The Computer Performance (CP) is determined by number of certain (well known) operations per time unity.
The generalized estimation of the CP is a number of transactions per second. The basic performance characteristics of a computer system: processor speed,memory capacity,interconnection data rates. 14. What’s Hardwired Program? (What’s programming in Hardware?)
16) What’s Software Program? (What’s programming in Software?)
Control signals
20) Describe each step of MCIP on the “Hypothetical Machine” for one concrete instruction. Fetch Cycle · Program Counter (PC) holds address of next instruction to fetch · Processor fetches instruction from memory location pointed to by PC · Increment PC ü Unless told otherwise · Instruction loaded into Instruction Register (IR) · Processor interprets instruction and performs required actions Execute Cycle · Processor-memory · data transfer between CPU and main memory · Processor I/O · Data transfer between CPU and I/O module · Data processing ü Some arithmetic or logical operation on data · Control ü Alteration of sequence of operations ü e.g. jump · Combination of above
22) Do we mean under the Interrupts? What is the main reason of using the Interrupt Mechanism? Mechanism by which other modules (e.g. I/O, memory) may interrupt normal sequence of processing. Interrupts are some changes in the control flow caused not by the program itself, but by something other, and usually connected with the I/O process. Interrupt is a temporary cessation of the process caused by an event, which is an external one as regards to this process. Interrupts are provided primarily as a way to improve processing efficiency 18) What’s the Main Cycle of Instruction Processing (MCIP)? Two steps: a)Fetch b)Execute The instruction fetch consists of reading an instruction from a location in the memory. The instruction execution may involve several operations and depends on the nature of the instruction.
19)Describe the architecture of “Hypothetical Machine”. What is the difference between translator and interpr… 0 3 4 15
Instruction Format Instruction Format 0 1 15
Integer Format
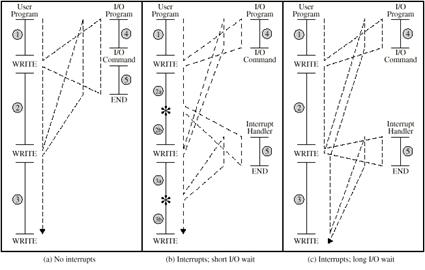
1, 2 and 3 – code seg 1, 2 and 3 – code segments refer to sequences of instructions that do not involve I/O. The WRITE calls are calls to an I/O program that is a system utility and that will perform the actual I/O operation. The I/O operation consists of three sections: 4 – a sequence of instructions which prepare for the operation. I/O command – the actual I/O command. 5 – a sequence of instructions which complete the operation.
|


 Instructions codes
Instructions codes
 Data Results
Data Results

 17) Describe the functional structure of Computer components …
17) Describe the functional structure of Computer components …
 23) Draw up diagrams of the Program Flow Control without interrupts and with interrupts, describe each fragment of
23) Draw up diagrams of the Program Flow Control without interrupts and with interrupts, describe each fragment of