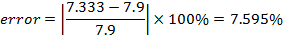Table 2.
Formulas. To find the mass of unknown mass, will be used the formula of the momentum (1). Hence, our system is in the equilibrium, can be clearly seen that the sum of the forces is equal to zero. Those means, force that acting to the right side, is equal to the force that acting to the left side. In formula form, it will look like:
In our Experiments that means:
In this formula was used the point of COM of the ruler, because in formula (1) should be used distance between object and COM, but in raw data in the Table 1 said that distance took from 0 cm. (Therefore, in calculations will not be used the gravitational force of the ruler, because it is fixed in the Centre of Mass). Calculating for Experiment 1. For calculation in the Experiment 1, need substitute raw data from Table 1 and Table to the formula (2).
Now, need to simplify formula (3):
Calculating for Experiment 2. For calculation in the Experiment 1, need to substitute raw data from Table 1 and Table to the formula (2).
Now, need to simplify formula (5):
Calculating the unknown masses using the formulas (4) and (6). To find the unknown values of masses need to get two simplified formulas from calculating in Experiment 1 and Experiment 2:
Now, for the easiest way of calculation, need to show
Now, need to minus formula (8) from formula (7). The result of that is:
Hence the result which was gotten from (9), could be find the first unknown mass of the pen:
=> =>
So, mass of the pan was found. Now substitute the value of the
The mass of the block was found. Part D (Calculating Errors) The original mass of the pen is Compare to experimental result, can be clearly seen that was made errors during the Experiments. Hence, errors should be calculated in the percentage.
Error of mass of the pen:
Error of mass of the block:
Object 2
In this object need to find the centre of mass of the two irregular shaped bars. To find the COM need to use at least two known masses. As the two known masses, will be used masses of the 10g and 50g.Hence, there will did 4 experiments. First of all, will be explained how each experiment was set up. Then will be shown the Table, which include the raw data during the experiment.
Part A1 (Experiment 1.1 with the 1st irregular shaped bar) First of all, will be explained how all system were set up. In the beginning iron stand was connected to the triple beam balance. Then, using light string, bar was randomly connected to the iron beam. Then two known masses hanged to the bar and fixed in position, where whole system was balanced. The Figure 4, which is above, will give the visual information about how equipment was set up.
|

 (Formula 1.1)
(Formula 1.1)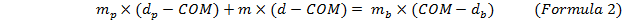
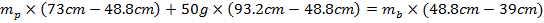 (3)
(3)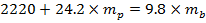 (Formula 4)
(Formula 4) (5)
(5) (Formula 6)
(Formula 6)
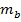 in terms of
in terms of 
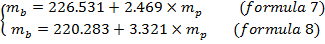
 (Formula 9)
(Formula 9)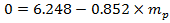 =>
=>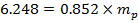 =>
=> =>
=>
 into the formula (7), to find the mass of the second object (block):
into the formula (7), to find the mass of the second object (block):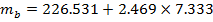 =>
=>
 and mass of the block is
and mass of the block is  .
.