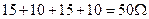D. Linear element of the circuit is such one whose characteristic is a straight line.
E. Battery is considered as voltage source.
Solution: D – wrong. Linear means that the defining characteristic is a straight line through the origin. Elements whose characteristics do not pass through the origin (even if it’s a straight line) or are not a straight line are said to be nonlinear. Answer: D.
71. We know RA, RB, and RC for delta. What is R2 for delta-to-star transformation? (see Fig. 1). A. R2 = (RA + RB + RC)/ RA B. R2 = RBRC/ (RA + RB + RC) C. R2 = RARC/ (RA + RB + RC) D. R2 = RBRA/ (RA + RB + RC) E. R2 = RBRC/ (RA + RB)
Fig.1
Solution:
Answer: C.
A. 2A B. – 1A C. 5A D. 1A E. – 2A
Solution: Both current sources are directed in the same direction, so the resulting current source will be presented as the sum I=2+3=5A. Answer: C.
Fig. 2
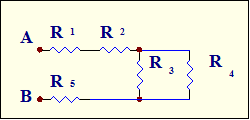
73. What is equivalent resistance for the circuit below if R1=15 Ω, R2=R5=10 Ω, R3=R4=30 Ω? A. 20 Ω B. 30 Ω C. 40 Ω D. 50 Ω; E. 60 Ω;
Solution: Let’s simplify R3 and R4 parallel arrangement:
Note: When two resistors connected in parallel and have the same value R, simplifying to one resistor will give value R/2. Now series arrangement of R1, R2, REQ and R5 will give Answer: D.
74. What is the value of VX for the circuit in Fig.5? A. 10V B.5V C.-5V D.-10V E. –15V
Solution: Let’s consider the node at the center of the circuit. Current from left branch is I1=8/2*103= 4mA. By KCL: 4+5–10–ix=0. ix= –1mA. Vx=10*103*(–1*10-3)= –10V
|



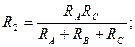

 72 What is the value of current I? (see Fig.2)
72 What is the value of current I? (see Fig.2)