Control test questions
1. Colloidal solutions include: 1) to true solutions 2) to molecular solutions 3) to ionic solutions 4) to microheterogeneous systems 5) to the homogeneous systems 2. The colloidal solutions consist of: 1) the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium 2) solute and molecular aggregates 3) solvent and molecular aggregates 4) ions and molecules 5) atoms and molecules 3. Expiration colloidal systems: 1) to precipitate 2) the coagulated 3) concentrated 4) the milled 5) dissolved 4. The electric double layer on the surface of colloidal particles provides: 1) the kinetic stability 2) sedimentation stability 3) the aggregate stability 5. On the surface ВаSO4 under rule Panetta -Faience predominantly adsorbed ion: 1) SO3-2 2) SO4-2 3) Cl- 4) Br - 5) I- 6. Coagulation is the result of: 1) the loss of kinetic stability 2) loss of sedimentation stability 3) loss of aggregate stability 7. Sedimentation - is: 1) the formation of the electric double layer 2) settling of the dispersed phase under the action of gravity 3) dispersing the particles of the disperse phase 4) disaggregation of particles 5) molecular dissociation into ions 8. Coagulation - is: 1) dispersing a disperse phase 2) disaggregation of particles 3) consolidation (sticking) of dispersed phase particles and their deposition 4) formation of the electric double layer 5) molecular dissociation into ions 9. The dispersion system, in which the dispersing medium - liquid dispersed phase - liquid: 1) suspension 2) spray 3) emulsion 4) gel 5) solution of 10. The dispersion system, in which the dispersing medium - liquid dispersed phase - solid: 1) emulsion 2) suspension 3) a true solution 4) spray 5) solid solution 11. Colloidal solutions are characterized by: 1) microheterogeneity and high dispersion 2) complete insolubility of the dispersed phase in the dispersion medium 3) complete solubility of the dispersed phase in the dispersion medium 4) homogeneity and high dispersion 5) microheterogeneity and low dispersity 12. According to the degree of interaction of the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium dispersion systems are classified into: 1) the lipophilic and hydrophilic 2) jellies and gels 3) aerozols, liozols, organozols 4) freeze and lyophobic 5) hydrophobic and lyophobic 13. The micelle of iron hydroxide (III), obtained from the precipitate Fe (OH)3 peptization solution of FeCl3, has the form: 1) {mFe(OH)3nFeO+ nCl-}x+ xCl- 2) {mFeCl3 nFe3+3(n-x) OH-}3x+ 3xOH- 3) {mFe(OH)3 nCl-(n-x)Fe3+}x- 3xFe3+ 4) {mFe(OH)3nFe3+3(n-x) Cl-}3x+ 3xCl- 5) {mFeCl3 nFe+3(n-x) OH-}x+ 3xOH- 14. When adding an excess of H2S formula As2S3 micelles is: 1) {mAs2S3 2nAs3+ 3 (n-x)S2-}3x+ 3xS2- 2) {mAs2S3 nHS- (n-x)H+}x- xH+ 3) {mAs2S3 nAs3+ (n-x)S2-}3x+ 3xS- 4) {mAs2S3 (n-x)As3+nS2-}3x+ 3xS2- 5) {mAs2S3 nHS+ (n-x)H-}x+ xH+ 15. Microheterogeneous system consisting of a liquid medium and the liquid phase: 1) spray 2) organosol 3) emulsion 4) suspension 5) gel 16. The mathematical expression of dispersion: 1) D = ka 2) D = 1 /a 3) D = a 4) a = 1/D 5) D = k / a 17. The state of aggregation microheterogeneous systems are divided into: 1) 7 type 2) 9 type 3) 8 types 4) 6 type 5) 12 types 18. Designation of colloidal systems in which the dispersion medium is a liquid: 1) т/г, т/ ж, г/ ж 3) т/т, г/ж, т/ж 5) г/ж, ж/т, т/т 2) г/ ж, т/г, ж/ж 4) г/ж, ж/ж, т/ж 19. Designation of colloidal systems in which the dispersion medium is a solid body: 1) г/т, ж/ж, г/ж 3) т/ж, г/ж, г/т 5) т/г, ж/г, г/т 2) г/т, ж/т, т/т 4) г/ж, ж/т, г/ж 20. Designation of colloidal systems in which the dispersion medium is a gas: 1) ж/г, т/г 3) г/т, ж/т, т/т 5) г/ж, ж/г, т/ж 2) ж/ж, т/ж, г/ж 4) г/т, ж/т, г/ж 21. The particle size of colloidal systems: 1) 10-2 – 10-5 m 3) 10-5 – 10-7 m 5) 10-10 – 10-12 m 2) 10-7 – 10-9 m 4) 10-2 – 10-10 m 22. The particle size of the coarse systems: 1) 10-2 – 10-8 m 3) 10-8 – 10-10 m 5) 10-10 – 10-12 m 2) 10-2 – 10-5 m 4) 10-5 – 10-7 m 23. The particle size of true solutions: 1) 10-5 – 10-7 m 3) 10-2 – 10-10 m 5) 10-7 – 10-9 m 2) 10-2 – 10-5 m 4) 10-9 – 10-10 m 24. Lyophilic systems says: 1) a strong interaction between the particles of the dispersed phase and the solvent 2) uniform distribution of the dispersed phase throughout the volume of the dispersion medium 3) the weak interaction of the dispersed phase with the solvent 4) non-uniform distribution of the dispersed phase throughout the volume of the dispersion medium 5) there is no right answer 25. Lyophobic systems says: 1) uneven distribution of the dispersed phase throughout the volume of the dispersion medium 2) the weak interaction of the dispersed phase with the solvent 3) a strong interaction between the particles of the dispersed phase and the solvent 4) The uniform distribution of the dispersed phase throughout the volume of the dispersion medium 5) there is no right answer 26. In excess of potassium iodide, silver iodide micelles formula is: 1) {m AgI nAg+ (n-x)I-}x+ xI- 2) {mAgI nAg+(n-x) NO3-}x+ xNO3- 3) {mAgI nI- (n-x)K+}x- xK+ 4) {mAgI nI- (n-x) Ag+}x- Ag+ 5) {mAgI nAg-(n-x) NO3+}x+ xNO3- 27. The reaction of Ba (NO3)2 with an excess of K2SO4, barium sulfate micelles formula is: 1) {m ВaSO4 nBa2+ 2(n-x)NO3-}2x+ 2xNO3- 2) {m ВaSO4 nSO42- 2(n-x)K+}2x- 2xK+ 3) {m ВaSO4 nBa+2 2(n-x)K+}2x 2xSO42- 4) {m ВaSO4 nNO3- 2(n-x)K+}2x- 2xK+ 5) {m ВaSO4 nSO42+ 2(n-x)K-}2x- 2xK+ 28. The reaction of NaOH with excess AlCl3, aluminum hydroxide micelles formula is: 1) {mAl(OH)3 nAl3+ 3(n-x)Cl-}3х+ 3xCl- 2) {mAl(OH)3 nOH-(n-x) Na+}x- xNa+ 3) {mAl(OH)3 nAl(n-x)OH-}x+ xOH- 4) {mAl(OH)3 nCl-(xn-x) Na+}x- xNa+ 5) {mAl(OH)3 nAl+ (n-x)Cl-}х+ xCl- 29. Micelles aluminum hydroxide sludge produced from the Al (OH)3 peptization solution of AlCl3, is: 1) {mAl(OH)3 nAl3+ 3(n-x)Cl-}3x+ 3xCl- 2) {mAl(OH)3 nCl- 3(n-x) Al3+}x- 3xCl3+ 3) {mAl(OH)3 nOH-(n-x)Na+}x- xNa+ 4) {mAl(OH)3 nOH-(n-x) Al3+}x- xAl3+ 5) {mAl(OH)3 nAl+ (n-x)Cl-}х+ xCl- 30. In excess of silver nitrate, silver iodide micelle is: 1) {m AgI nI- (n-x)K+}x- xК+ 2) {mAgI nAg+(n-x) NO3-}x+ xNO3- 3) {mAgI nI- (n-x)Ag+}x- xAg+ 4) {mAgI nAg+ (n-x) I-}x+ xI- 5) {mAgI nAg-(n-x) NO3+}x- xNO3+
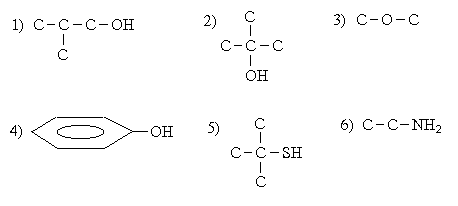
Theme number 8: Acidic and basic organic compounds. The reactivity of alcohols, phenols, thiols and amines. Session Purpose: to generate knowledge of acidity and basicity organicheskih compounds as the most important properties that determine most of the chemical reactions in living organisms. The main questions of the theme: 1. What is a functional group? 2. The acidity and basicity of the theory of Bronsted definition. 3. Alcohols classification. Homologous series of monobasic alcohols. Nomenclature. Primary, secondary, tertiary alcohols. Polyhydric alcohols. Glycerol. Phenols. Nomenclature. 4. Thiols, mercaptans. Homologous series of thiols. 5. Properties of alcohols, phenols and thiols are: a) proving the acid properties of these classes of compounds (metallic sodium and NaOH); b) oxidation of alcohols; c) oxidation of thiols in soft and hard conditions; g) oxidation of dihydric phenols. 6. Amines. Definition, classification. Primary, secondary, tertiary amines. 7. Reactions of proving basic amines. 8. Hydrogen bonds. See the example of alcohols and amines. 9. Preparation of ethers for example diethyl ether. Methods of teaching and learning: effective formative feedback on the development of competencies, training in small groups SGL.
References: 1. Петров А.А., Бальян Х.Б. и др. «Органическая химия», М. Высшая школа, 1984 г. 2. Н.А.Тюкавкина, Ю.И.Бауков., «Биоoрганическая химия», Москва. «Медицина». 1991 г. 3. Степаненко Б.Н. «Курс органической химии», Москва, 1991 г. 4. Грандберг И.А. «Органическая химия», Москва, 2001 г. 5. Петров А.А., Бальян Х.Б. и др. «Органическая химия», М. Высшая школа, 1984 г. каз.яз 6. А.Н.Несмеянов, Н.А.Несмеянов «Начала органической химии», Изд.Химия, Москва 1974 г. 7. Овчинников Ю.А. «Биоорганическая химия». М. Высшая школа, 1986 г. 8. Плешкова С.М., Р.Д. Асанбаева, М.И. Ильясова, Ш.Г. Салықова 1-ші курс студенттерінің биоорганикалық химиядан өз бетімен дайындалуына арналған тесттер, Алматы, 2001 ж. 9. Шабаров Ю.Ф. «Органическая химия», учебник для вузов; М. Химия, 1996 г. в 2-х томах. Test questions: 1. Write the esterification reaction of ethyl alcohol with: 1) formic acid; 2) phosphoric acid. 2. Write the reaction with bromine water (Br2): 1) phenol; 2) aniline. 3. Write the oxidation reaction of the following compounds: 1) 2-propanol; 2) benzyl alcohol; 3) hydroquinone; 4) methanol; 5) methanethiol. Which of these reactions is the basis of action of coenzyme Q? 4. How does the nature of the radical on the main following amines: methylamine, methylethylamine, aniline. Write reaction form salts of the compounds with hydrogen chloride. 5. Write the acylation reaction of methylamine. 6. Write the deamination of putrescine / butanediamine 1,4 / with nitrous acid.
8. Adrenaline-hormone of the adrenal medulla, norepinephrine and dopamine is a precursor of adrenaline:
Give a classification characteristic functional groups in these compounds and to determine their acid-base character. For some reactions can get the adrenaline of noradrenaline. Write this reaction scheme. 9. Write the formation of hydrogen bonds between the molecules: 1) ethanol; 2), phenol and water; 3) methylamine. 10. Prove acidic character of 2-propanol, benzyl alcohol, phenol, hydroquinone, ethanethiol. Which of these compounds exhibit their acidity by reaction with sodium hydroxide? Write the reaction.
Тема 9
Theme number 9: Aldehydes and ketones. Nucleophilic addition reactions. Carbon and dicarbon acids. Nucleophilic substitution reactions. Session Purpose: to generate knowledge of the chemical properties of carbonyl compounds for the understanding of their reactivity, as well as patterns and features in the chemical behavior of carboxylic acids and their functional derivatives, causing the occurrence of a number of reactions in biological systems.
The main questions of the theme: 1. Aldehydes and ketones. The class definition. 2. Structure of the carbonyl group and the influence of the substituents in the radical at its reactivity. 3. Isomerism and nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones. 4. Effect of a carbonyl group on the mobility of the hydrogen atoms have -carbon (CH acidity). 5. The mechanism of the reactions of carbonyl compounds with water, alcohols, thiols, primary amines. Hydrolysis of the acetals and hemiacetals. 6. The biological significance of the aldol accession. 7. Oxidation reactions in recovery. 8. Carboxylic acids. The class definition. Classification radical nature and number of carboxyl groups. Nomenclature. 9. Monocarboxylic (to C6) and dicarboxylic (up to C5) acid. Unsaturated acids: propenoic, butenedioic. Higher fatty acids, stearic, palmitic, oleic, linoleic, linolenic, arachidonic. Communication structure with biological activity. 10. The electronic structure of a carboxyl group and a carboxylate ion. 11. The intermolecular hydrogen bonds of carboxylic acids. 12. The acidic properties of carboxylic acids, dissociation degree of salts. 13. The acylation reactions, anhydrides, esters and thioesters, amides and their reverse hydrolysis reaction. Acylphosphates, acetyl coenzyme - A - natural macroergic acylating reagents. The biological role of acylation and phosphorylation. 14. The ability of acids to decarboxylation according to the number and arrangement of the carboxyl groups. 15. The derivatives of carbonic acid: urea, guanidine. Methods of teaching and learning: effective formative feedback on the development of competencies, training in small groups SGL, training based on case studies CBL.
References: 1. Петров А.А., Бальян Х.Б. и др. «Органическая химия», М. Высшая школа, 1984 г. 2. Н.А.Тюкавкина, Ю.И.Бауков., «Биорганическая химия», Москва. «Медицина». 1991 г. 3. Степаненко Б.Н. «Курс органической химии», Москва, 1991 г. 4. Грандберг И.А. «Органическая химия», Москва, 2001 г. 5. Петров А.А., Бальян Х.Б. и др. «Органическая химия», М. Высшая школа, 1984 г. каз.яз. 6.А.Н.Несмеянов, Н.А.Несмеянов «Начала органической химии», Изд.Химия, Москва 1974 г. 7. Овчинников Ю.А. «Биоорганическая химия». М. Высшая школа, 1986 г. 8. Плешкова С.М., Р.Д. Асанбаева, М.И. Ильясова, Ш.Г. Салықова 1-ші курс студенттерінің биоорганикалық химиядан өз бетімен дайындалуына арналған тесттер, Алматы, 2001 ж. 9. Шабаров Ю.Ф. «Органическая химия», учебник для вузов; М. Химия, 1996 г. в 2-х томах.
|