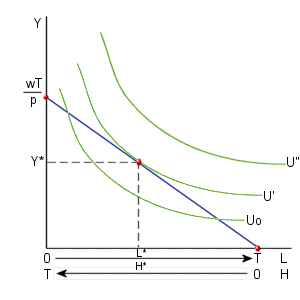
In the diagram below, three indifference curves have been added to the diagram containing the budget constraint. Each point on the budget constraint is a feasible combination of income and leisure. It is assumed that the individual will select the combination of income and leisure that provides the highest possible level of utility. As indicated by the diagram below, this optimal combination of L and Y occurs at a point of tangency between the budget constraint and an indifference curve. In the diagram below, this optimal point occurs when real income equals Y* and hours of leisure equals L*. At this point, the individual chooses to work H* hours.
Topic 5, 6: Demand for Labor (1,2 part)





