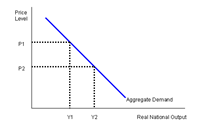
The Aggregate Demand Curve
Aggregate demand normally rises as the price level falls. This can be explained in three main ways: 1.Real money balances effect. As the price level falls, the real value of money balances held increases. This increases the real purchasing power of consumers. 2.Prices and interest rates. A lower price level increases the real interest rate - there will be pressure on the monetary authorities to cut nominal interest rates as the price level falls. Lower nominal interest rates should encourage an increase in consumer demand and planned investment. 3.International competitiveness. If the country’s price level is lower than other countries (for a given exchange rate), this country goods and services will become more competitive. A rise in exports adds to aggregate demand and therefore boosts national output.
|