, i.e., sets of data (covering periods of time) for part or all of a single economy or the international economy. When they are time-series the data sets are usually monthly but can be quarterly and annual. Economic data may also describe functions or inter-relationships between variables and they may describe a static as opposed to a dynamic relationship Econometric analysis may also be classified on the basis of the number of relationships modeled. Single-equation methods model a single variable (the dependent variable) as a function of one or more explanatory (or independent) variables. In many econometric contexts, the commonly-used ordinary least squares method may not recover the theoretical relation desired or may produce estimates with poor statistical properties, because the assumptions for valid use of the method are violated. Four types of Economic Data: Cross-sectional data are data on one or more variables (consumers, firms etc) collected at a single point in time. For example: expenditure on apples of one household in Moscow in 05.06.2012. This data is obtained by “true” random sampling (выборка) from the underlying population (генеральная совокупность). For this reason it is the easiest type of data to analyze. Time series data, as the name suggests, are data that have been collected over a period of time on one or more variables. For ex. expenditure on apples of one household in Russia in 2010-2012. In the time-series data the period (year, quarter, month) is important. This data CANNOT be obtained at random sampling. What we observed this period is based on what we observed previous period (we should observe a particular family). This data is more complex to analyze. Panel data have the dimensions of both time series and cross-sections, For ex. the daily prices of n blue chip stocks over year 2010 and year 2011. Multidimensional (Pooled) panel data -we observe n cross-sections data at periods T. For ex. The wage of n workers in 06.2010 and in 06.2011. Role of econometrics – develop statistical methods for: 1) estimating economic relationship 2) testing economic theories 3) evaluating and implementing government and business policy. Main application of econometrics – forecasting macroeconomic and financial variables. Forecasting the effect of specific policy i.e. the effect of school spending on student performance. 24. Financial Econometrics, it’s object. Type of equations in mathematical modeling: behavioral equations and identities. The literal meaning of the word econometrics is ‘measurement in economics’. However, the main techniques employed for studying economic problems are of equal importance in financial applications. Financial econometrics will be defined as the application of statistical techniques to problems in finance. Econometrics is the application of statistical and mathematical methods in the field of economics to test and quantify economic theories and the solutions to economic problems. The Values of Fin. Econometrics (Objectives):1) Testing whether financial markets are weak-form informationally efficient; 2) Testing whether the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) or Arbitrage Pricing Theory; 3) (APT) represent superior models for the determination of returns on risky assets; 3) Measuring and forecasting the volatility of bond returns; 4) Explaining the determinants of bond credit ratings used by the ratings agencies; 5) Modelling long-term relationships between prices and exchange rates; 6) Determining the optimal hedge ratio for a spot position in oil; 7) Testing technical trading rules to determine which makes the most money; 8) Testing the hypothesis that earnings or dividend announcements have no effect on stock prices; 9) Testing whether spot or futures markets react more rapidly to news; 10) Forecasting the correlation between the stock indices of two countries. Model - a simplified representation of a limited part of reality with related elements Models can roughly classified as 1) Logical models – a set of logical constructions (objects, relationships); 2) Mathematical models – a set of mathematical functions/equations, describing objects and relationships. The first step in developing an econometric model is to express relevant economic relations in the form of an equation. Single-equation model for forecasting the regional demand for portable personal computers: C(demand)= where P-price, I-disposal income, Pop-population, i-interest rates, A-advertising expenditure. Multi-equation econometric models are composed of 2 basic kinds of expressions: identities and behavior equations. Identities express relations that are true by definition. The statement that profit (П) equal total revenue (TR) minus total cost (TC) is an example of identity: П=TR-TC Identities economic relations that are true by definition. Behavior equations may indicate how individuals and institutions are expected to react to various stimuli. Behavioral equations economic relations that are hypothesized to be true. For example, there is three-equation forecast model for equipment and related software sales for a personal computer retailer.
|

 ,
, ;(1)
;(1)  ;(2)
;(2) 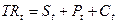 (3), where S-software sales, TR-total revenue, P-peripheral sales, C-personal computer sales, t is current time period, u-error or residual terms. (1)(2) are behavioral hypotheses. Equations (1) hypothesizes that current-period software sales are a function of the current level of total revenues; equation (2) hypothesizes that peripheral sales depend on previous-period personal computer sales. Equation (3) is an identity, that defines total revenue as being the sum of software, peripheral equipment, and personal computer sales.
(3), where S-software sales, TR-total revenue, P-peripheral sales, C-personal computer sales, t is current time period, u-error or residual terms. (1)(2) are behavioral hypotheses. Equations (1) hypothesizes that current-period software sales are a function of the current level of total revenues; equation (2) hypothesizes that peripheral sales depend on previous-period personal computer sales. Equation (3) is an identity, that defines total revenue as being the sum of software, peripheral equipment, and personal computer sales.


