Answer: E. 79. What is the voltage across points A and B (Fig.6)?
A. 5V B. – 5V C. 29V D. 1V E. – 1V
Solution: VAB=2+15–12=5V Answer: A. Fig.6
80. What is the correct equation according to KCL for node B for the circuit below? A. i3+i2+iS2=0 B. i3-i2+iS2=0 C. i3-i2-iS2=0 D. - i3+i2+iS2=0 E.- i3+i2-iS2=0
Solution: KCL states that the algebraic sum of the currents entering a node is zero at every instant. According to KCL equation for node B is following: – i3 + i2 – iS2 = 0 Answer: E.
81. When ideal switch is closed, the voltage is equal to______ and current is___, but when it is open current is equal to _____ and voltage is _________.
A. any value, 0, any value,0 B. any value, 0, 0, any value C. any value, any value, 0, 0 D. 0, any value, 0, any value E. 0, any value, any value, 0
Solution: When switch is closed, it’s a short circuit: v=0 when R=0 and i=any value. When switch is opened it’s an open circuit: i=0 when R=∞ and v=any value. Answer: D.
82. What element(s) can be used as voltage divider? A. resistor B. diode C. Transistor D. potentiometer E. resistor, potentiometer Answer: E.
83. When star-connected circuit is balanced and transformed into the delta, the value of side of equivalent delta is equal to ___ of the star’s ray. A.3 B.1/3 C.2/3 D.1/2 E. 2
Solution: Let all resistors in star-connected circuit have the value R, then the value of side of equivalent delta is
|

 79. What is the voltage across points A and B (Fig.6)?
79. What is the voltage across points A and B (Fig.6)?
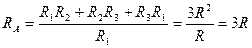 , which is equal to 3 times of the star’s ray.
, which is equal to 3 times of the star’s ray.


