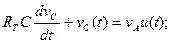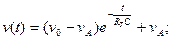Answer: A. 58. The first-order step response for RC circuit can be represented as ____ for t≥0
58. The first-order step response for RC circuit can be represented as ____ for t≥0 A. vC(t)=[vC(0) – vC(∞)]e-t/Tc B. vC(t)=[vC(∞) – vC(0)]e-t/Tc+ vC(∞) C. vC(t)=[vC(∞) – vC(0)]e-t/Tc D. vC(t)=[vC(∞) – vC(0)]e-t/Tc- vC(∞) E. vC(t)=[vC(0) – vC(∞)]e-t/Tc + vC(∞) Solution:
1)
2)
Answer: E. The real part of impedance is called ______ and imaginary part is called _____. The real part of admittance is called ______ and imaginary part is called _____. A. resistivity,…conductivity,… susceptance,… conductance B. reactance,…resistance,… susceptance,… conductance C. resistance,…reactance,… susceptance,.. conductance D. reactance,…resistance,…conductance,…susceptance E. resistance,…reactance,…conductance,…susceptance
Solution: Z = R ± jX Y = G ± jB The real part of impedance is called resistance and imaginary part is called reactance. The real part of admittance is called conductance and imaginary part is called susceptance. Answer: E.
60. The general view of exponential function is A. v(t)=[VAe-t] B. v(t)=[VAe-t] u(t) C. v(t)=[VAe-t/Tc] D. v(t)=[VAe-t/Tc]u(t) E. v(t)=[VAet/Tc]u(t) Answer: D.
61. Two circuits are said to be equivalent if they have A. the same view after reduction process B. identical i-v-characteristics after reduction process C. identical i-v-characteristics at a specified pair of terminals D. identical i-v-characteristics E. identical parameters of elements
|