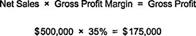Perpetual LIFO
Under the perpetual system the Inv account is constantly (or perpetually) changing. When a retailer purchases merch&ise, the retailer debits its Inv account for the cost of the merch&ise. When the retailer sells the mechandiseto its customers, the retailer credits its Inv account for the cost of the goods that were sold & debits its Cost of Goods Sold account for their cost. Rather than staying dormant as it does with the periodic method, the Inv account balance is continuously updated. Under the perpetual system, two transactions are recorded at the time that the merchandise is sold: (1) the sales amount is debited to Accounts Receivable or Cash & is credited to Sales, & (2) the cost of the merchandise sold is debited to Cost of Goods Sold & is credited to Inv.
perpetual system, "average"; Under the perpetual system, "average" means the average cost of the items in Inv as of the date of the sale. This average cost is multiplied by the № of units sold & is removed from the Inv account & debited to the Cost of Goods Sold account. We use the average as of the time of the sale because this is a perpetual method. (Note: Under the periodic system we wait until the year is over before computing the average cost.)
Companies sometimes need to determine the value of Inv when a physical count is impossible or impractical- in fire.
Gross profit method. The gross profit method estimates the value of Inv by applying the company's historical gross profit percentage to current-period infoabout net sales & the cost of goods available for sale. Gross profit equals net sales minus the cost of goods sold. The gross profit margin equals gross profit divided by net sales. If a company had net sales of $4,000,000 during the previous year & the cost of goods sold during that year was $2,600,000, then gross profit was $1,400,000 & the gross profit margin was 35%. If gross profit margin is 35%, then cost of goods sold is 65% of net sales. Net sales for the month were $500,000, beginning Inv was $50,000, & purchases during the month totaled $300,000. First, the company multiplies net sales for the month by the historical gross profit margin to estimate gross profit.
500-175= 325 (COGS); available for sale ( 50+300)-325=25 END INV The gross profit method produces a reasonably accurate result Retail Inv method. Retail businesses track both the cost & retail sales price of Inv.
Then, the estimated cost of ending Inv is found by multiplying the retail value of ending Inv by the cost-to-retail ratio.
Inv turnover = COGS/Average inv (№ of times) Days Inv on h& = 365 / inv turnover (days it takes to sell inv
|