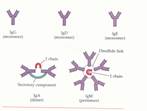
Classes of immunoglobulins
5 classes 1. Jg G- largest group, penetrate placenta Jg M 3. Jg A- secretory 4. Jg E- constitute the bulk of allergic antibodies Jg D
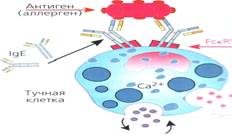
structure of immunoglobulins Allergy - immune response, accompanied by damage to the body's own tissues (VI Pytsky). Causes allergies - allergens. classification of allergens (By ADAdo) 1. Ekzoallergeny (household, food, medicines, animal, vegetable, industrial, microbial, fungal). 2. Endoallergeny (autoallergens) - natural (primary - nervous tissue, the lens, the colloid thyroid, testicular tissue); acquired (secondary - proteins altered the structure). Conditions conducive to the development of allergies. Classification of allergic reactions: immediate type hypersensitivity (ITH), delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) Classification Pathogenesis (P. and R. Coombs Jell 1969). I. reaginic Allergic reactions (anaphylactic) type II. Allergic reactions cytotoxic type. III. Allergic reactions type of immune IV. Allergic reactions of cell-mediated type Stage allergic reactions: - Immunological stage (stage immune responses) - Pathochemical (pathobiochemical) stage (stage biochemical reactions) - Pathophysiological stage (stage clinical manifestations) - Formation of antibodies or sensitized T lymphocytes (T c) at a primary contact with an allergen (sensitization) - The formation of an allergen or allergen antibody + + (c-T) repeated contact with an allergen Desensitization - reducing the body's sensitivity to an allergen (specific or nonspecific). Pseudoallergy reaction - group of reactions to similar manifestations of allergy, but differs in the absence of immunological stage. Developed under the influence of the factors causing mast cell degranulation and the release of biologically active substances.
|