Rationale for extending the marketing mix
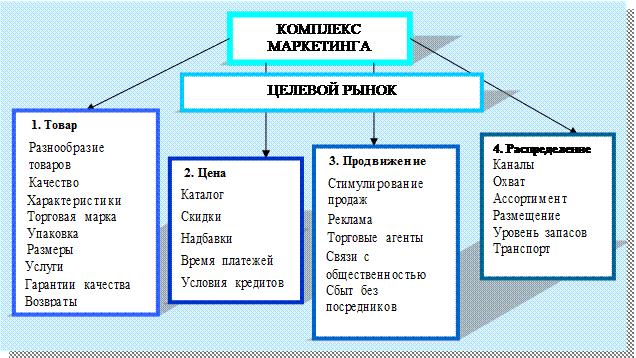
Different mixes are required for different objectives. There are multiple marketing mix models, each with different ingredients. The most famous and popular mix of all has become known as the 4 P model, the key ingredients being product, price, promotion and place (or distribution), which was developed by E. Jerome McCarthy. Since its inception this model has been much debated and much contributed to. There are alternatives that talk of 6 Ps (to include politics and public relations). For example Booms and Bitner (1981) extended the 4Ps to 7Ps to include participants (now referred to in the literature as people), physical evidence (the physicality of the environment) and process. In their original article Booms and Bitner (1981) intended their additional 3Ps to be limited to service marketing. However, there are academics and writers, for example Levitt, who suggest that 'there are only industries whose service components are greater or lesser than those of other industries. Everybody is in service' (Levitt 1972). Various academics have offered an alternative: the 4 Cs, which takes a buyer’s view of the market (in contrast to 4 Ps that take a seller’s view of the market). These 4 Cs are: customer value (customer solution – to find a solution to a customer ‘problem’ by offering the right combination of products and services), cost (to consumer), convenience (to consumer) and communication with customers. The 4 P model is now regarded as too simplistic for current marketing conditions, as well as being too focused on traditional consumer product marketing. The 4 P model of marketing mix can be described as follows:
Whatever mix is chosen, the important part of the process is to allocate the right level of resources and to find the balance appropriate to the target market. (Jonathan Groucutt, Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 155-164; Ch. Doyle, pp.228-229) Questions and tasks to the text:
1) развитие концепции комплекса маркетинга 2) происхождение концепции комплекса маркетинга 3) обоснование расширения комплекса 4) 12 компонентов комплекса маркетинга 5) продуктовые линии 6) политика разработки нового продукта 7) соответствующие уровни цен 8) ценовая политика 9) марочная политика 10) каналы между производством и конечным потребителем 11) добиться сотрудничества в отрасли 12) корпоративный имидж 13) продвижение для потребителей и В2В 14) упаковка и этикетка (ярлык) 15) создавать ми поддерживать продажи 16) склады 17) уровень запасов 18) характеристики и преимущества. которые создают удовлетворенность потребителей 19) затраты на производство 20) личные продажи, 21) связи с общественностью 22) продвижение и продвижение «из уст в уста» («сарафанное радио») 23) добавлять к каждой модели комплекса маркетинга различные ингредиенты 24) существующие маркетинговые условия
For more information about marketing mix - see units 1, 2 “Professional English in Use”
|