Control test questions. 1. Bidentate complex compound:
1. Bidentate complex compound: 1) [Cu(NH3)4] Cl2 3) K[Cr(SO4)2] 5) K3[Fe(CN)6] 2) Na3[Cr(CN)6] 4) K4[Fe(CN)6] 2. Bidentate complex compound: 1) K3[Al(C2O4)3] 3) [Cd(NH3)4](NO3)2 5) K[Ag(CN)2] 2) [Ag(NH3)2] Cl 4) Na3[BiCl6] 3. Monodentate complex compound: 1) K[Cr(SO4)2] 3) (NH4)2[Fe(SO4)2] 5) K3[Al(C2O4)3] 2) K3[Fe(CN)6] 4) [Cr(NH3)4C2O4]Cl 4. The degree of oxidation of complexing in the complex K2[Zn(OH)4]: 1) -2 3) +4 5) +3 2) +2 4) +1 5. The degree of oxidation state of complexing in the complex K3[Cr(CNS)6]: 1) +4 3) +3 5) +5 2) +2 4) +6 6. The degree of oxidation in the complexing compound complex [Co(NH3)5Cl] Cl2: 1) +4 3) +1 5) -3 2) +2 4) +3 7. The degree of oxidation of complexing in the complex [Ag(NH3)2] Cl: 1) +1 3) +4 5) -1 2) +2 4) +3 8. The degree of oxidation complexing agent in the complex K[Co(H2O)2 (CN)4]: 1) +1 3) +4 5) -3 2) +2 4) +3 9. The degree of oxidation of complexing compound in the complex (NH4)2[Fe(SO4)2]: 1) +2 3)+1 5) –2 2) +4 4)+3 10. The charge of the complex ion in the complex [Cr(NH3)3H2OCl2]Cl: 1) +1 3) +2 5) –3 2) +3 4) +6 11. The charge of the complex ion in the complex K2[HgI4]: 1) -4 3) –1 5) +1 2) -2 4) +2 12. The charge of the complex ion in the complex compound [Ni(NH3)6](NO3)2: 1) +4 3) –1 5) -2 2) -3 4) +2 13. The charge of the complex ion in the complex [Co(NH3)2 (H2O)4]Cl3: 1) +3 3) –2 5) -3 2) +4 4) +4 14. The charge of the complex ion in the complex [Pt(NH3)4 Cl2]Cl2: 1) -2 3)+3 5) +4 2) +2 4)-3
15. Type of communication between the complexing ligand: 1) ion 3) hydrogen 5) metal 2) covalent 4) donor-acceptor 16. Sustainable complex compound: 1) K2[PbI4] Kнест= 1,2. 10-4 3) K2[HgI4] Kнест= 1,4. 10-30 2) K3[AgI4] Kнест= 1. 10-13 4) K3[BiI6] Kнест= 7,6. 10-20 5) K2[HgBr4] Kнест= 1. 10-21 17. Sustainable complex compound: 1) Na2[HgCl4] Kнест= 5,8. 10-16 3) Na3[SbCl6] Kнест= 7,6. 10-4 2) Na3[AgI4] Kнест= 5. 10-6 4) Na2[BiCl6] Kнест= 3,8. 10-7 5) Na[Ag(NO2)2] Kнест= 1,8. 10-3 18. Unsustainable complex compound: 1) [Cu(NH3)4]Cl2 Kнест.= 9. 10-13 3) [Ni(NH3)4] Cl2 Kнест.= 1. 10-8 2) [Co(NH3)6]Cl Kнест.= 6,2. 10-36 4) [Cd(NH3)4] Cl2 Kнест.= 2,7. 10-7 5) [Ag(NH3)2]Cl Kнест.= 9,3. 10-8
19. Expression of instability constants of complex compounds K4[Fe(CN)6]: 1)
2)
20. Expression of instability constants of complex compounds K2[HgI4]: 1)
2)
21. Expression of instability constants of complex compounds [Cu(NH3)4]SO4: 1)
4)
22. The coordination number in the complex [Cd(NH3)4 (H2O)2]Cl2 is: 1) 8 3) 2 5) 5 2) 4 4) 6 23. The coordination number in the complex compound [Ni (H2O)2 (NH3)4](NO3)2 is: 1) 2 3) 4 5) 3 2) 6 4) 8 24. The coordination number in the complex compound [PtCl(NH3)4]Br3 is: 1) 3 3) 6 5) 2 2) 4 4) 5
25. The coordination number in the complex compound Na3[Fe(C2O4)3] is:
1) 2 3) 4 5) 5 2) 3 4) 6 26. Complex compounds include: 1) KAl(SO4)2 3) NaOH . 2H2O 5) CrCl3. 6H2O 2) CuSO4. 5H2O 4) K4[Fe(CN)6] 27. Complex compounds include: 1) KAl(SO4)2 3) Al(OH)3 5) K2HPO4 2) Na2SO4 4) K3[Fe(CN)6]
28. Complex compounds include: 1) Na2SO4. 10H2O 3) K2[HgI4] 5) KH2PO4 2) NaHCO3 4) MgOHCl
29. The complex compounds are: 1) [Cu(NH3)4](OH)2 3) FeOHCl2 5) K2HPO4 2) NaHCO3 4) MgOHCl
30. Complex compounds include: 1) [Zn(NH3)4](OH)2 3) CuOHCl 5) K2HPO4 2) NaHCO3 4) MgOHCl
Theme number 6: Redox processes. Electrode potentials. Potentiometry in medical practice.
Session Purpose: To study the basic methods of oxidation-reduction (oxidimetry) used in quantitative analysis, as well as in clinical practice, sanitary, pharmaceutical research, and explore the method of potentiometric titration to determine the endpoint, build potentiometric titration curve, calculate the concentration analytes.
The main questions of the theme: 1. Redox titration, the nature and value of the method. 2. Classification method oxidimetry. Indicators used in oxidimetry. 3. What two groups are divided all chemical reactions? What reactions are called redox? 4. Classification of redox reactions. 5. Intermolecular, intramolecular, self-healing, self-oxidation reaction (disproportionation). 6. Define the oxidation process and the recovery process. 7. What is the degree of oxidation of the element? 8. What substances are called reducing agents, oxidizing agents and which? 9. List the major oxidizing and reducing agents? Which of them are widely used in medical practice? 10. Preparation of the redox reactions. Method of electronic balance. Ion-electron method. 11. Explain electrode potential. Standard electrode potential. 12.Galvinical element. Element Daniel Jacobi. 13. Nernst equation. The dependence of the electrode potential on the concentration and temperature. 14. The essence of the potentiometric titration. 15. Reference electrodes used in potentiometric titrations. 16. The display electrodes used in potentiometric titrations. 17. As determined by endpoint titration in potentiometric titration? Methods of teaching and learning: effective formative feedback on the development of competencies, training in small groups SGL, training based on case studies CBL.
Literature
1. Lenski A.S.Introduction to bioinorganic and biophysical chemistry.- М.: VW, 1989.- 256 page. 2. Glinka N.L.. General chemistry.Edited by V.A. Rabinovich.- L.: Chemistry,1988.- 704 с. 3.Glinka N.L.. exercises and works in chemistry.Edited by A.Rabinovich and X.MRubin.- Chemistry 1985.- 264 page. 4Vasileva Z.G., Granovskaya А.А., Taperova А.А. Laboratorial works in inorganic chemistry.- Chemistry, 1986. - 288 page. 5.Lectures and synopsis. 6.Ahmetov N.B. Genaerally and inorganic chemistry. М.: VW, 1981. – 679 page.
|

 3)
3) 
 4)
4)  5)
5) 
 3)
3) 
 4)
4)  5)
5) 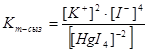

 2)
2)  3)
3) 
 5)
5) 



