Introduction. The object is in equilibrium, when sum of all forces operating on this object, is equal to zero
The object is in equilibrium, when sum of all forces operating on this object, is equal to zero. That means that the object has no any forces which make it rotate or being unsteady. According to Newton’s 3rd law, each action has counteraction which has same force, but directed to opposite direction. Force of reaction, is that kind of force, which keeps an object to be in equilibrium without participation of surrounding forces. As an example to it, the object which lies on the flat surface can serve. The object operates on a surface and a surface operates on object with the same force. Force with which object operates on a surface passes through its centre of gravity and perpendicular to the surface. Force of the reaction also passes through the centre of gravity of the object. Thereby, it is possible to confirm that the object which lies on the flat surface, without surrounding forces, is in equilibrium. Hence, if the force acting on object does not pass through its centre, when object is in equilibrium, the object will start to rotate aside to which force is directed. The reason for it, is the momentum. Momentum can be defined by the formula:
Where The experiment is made from two different objectives. Idea of the experiment is using the system if objects, which are in equilibrium, is to learn how to use and how balancing is important for. The first objective is to find the mass of the unknown object using balanced system of known objects and one metre ruler. For that part should know at least one known mass, which will be used, to find the mass of the unknown object or objects. The second part of the experiment is to find the mass and the centre of gravity of two irregular shaped bars, using at least two known masses.
|

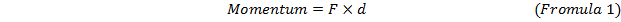
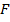 is the force that acting to object, and
is the force that acting to object, and 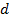 is the distance between centre of gravity of the object and the acting force.
is the distance between centre of gravity of the object and the acting force.


