Reading Comprehension
1. Review the whole text again. Outline the subject matter of the text, its components structure, topic sentences and main ideas. Use the following phrases: – The text deals with … (speaks about, presents, shows, points out, discusses, reviews, throws light on, traces the history of, etc) – The subject matter of the text is … – The text can be segmented into … paragraphs. – The first (second, third, fourth, etc.) paragraph considers … (deals with, informs of, describes, etc.) – The topic sentence of the first (second, third, fourth, etc.) paragraph is … – The main idea of the first (second, third, fourth, etc.) paragraph is … – The main idea of the text is … – The conclusion the author came to is … – The reasons for this conclusion are … 2. Say whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your choice. Use the given phrases: That’s right… Exactly. Quite so… I fully agree to it… I don’t think this is the case… Quite the contrary… Not quite. It’s unlikely… Just the reverse…
1. The rational numbers complete the system of real numbers. 2. A simple quadratic equation like 3. Early consideration of the square root of a negative number was crowned with success. 4. An equation has as many roots as its degree. 5. No general algebraic solution is possible for the polynomial equation of degree greater than four. 6. In algebra x always stands for number. 7. A complex number 8. L.Euler introduced the term “complex number”. 9. Gauss gave the last proof for the theorem when he was seventy. 10. For the purpose of solving polynomial equations we need to extend the number system further. 3. Answer the following questions: 1. Is there any necessity for the invention of new numbers in the evolution of math? 2. Why were fractions invented? 3. Why were negative numbers, rational numbers and irrational numbers invented? 4. What numbers complete the system of real numbers? 5. Does a simple quadratic equation like 6. What caused the invention of the pure imaginary numbers and the complex numbers? 7. What does the word “imaginary” reflect? 8. Why did early consideration of the square root of a negative number bring unvarying rejection? 9. What is G.Cardano credited with? 10. Who contributed the terms “real” and “imaginary”? 11. Who introduced the term “complex number”? 12. What theorem did K.F.Gauss prove in 1799? 13. How many proofs of this theorem are there? 14. What theorem is called “fundamental theorem of algebra”? 15. Do they need to extend the number system further? 4. For each definition choose a term from the left column:
|

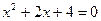 has no roots among either the real or pure imaginary numbers.
has no roots among either the real or pure imaginary numbers.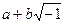 is essentially a pair of real numbers
is essentially a pair of real numbers 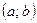 .
.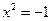 have no root among all real numbers?
have no root among all real numbers?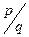 , where
, where  and
and 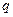 are integers, with
are integers, with  , where
, where 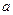 and
and  are real numbers and
are real numbers and 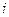 is called the imaginary unit, where
is called the imaginary unit, where 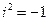 .
.
 .
.



