Control test questions. 1. Where is acid Cn and CM is the same:
1. Where is acid Cn and CM is the same: 1) H2SO4 3) HCl 5) H2SO3 2) H3PO4 4) H2CO3 2. Mass fraction of a solution consisting of 200 g. of water and 40 g. of glucose, is: 1) 0.32 3) 2.4 5) 4.2 2) 0.16 4) 3.2 3. Where is a base Cn twice larger than CM: 1) LiOH 3) Ca(OH)2 5) Fe(OH)3 2) Al (OH)3 4) KOH 4. The equation for calculating the molar concentration: 1) CM = m / M 3) CM = n / mV 5) CM = MV / m 2) CM = n / M . V 4) CM = m / M . V 5. The equation for calculating the titer: 1) T = N . E / 1000 3) T = N . 1000 / E 5) T = N . M / 1000 2) T= msub / msol 4) T = E . 1000 / N 6. The weight of potassium permanganate required for the preparation of 50 g 5 % solution: 1) 1.5 g 3) 10 g 5) 25 g 2) 5.1 g 4) 2.5 g 7. The expression for calculating the normal concentration: 1)
2) 8. The mass fraction of the solution consisting of 80 g H2O and 20 g NaCl: 1) 0.8 3) 0.2 5) 0.02 2) 0.1 4) 0.4 9. The equation for calculating the mass fraction (%) 1) 2) 10. If at this temperature the solute is not soluble, such a solution is: 1) a saturated 3) unsaturated 5) homogeneous 2) diluted 4) supersaturated 11. Mass fraction of solute - is: 1) the ratio of the mass of solute to the total weight of the solution 2) the mass of the solute in solution of 1000 g 3) the mass of the solute in 100 g water 4) The weight of the solute in 100 g solvent 5) the mass of the solute in 1 liter of solution 12. In the 1 liter of solution contained 20 g of NaOH. The molar concentration of this solution is: 1) 0.1 M 3) 0.5 M 5) 2 M 2) 0.2 M 4) 1 M 13. In 250 ml of a solution of 4.9 g of H2SO4. Equivalent concentration of this solution is: 1) 0.52 n 3) 1.05 n 5) 0.1 n 2) 0.32 n 4) 0.4 n 14. To prepare 500 g 10% solution of glucose is necessary to take glucose: 1) 60 g 3) 98 g of 5) 25 g 2) 50 g of 4) 40 g 15. How many grams of copper sulfate should be taken to prepare 250 ml of 0.25 M solution: 1) 12 g 3) 25 g 5) 30 g 2) 10 g 4) 15 g 16. To prepare 100 g of a 5% solution of salt is necessary to take: 1) 7.5 g 3) 10.0 g 5) 0.5 g 2) 2.5 g 4) 5.0 g 17. Unit of Titres: 1) mol / ml 3) mol 5) mol / kg 2) g / ml 4) moles / l 18. Unit of measurement equivalent concentration: 1) % 3) mol / l 5) g / mol 2) g / cm3 4) mol / kg 19. Unit of measurement of the molar concentration: 1) mol / l 3) mol / kg 5) g / mol 2) g / cm3 4) moles 20. Factor equivalence Ca (NO3)2: 1) 1/3 2) 1/2 3) 2 4) 1 5) 1/5 21. To prepare 100 ml of a 0.2 N solution of calcium chloride to take: 1) 4.12 g 2) 1.11 g 3) 0.75 g 4) 10.21 g 5) 7.5 g 22. To prepare 200 ml of a 0.5 N solution of potassium nitrate to take: 1) 24.5 g 2) 16.2 g 3) 54.4 g of 4) 8.5 g of 5) 10 g 23. To prepare 2 liters of a 0.1 N solution of potassium nitrate to take: 1) 20.2 g 2) 6.2 g 3) 4 g 4) 0.1 g 5) 10 g 24. How many moles contained in 250 g of calcium sulphate: 1) 1.8 moles 2) 6 moles 3) 2 moles 4) 3 moles 5) 0.5 mole 25. Normal concentration corresponding to a 1 M solution of H2SO4: 1) 1 n 2) 2 n 3) 0,5 n 4) 0,1 n 5) 0,25 n 26. Factor equivalence Al2 (SO4) 3: 1) 1/4 2) 1 3) 1/2 4) 1/6 5) 1/3 27. Expression of molal concentration is: 1) Cm = nвещ-ва / m р-ля 3) Cm = nр-ля / mвещ-ва 5) Cm = n /V 2) Cm = n вещ-ва /V 4) Cm = n / М.m 28. Expression of the normal concentration is: 1) CН = m /V 3) CН = m / Э . V 5) CН = n / V 2) CН = m1/m2 4) CН = n / m 29. Unit of measurement of mass fraction: 1) % 3) moles / l 5) mol / kg 2) g / l 4) g / ml 30. Factor of equivalence H3PO4: 1) 1/2 2) 1 3) 1/3 4) 3 5) 1/4
Theme number 2: Chemical kinetics. Factors affecting the rate of reaction.
The purpose of the activity: Cformirovat knowledge about the teachings of the rate and mechanism of chemical reactions, the doctrine of chemical equilibrium (the principle of Le Chatelier-Braun), learn the basic concepts and laws of chemical kinetics, the influence of different factors: the nature and concentration of the reactants, temperature, pressure, catalyst the rate of chemical reactions.
The main questions of the theme:
1. What is the subject of studying chemical kinetics? 2. What is called the speed of a chemical reaction? As it is expressed for homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions? 3. State the law of mass action (Guldberg and Waage law) and write their mathematical expressions for the rates of the forward and reverse reactions. 4. What is called the order and molecular reactions? 5. Effect of pressure and temperature on the reaction rate. 6. An approximate rule of van't Hoff and his mathematical expression. 7. The activation energy and the Arrhenius equation. 8. Effect of catalysts on the reaction rate. Positive and negative catalysis. Homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. 9. The role of catalysis in the vital activity of living organisms. Enzymatic reactions. Meaning enzymes. Michaelis-Menten equation. 10. What is called chemical equilibrium? 11. The equilibrium constant and its physical meaning. 12. State the principle of Le Chatelier - Brown. 13. Effect of temperature, concentration of reactants, and the pressure on the direction of displacement of the chemical equilibrium in reversible reactions. Methods of teaching and learning: effective formative feedback on the development of competencies, training in small groups SGL.
Literature 1. Lenski A.S.Introduction to bioinorganic and biophysical chemistry.- М.: VW, 1989.- 256 page. 2. Glinka N.L.. General chemistry.Edited by V.A. Rabinovich.- L.: Chemistry,1988.- 704 с. 3.Glinka N.L.. exercises and works in chemistry.Edited by A.Rabinovich and X.MRubin.- Chemistry 1985.- 264 page. 4Vasileva Z.G., Granovskaya А.А., Taperova А.А. Laboratorial works in inorganic chemistry.- Chemistry, 1986. - 288 page. 5.Lectures and synopsis. 6.Ahmetov N.B. Genaerally and inorganic chemistry. М.: VW, 1981. – 679 page. Control test questions:
1. With increasing concentration of the reactants the reaction rate: 1) is increased 3) is not changed 2) decreases 4) no correct answer 5) significantly reduced 2. The activation energy determines: 1) the chemical equilibrium 2) the possibility of chemical interaction 3) a chain reaction 4) parallel reactions 5) the order of reaction 3. The temperature coefficient of the reaction (g = 2). When the temperature rises to 20 ° C the reaction rate increases: 1) 3 times 3) 4 times 5) is reduced by 4 times 2) 2 times 4) does not change 4. The temperature coefficient of the reaction (g = 2). When the temperature is lowered to 30 ° C the reaction rate change: 1) decreases by 6 times 3) decreases by 8 times 5) does not change 2) increase of 6 times 4) increase of 8 times 5. To direct the endothermic reaction shifts the equilibrium temperature increase: 1) left 3) does not change 2) right 4) no correct answer 6. The law of mass action: 1) chemical reaction rate is directly proportional to the product of the concentrations of the reactants 2) at increasing temperature every 10 ° C, the reaction rate increases by 2-3 times 3) the rate of a chemical reaction is the change in the amounts of reactants per unit time per unit volume of the system 4) chemical reaction rate is the change amounts of the reactants per unit of time per unit of interfacial surface 5) if the system is in equilibrium, outside influence, the system processes develop, shifts the equilibrium in the direction in which the effect is produced by the impact will be weakened 7. The temperature coefficient of the reaction g = 3. When the temperature rises to 40 ° C, the reaction rate increases: 1) 21 times 3) 81 times 5) 43 times 2) 27 times 4) 12 times 8. With increasing concentration of the reactants equilibrium constant: 1) does not change 3) decreased 5) tends to infinity 2) increase 4) tends to zero 9. Effect of catalyst on the rate of chemical reaction is: 1) to reduce the activation energy 2) to increase the activation energy 3) to increase the number of active molecules 4) active in reducing collisions 5) in the constancy of the activation energy 10. When the temperature rises from 10 ° C to 50 ° C the reaction rate increased by 16 times. The temperature coefficient of this reaction is: 1) 3 3) 2.5 5) 3.5 2) 2 4) 1.5 11. The temperature coefficient is equal to 3. When the reaction temperature rises from 40 ° C to 70 ° C the reaction rate increases: 1) 30 times 2) 18 times 3) 3 times 4) 27 times 5) 21 times 12. As the temperature increases the reaction rate increases, where in: 1) the number of collisions is not changed 2) the average kinetic energy of the molecules decreases 3) the number of active molecules increases 4) the number of active molecules decreases 5) the number of collisions decreases 13. For the reaction 2H2 (g) + O2 (g) = 2H2O (g) the mathematical expression of the law of mass action has the following form: 1) u=k [H2].[O2]3 3) u=k [H2]2.[O2] 2) u=k [H2].[O2] 4) u=k [H2] 5) u=k [H2О]2 14. For the reaction Cl2 + H2 = 2HCl mathematical expression of the law of mass action has the following form: 1) u=k [Cl2] + [H2] 3) u=k [Cl] + [H]3 2) u=k [Cl2].[H2] 4) u=k [HCl] 5) u=k [Cl2] - [H2]
15. In the system of N2 + 3H2 = 2NH3 increase in pressure will shift the equilibrium: 1) left 2) right 3) does not change 4) no correct answer 16. The system N2 + 3H2 = 2NH3 with increasing concentration of N2 equilibrium shift: 1) right 2) left 3) does not change 4) no correct answer 17. The equilibrium constant for the reaction N2 + 3H2 = 2NH3: 1)
2) 18. The system 2NO + O2 ® 2NO2, if the volume of the reaction vessel 2 times the speed of the direct reaction: 1) decreased by 4 times 3) increased by 4 times 5) increased by 2 times 2) reduced by 8 times 4) increased by 8 times 19. On the basis of the law of mass action expression rate of a chemical reaction 2Fe(тв) +3Cl2(г) = 2FeCl3(тв) has the form: 1 1) u=k [Cl2]3 3) u=k [Fe] 5) u=k [Cl2] 2) u=k [Fe][Cl2] 4) u=k [Fe] 2 [Cl2]3
20. The system CaCO3(к) Û CaO(к)+CO2(г); DH=179 kJ (кДж) at higher temperatures the equilibrium will shift: 1) left 2) right 3) does not change 4) no correct answer 21. When the concentration of NO increased in 4 times the speed of the direct reaction 2NO + Cl2 Û 2NOCl: 1) increase by 4 times 3) increased by 16 times 2) reduced by 16 times 4) decreases by 12 times 5) decreases by 4 times 22. The system Cl2 + H2 = 2HCl with decreasing volume, the balance will shift: 1) left 2) right 3) does not shift 4) no correct answer 23. On the basis of the law of mass action, rate expression for the reaction 2NO + O2 ® 2NO2 is: 1) u=k [NO]2[ O2] 3) u= k[NO2] 5) u=k [NO2]2 2) u=k [NO][O2] 4) u=k [O2]
24. For the reaction 4NH3+ 5O2 Û 4NO+ 6H2O, the equilibrium constant expression is: 1) K = k [NH3]4[O2]5 3) K = k[NO]4[H2O]6 5) 2) 25. When the pressure in the system 2F2(г)+2Н2О(г)Û 4HF(г)+O2(г), the equilibrium will shift: 1) left 2) right 3) does not shift 4) no correct answer 26. When the concentration of hydrogen 3 times N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) reaction rate: 1) increases by 81 times 3) decrease in 9 times 2) increased by 9 times 4) increase in 5 times 27) is reduced by 27 times 27. In the system of N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) when the pressure balance will be shifted: 1) toward the reverse reaction 2) in the direction of the direct reaction 3) does not shift 28. By reducing the volume of the reaction vessel at 5 times the rate of reaction 2NO (g) + O2 (g) = 2NO2 (g): 1) increases 5 times 3) increase 125 times 2) reduced 5 times 4) is reduced to 75 times 5) is reduced 125 times 29. The temperature coefficient of the reaction is equal to 3.When the temperature rises to 10 o C the reaction rate will increase: 1) 33 times 2) in 30 times 3) in 3.3 times 4) 3 times 5) 10 times 30. For the reaction of C (k) + O2 (g) = CO2 (g) the expression of the law of mass action has the form: 1) u=k [C] [O2] 3) u=k [O2] 5) u=k [C] 2) u=k [CO2] 4) u=k [O2] /[CO2]
Theme number 3: Acid-base balance in life processes. The ionic product of water. Hydrogen index as a quantitative measure of the active acidity and alkalinity. Buffer systems.
The purpose of the activity: Cformirovat knowledge on the theory of electrolytic dissociation, learn the basic definitions and terms on this topic, highlighting the role of electrolytes in the activity of organisms.
The main questions of the theme:
1. Expand the essence of electrolytic dissociation of Arrhenius. What are the weaknesses of this theory. What are its advantages? 2. Modern physico-chemical theory of solutions of electrolytes (theory and I.A.Kablukova V.A.Kistyakovskogo). 3. Explain the process of solvation and hydration, based on chemical theory of solutions Mendeleev. 4. What substances are called electrolytes? Strong and weak electrolytes. Give examples. 5. What is the degree of electrolytic dissociation? How to change the value of the degree of electrolytic dissociation, depending on the strength of the electrolyte? 6. Formulate Law of dilution and write its mathematical expression. 7. The application of the law of mass action to the processes of dissociation of weak electrolytes. What characterizes the electrolytic dissociation constant and what factors it zavisisit? 8. The theory of strong electrolytes and P.Debaya E.Hyukkelya. 9. What is called the activity and how is it calculated? 10. How is the ionic strength of the solution and the activity coefficient? 11. The electrolytic dissociation of water. What is called the ionic product of water? What did it matter? Output value of the ion product of water. 12. Hydrogen and gidrokislny indicators. 13. What substances are called indicators? Their use in chemical practice. 14. What system called buffer? 15. As classified buffer systems? 16. As the pH buffer system is calculated, a weak acid and a salt of the acid? Give a formula to calculate the pH of this buffer solution? 17. How do you calculate the pH of the buffer system, weak base - salt of this base? Give a formula to calculate the pH of the buffer solution. 18. What is called the buffer capacity? What it depends on, and how can it be calculated? 19. What buffer systems in the human body maintain a constant pH in blood and tissue fluids? 20. What is the value of the buffer systems to the human body? Methods of teaching and learning: effective formative feedback on the development of competencies, training in small groups SGL, training based on teamwork TBL.
Literature 1. Lenski A.S.Introduction to bioinorganic and biophysical chemistry.- М.: VW, 1989.- 256 page. 2. Glinka N.L.. General chemistry.Edited by V.A. Rabinovich.- L.: Chemistry,1988.- 704 с. 3.Glinka N.L.. exercises and works in chemistry.Edited by A.Rabinovich and X.MRubin.- Chemistry 1985.- 264 page. 4Vasileva Z.G., Granovskaya А.А., Taperova А.А. Laboratorial works in inorganic chemistry.- Chemistry, 1986. - 288 page. 5.Lectures and synopsis. 6.Ahmetov N.B. Genaerally and inorganic chemistry. М.: VW, 1981. – 679 page. Control test questions:
1. Mathematical expression law of dilution: 1) 2) 2. Expression of the ion product of water: 1) KW = [H+]. [OH-] 2) 4) 3. The equation of the hydroxyl index: 1) pOH = -lg [H+] 3) pOH = -lg [OH-] 4) pOH= - lg[Cкисл.] 2) 4. The equation of hydrogen index: 1) pH = -lg [H+] 2) 4) pH= - lg[Cb] 5) рН = - lg [ОH-]
5. The dissociation constant of hydrocyanic acid: 1) 4) K д= [H+] [CN-] 5) K д= [НCN] 6. [H+] = 10-4 mol / l, the pH value is: 1) рН=2 2) рН=10 3) рН=4 4) рН=8 5) рН= 6 7. [H+] = 10-3 mol / l, pOH value is: 1) рОН=9 2) рОН=11 3) рОН=3 4) рОН=13 5) рОН = 7 8. By increasing the pH value per unit concentration of hydrogen ions in solution: 1) decreases by 10 times 3) decreases by 100 times 2) increased 10 times 4) increases 100 times 5) no change 9. When the pH is increased to 3 units, the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution: 1) decreases by times 100 3) increased by 100 times 2) reduced 1000 times 4) increases 1000 times 5) decreases by 3 times 10. [H+] = 10-8 mol / l, the concentration [ОH-] is: 1) 10-5 mol / l 3) 10-6 mol / l 5) 10-10 mol / l 2) 10-4 mol / l 4) 10-8 mol / l 11. Law of dilution is valid for: 1) dilute solutions of weak electrolytes 2) non-electrolyte solutions 3) dilute solutions of electrolytes 4) concentrated solutions of electrolytes 4) solutions of strong electrolytes 12. Expression of the degree of dissociation: 1) a = Nобщ / nдис 2) a =nдис / Nобщ 3) a = Nобщ /nчисло ионов 4) a = nчисло ионов . Nобщ 5) a=Nобщ – nдис
13. The dissociation constant of CH3COOH: 1) 2) 5) Кд= [H+] . [CН3СОО-] 14. The dissociation constant of HNO2: 1) 2) 15. The ionic product of water is equal to: 1) Kw = 1014 2) Kw = 10-10 3) Kw = 10-14 4) Kw =10-7 5) Kw =107 16. The concentration of hydrogen ions in solution of 10-2 mol / l, the pH value of the solution: 1) рН=3 2) рН=2 3) рН=1/2 4) рН=0,2 5) рН= 12 17. Hydrogen ion concentration (mol / l) at pH = 3 is: 1) [H+] = 1013 2) [H+] = 103 3) [H+] = 10-3 4) [H+] = 10-5 5) [H+] = 10-11 18. Hydrogen ion concentration (mol / l) at pOH = 4 is: 1) [H+] = 10-4 2) [H+] = 10-5 3) [H+] = 1010 4) [H+] = 10-10 5) [H+] = 10-2 19. The concentration of hydroxyl ions (mol / l) at pH = 5 is equal to: 1) [ОH-] = 1 .10-10 2) [ОH-] = 1 .105 3) [ОH-] = 1 .10-9 4) [ОH-] = 1.10-5 5) [ОH-] = 1 .10-8 20. Weak electrolyte: 1) H3PO4 3) KCl 5) КОН 2) NaCl 4) H2SO4 21. Strong electrolyte: 1) NH4OH 3) Be(OH)2 5) СН3СООН 2) Mg(OH)2 4) KOH 22. In dilute solution dissociation occurs reversibly: 1) KOH 3) NaOH 5) НСl 2) NH4OH 4) Ba(OH)2 23. pH 0.01 N KOH solution is equal to: 1) 2 2) 0.01 3) 12 4) 14 5) 10 24. The pH of the 0.1 M solution of NH4OH (a= 0,01) is: 1) 12 2) 2 3) 3 4) 11 5) 8 25. The pH of a 0.1 M solution of acetic acid КД = 1,8. 10-5 (pK = 4,76) is equal to: 1) 2.88 2) 3.55 3) 1.0 4) 10.5 5) 12 26. The pH of 0.001 M formic acid (a= 0,1) is equal to: 1) 3 2) 6 3) 4 4) 2 5) 7 27. When added to 1 l of water 10-2 mol NaOH, the pH of the solution: 1) will increase by two units 3) reduced by two units 2) increase by five units 4) decrease by five units 5) decreases by one unit 28. To increase the pH to 2 units, a hydrogen ion concentration is necessary to: 1) reduce to 100 times 3) increased 10 times 2) to reduce to 10 times 4) increase 100 times 5) increased 2 times
29. The degree of dissociation of a 0.2 N solution of weak monobasic acid is 0.03. The quantity pOH of this solution equal: 1) 11.78 2) 6.4 3) 3.2 4) 7 5) 3.6 30. The pH value of blood is 7.53, then the concentration of hydrogen ions is: 1) 2,3. 10-7 3) 2,95. 10-8 5) 8,2. 10-3 2) 1,27. 10-5 4) 0,01 Theme number 4: The nature of the chemical bond. Biogenic s-, p-, d-elements and their biological role.
Session Purpose: To study the chemical properties of biogenic elements (s-, p-, d-, f-elements), to disclose the value of the macro- and micronutrients for the life of the organism.
The main questions of the theme:
1. The structure of the atom and the four main characteristics of the energy state of an electron in an atom. 2. What characterizes the main, side or orbital magnetic and spin quantum number? 3. State the Pauli exclusion principle. 4. Give the definition of the principle of least energy. 5. Give two formulations Aufbau principle. 6. Formulate Hund's rule. 7. What elements of the Mendeleev periodic table are s-elements? What properties are characteristic of them. Give examples. 8. What elements belong to the p-elements? What properties exhibit p-elements? Give examples. 9. What elements are among the d-elements? What are the chemical properties characteristic of the d-elements? 10. What elements are among the f-elements? Give examples. 11. The concept of the biosphere and biogenic elements. Classification of nutrients. The biological role of the elements in the life of the organism. Methods of teaching and learning: effective formative feedback on the development of competencies, training in small groups SGL, task-based learning TaskBL.
Literature
1. Lenski A.S.Introduction to bioinorganic and biophysical chemistry.- М.: VW, 1989.- 256 page. 2. Glinka N.L.. General chemistry.Edited by V.A. Rabinovich.- L.: Chemistry,1988.- 704 с. 3.Glinka N.L.. exercises and works in chemistry.Edited by A.Rabinovich and X.MRubin.- Chemistry 1985.- 264 page. 4Vasileva Z.G., Granovskaya А.А., Taperova А.А. Laboratorial works in inorganic chemistry.- Chemistry, 1986. - 288 page. 5.Lectures and synopsis. 6.Ahmetov N.B. Genaerally and inorganic chemistry. М.: VW, 1981. – 679 page. Control test questions: 1. The electronic formula of atomic Na: 1) 1s22s22p63s1 3) 1s22s22p43s1 5) 1s22s22p63s2 2) 1s22s22p53s1 4) 1s22s22p3 2. E-atom formula Mg: 1) 1s22s22p43s1 3) 1s22s22p63s2 5) 1s22s22p63s23p2 2) 1s22s22p63s1 4) 1s22s22p43s2
3. Electronic formula atom K: 1) 1s22s22p63s64s1 3) 1s22s22p63s23p4 5) 1s22s22p63s23p5 2) 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 4) 1s22s22p63s2 3p44s1
4. Refers to the d - elements: 1) P 3) As 5) Hg 2) Rb 4) Ba 5. Refers to the s - elements: 1) Zn 3) Fe 5) Hg 2) Cu 4) Ra 6. Shows amphoteric properties: 1) Zn(OH)2 3) Mn(OH)2 5) Ca(OH)2 2) Fe(OH)2 4) Cr(OH)2 7. Electronic formula corresponding atom Zn: 1) 1s22s22p63s23p54s23d10 3) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d10 2) 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 3d7 4) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d8 5) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d9 8. s - elements include: 1) Na, B, C 3) K, Be, Mg 5) N, P, As 2) Li, Pb, Zn 4) Cl, P, Na 9. s - elements include: 1) Ca, Mg, Be 3) Li, H, Cl 5) Cu, Ag, Au 2) Pb, Nb, Mg 4) F, Co, Ni 10. s - elements include: 1) Ag, Au, Cu 3) Zn, Ca, Ge 5) As, Sb, Bi 2) Rb, Cs, Fr 4) Be, B, O 11. d - elements include: 1) Zn, Ca, Ge 3) Ca, K, S 5) F, Cl, Br 2) O, F, Cl 4) Zn, Cu, Ag 12. d - elements include: 1) Zn, Ca, Ge 3) Cr, Mn, Fe 5) F, Cl, Br 2) O, F, Cl 4) C, N, O 13. d - elements include: 1) Sb, Te, I 3) S, Cl, Fe 5) O, Se, I 2) Ru, O, F 4) Hg, Ag, Au 14. Electronic structure of the outer energy level of an atom of Ca: 1) 4s2 3) 4s13p6 5) 3s2 2) 4s1 4) 4s03p8 15. Electronic structure of the outer energy level of an oxygen atom: 1) 2s13p5 3) 2s03p6 5) 2s22p3 2) 2s22p4 4) 2s22p6 16. Electronic structure of the outer energy level of phosphorus atom: 1) 2s23p3 3) 3s23p3 5) 2s22p2 2) 3s23p4 4) 3s23p5 17. d - elements include: 1) Cu, Zn, Ca 3) Cu, Au, Ag 5) Cl, Br, I 2) Cu, Zn, S 4) K, Zn, Ca 18. p - elements include: 1) Mn, Co, Fe 3) F, Cl, Br 5) K, Rb, Cs 2) B, C, Ni 4) B, Be, Li 19. p - elements include: 1) P, S, C 3) Se, Te, Pd 5) Li, Ca, Ba 2) Ti, V, Cr 4) B, Al, Cu 20. d - elements include: 1) Zn, Nb, Mo 3) Cr, Mn, Cl 5) Cs, Ba, Ra 2) O, F, Cl 4) Al, Si, Li 21. The element with the highest electronegativity: 1) Cl 3) F 5) Ca 2) O 4) N 22. A compound, where in the degree of oxidation of nitrogen is 5: 1) HNO3 3) NaNO2 5) NO2 2) NO 4) NH3 23. A compound, wherein the degree of sulfur oxidation is 4: 1) К2SO4 3) SO3 5) Na2S2O3 2) (NH4)2SO3 4) Na2S 24. A compound, wherein the degree of oxidation of chlorine is 3: 1) HClO4 3) HClO3 5) HCl 2) HClO 4) HClO2 25. The strongest acid: 1) HCl 3) HOCl 5) HClO2 2) HOBr 4) HBr 26. Electronic structure of the outer energy level of an atom Li: 1) 2s2 2) 1s1 3) 2s1 4) 2s22p1 5) 2s22p2 27. With the increase in the number of electrons in the outer energy level of p-elements in periods from left to right their electronegativity: 1) increases 2) is reduced 3) is not changed 4) equals zero 5) there is no right answer 28. With the reduction of the number of electrons in the outer energy level of the p elements in the periods from right to left their electronegativity: 1) increases 2) is reduced 3) is not changed 4) equals zero 5) there is no right answer 29. The element with the highest electronegativity: 1) C 2) B 3) S 4) O 5) N 30. Electronic structure of the outer energy level of an atom of aluminum: 1) 3s23p1 2)3s13p4 3) 3s13p2 4) 4s13p6 5) 3s23p6
Theme number 5: The complex compounds and their properties. Medical - biological role of complex compounds.
The purpose of the activity: to systematize knowledge of the main provisions of the coordination theory, learn the basic types, nomenclature and chemical properties of complex compounds.
The main questions of the theme: 1. The main provisions of the coordination theory A.Vernera. 2. Define the following terms: complexing agent (central ion), ligands, the inner coordination sphere, the outer coordination sphere, the coordination number. 3. Methods of establishing coordination complex compounds of formulas. 4. The main types of complex compounds: ammines, aqua complexes, acidocomplexes, cyclic (chelate) complex compounds, chelate compounds. 5. The range of complex compounds. 6. Dissociation of complex compounds in solution. Instability constants and stability constants of complex compounds. 7. Spatial structure and isomerism of complex compounds. Methods of teaching and learning: effective formative feedback on the development of competencies, training in small groups SGL, training in using peer PAL.
Literature 1. Lenski A.S.Introduction to bioinorganic and biophysical chemistry.- М.: VW, 1989.- 256 page. 2. Glinka N.L.. General chemistry.Edited by V.A. Rabinovich.- L.: Chemistry,1988.- 704 с. 3.Glinka N.L.. exercises and works in chemistry.Edited by A.Rabinovich and X.MRubin.- Chemistry 1985.- 264 page. 4Vasileva Z.G., Granovskaya А.А., Taperova А.А. Laboratorial works in inorganic chemistry.- Chemistry, 1986. - 288 page. 5.Lectures and synopsis. 6.Ahmetov N.B. Genaerally and inorganic chemistry. М.: VW, 1981. – 679 page.
|

 3)
3)  5)
5) 
 4)
4) 
 3)
3)  5)
5) 
 4)
4) 
 3)
3) 
 4)
4)  5)
5) 

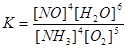 4)
4) 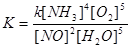
 3)
3) 
 4)
4)  5)
5) 
 3)
3) 
 5)
5) 
 5) pOH= 14 + рН
5) pOH= 14 + рН 3)
3) 
 2)
2)  3)
3) 
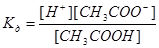 3)
3) 
 4)
4) 
 3)
3) 
 4)
4)  5) Кд= [H+] . [NO2-]
5) Кд= [H+] . [NO2-]


