Fig. 3.2. The building blocks of TQM
Everything we do is a Process, which is the transformation of a set of inputs, which can include action, methods and operations, into the desired outputs, which satisfy the customers’ needs and expectations. The only point at which true responsibility for performance and quality can lie is with the People who actually do the job or carry out the process. An appropriate documented Quality Management System will help an organisation not only achieve the objectives set out in its policy and strategy, but also, and equally importantly, sustain and build upon them. Once the strategic direction for the organisation’s quality journey has been set, it needs Performance Measures to monitor and control the journey, and to ensure the desired level of performance is being achieved and sustained.
2 Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
1. What is Total Quality Management? 2. What are the characteristic features of TQM? 3. What are two main objectives of TQM. What is the core of TQM? 4. What are the essential requirements of TQM? 5. How is the organization’s culture defined? 6. When can zero defects become a part of a firm’s culture? 7. What are the building blocks of TQM? 8. What is the function of Performance Measures? 9. What do you think the difference between a national view and an organizational view of competitiveness is? 10. What is meant by continuous improvement? VOCABULARY PRACTICE 1 Refer back to the text and match a line in A with a line in B to define English-Russian equivalents.
2 Match the words which are very close in their meaning:
3 Match the words having the opposite meaning:
4 This pair of words is often confused. Read and translate the sentences paying attention to the difference in their meaning.
Effective – efficient
5 Look back in the text and find the words which have a similar meaning to: a the fact or state of continuing to live or exist, especially in difficult conditions (1); b a system of beliefs that influences someone’s decisions and behaviour (2); c the final result of a process, activity, etc. (2); d something that you try to achieve (2); e someone who other people respect and go to for advice about a particular subject (4); f the standard of someone’s work, or the skill they use in making something (4); g a person or a company that has invested in a business and owns part of it; someone who has an interest in the success of a plan, system, or organization (4); h work that you do together with other people (6); i a worried feeling that you get when you have to deal with a difficult or complicated situation (6).
6 Read the text below. Use the word given in capitals at the end of each line to form a word that fits in the space in the same line. There is an example at the beginning (0).
7 Read the text and identify the nouns, adjectives, adverbs and verbs in the following groups of words. Use the appropriate ones in the sentences below. Choose the correct form of the word.
A. a. compete, b. competition, c. competitor, d. competitiveness,
COMPETITION: FACT AND FICTION
“Declinism” has been persistent in America ever since the first oil shock in 1973 shook the self-confidence characterizing the country after the second World War. Since then, Japanese companies’ success in highly visible markets such as consumer electronics and cars, together with a flood of imported products from dozens of other countries, has added support forecasts of America’s economic decline. Now to say that American business can no longer 1)____________ and that Americans have lost their ability to innovate is no longer controversial – it’s conventional wisdom. The belief that American business is no longer 2)____________________ is wrong. American firms lead 3)_____________________ in a slew of technology-based industries: computer software and hardware of all types, microprocessor chips, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, new materials, energy, and environmental control. America companies that are world beaters in these fields include General Electric, Microsoft, Apple, Motorola, Intel, etc. Even the Japanese agree that American companies remain the major 4)________________ in many leading high tech industries. “Whenever there is an open 5)_____________ overseas, an American firm tends to win,” says Joseph Jacobs, founder of Jacobs Engineering. Outside such high-tech industries, it’s also possible to identify plenty of world-beating American firms among consumer goods companies: Procter & Gamble, Philip Morris, and Johnson & Johnson are among the world’s best. Service industries are another area in which America has world-class companies. There are no European or Japanese fast-food chains to rival McDonald’s, Pizza Hut, or Kentucky Fried Chicken. Worry about America’s loss of 6)____________________ tends to center on its trade deficit. In fact, this shrunk significantly (from $160 billion in 1987 to an estimated $72 billion in 1991). In any case, a trade deficit, by itself, says nothing about a country’s 7)________________. That requires deeper examination. Far from being 8)_____________________ in manufacturing, America is actually one of the industrial world’s cheapest producers of many goods. This is partly due to the cheap dollar, which has fallen by half from its 1985 value. The best and brightest people from other countries have regularly sought to make their fortunes in America. Skilled immigrants from Europe and Asia have played a big part in building many of America’s high-tech industries. An estimated one third of the engineers working in Silicon Valley were born in Asia. Growing numbers of these Chinese, Korean, and Indian engineers are establishing their own firms in California with the help of money from family and contracts abroad. If such firms succeed, they’ll help keep America 9)________________. In any high-tech rivalry with Japan or other East Asian countries, one Wall Street banker predicts, “America will win because our Asians will beat their Asians.” There’s no reason to be alarmed about that.
COMPREHENSION 1 Match terms in column A with their definitions in column B.
2 Mark the following statements as true (T) or false (F). If you think a statement is false, change it to make it true. Prove your point of view.
3 Fill in the blanks using the words from the list in the bottom.
CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
Achieving the highest level of 1)_________________ requires a well-defined and well-executed approach to continuous improvement. Such improvement needs to be part of all operations and of all work unit activities of a company. Improvements may be of several types: - enhancing 2)_____________ to the customer through new and improved products and services; - reducing 3)_________________________; - improving responsiveness and cycle time performance; - improving 4)___________________________ in the use of all resources. Thus, improvement is driven not only by the objective 5)___________________, but also by the need to be responsive and efficient – both conferring additional 6)____________________. To meet all of these objectives, the process of continuous improvement must contain regular cycles of 7)_______________________. This requires a quantitative basis for assessing progress, and for deriving information for 8)___________________.
a. planning, execution, and evaluation; b. value; c. quality and competitiveness; d. future cycles of improvements; e. errors, defects, and wastes; f. to provide better quality; g. productivity and effectiveness; i. market place advantage.
DISCUSSION POINTS
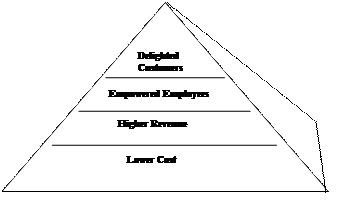
Comment on Figure 3.3. answering the questions below. What do you think it illustrates? Give a suitable title to the Figure.
1. Does higher quality mean lowering costs? Do you agree that the costs associated with preventing errors during design are often far less than correcting the errors during the production, the costs of preventing errors during the production are far less than correcting the errors after the final inspection, and the cost of finding and correcting errors during final inspection are far less than fixing the errors after the customer has received the goods or services? 2. How do higher revenues depend on higher quality? When are customers ready to pay a price premium? 3. Who are delighted customers? What is their role in advertising goods and services? 4. Why do you think creating empowered employees is a major goal of total quality management?
Fig. 3.3. ____________________________________.
SELF-CHECK QUESTIONS 1. Why has a quality focus become imperative in a globalizing world? 2. What is Total Quality Management? 3. What are the characteristic features of TQM? 4. What are two main objectives of TQM. What is the core of TQM? 5. What are the essential components of TQM? 6. How is the organization’s culture defined? 7. Define zero defects. 8. When can zero defects become a part of a firm’s culture? 9. What are the building blocks of TQM? 10. What is the role of Quality Management System? 11. What is the function of Performance Measures? 12. How do you think what the difference between a national view and an organizational view of competitiveness is? 13. What is meant by continuous improvement? GLOSSARY
|