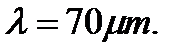Action potential.
2. Propagation of nervous impulse. 3. Mechanism of generation and propagation of action potential. 4. Telegraph equation. 5. Reliability factor. Break - 10 minutes Learning and teaching methods: - analysis and discussing of main and control questions; - solving of standard and situational problems; - testing; - correction of mistakes. Methods of the control of formed at classes competencies: - checking of the solution of standard and situational problems; - opinions exchanging at the studying of educational material; - testing on a computer (a student has to give the answers for test questions that contain minimal knowledge and skills – main definitions, theoretical questions of the theme). Students’ independent work - 25 minutes · Explain the context and find the ways of solving the problems. · Transform the formula and convert the unit of physical quantities to the International System of Units. · To find the ways of solution of given problems Problems: 1. At what distance х in unmyelinated nervous fiber the transmembrane potential difference 2. Transmembrane potential difference in unmyelinated nervous fiber decreases in two times at 3. Calculate the diameter D of axon if the electrical resistivity of the unit of membrane thickness is 4. In the place of unmyelinated nervous fiber transmembrane potential difference is
|

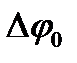 decreases in four times if the constant of fiber length is
decreases in four times if the constant of fiber length is 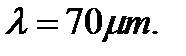
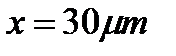 distance. Calculate the constant of fiber length
distance. Calculate the constant of fiber length  .
.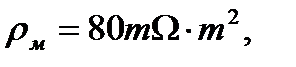 electrical resistivity of axoplasm is
electrical resistivity of axoplasm is 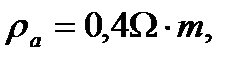 constant of length is
constant of length is 
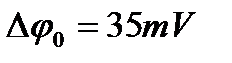 . Determine the potential difference
. Determine the potential difference 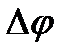 at the distance
at the distance 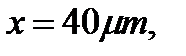 if the constant of length of this fiber is
if the constant of length of this fiber is