Determining the principal stresses and the principal planes position
Let us consider the reverse problem. The normal and shearing stresses acting on the element plane are given (Fig. 2.8 a). It is necessary to determine the principal planes positions and the principal stress values. Let us consider the trihedral prism with the ABC base (Fig. 2.8 b). Take Projecting all forces on the direction Now we will project all forces on the
Having cancelled by dA introducing the function of double angles, we get
a) b)
Fig. 2.8. The
After the transposition we have
We get the formulae of the principal stresses determination when to use double angle functions are applied to transpose:
The shearing stresses on the principal plane are always equal to zero.
2.12. The relation between the deformations and the stresses for the plane and general stresses (a general form of Hook’s law)
Determine the
Fig. 2.9.
The
and simultaneously the unit lateral strain in the horizontal direction is equal to
Under the action of Summing up the deformations we get
The formulas express the general form of Hook’s law of the plane stress. If the
Analogously for the volumetric stress (the three
The equations (2.19) are the general form of Hook’s law for the general state of stress. The deformations in the principal stress directions are called principal strains. We can determine the volume change under deforming if The unit volume change:
Substituting the
From the formula (2.20) it follows that Poisson’s ratio cannot be more than 0, 5.
|

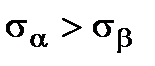 . The angle
. The angle  will be counted off from the larger stress direction until the normal to the plane. We will take the against the clock direction as positive. The inclined plane area will be denoted by dA. Then, the vertical plane area will be
will be counted off from the larger stress direction until the normal to the plane. We will take the against the clock direction as positive. The inclined plane area will be denoted by dA. Then, the vertical plane area will be  and the horizontal one will be -
and the horizontal one will be - 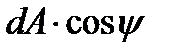 .
. , we get
, we get 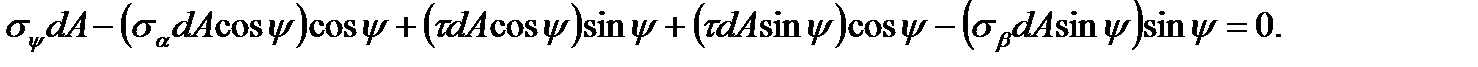
 direction:
direction: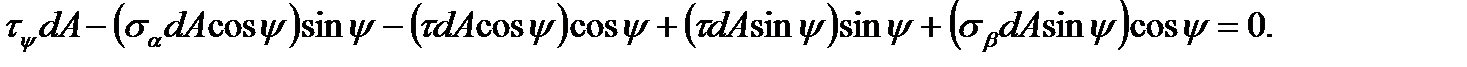
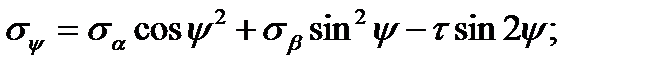 (2.11)
(2.11)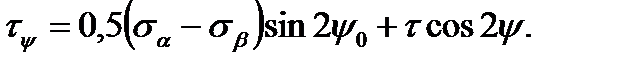 (2.12)
(2.12)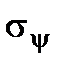 value is continuously changing with the angle change of the y plane incline. To find the principal planes position we have to equal the
value is continuously changing with the angle change of the y plane incline. To find the principal planes position we have to equal the 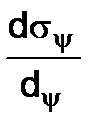 derivative to zero, then we get:
derivative to zero, then we get: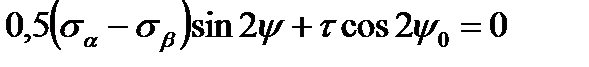
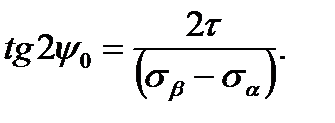 (2.13)
(2.13)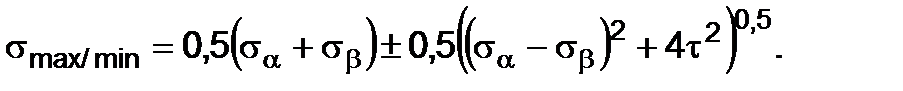 (2. 14)
(2. 14) and
and  deformations for the plane stress in the principal stress directions (Fig. 2.9).For this Hook’s law is used in the unaxial state of stress.
deformations for the plane stress in the principal stress directions (Fig. 2.9).For this Hook’s law is used in the unaxial state of stress.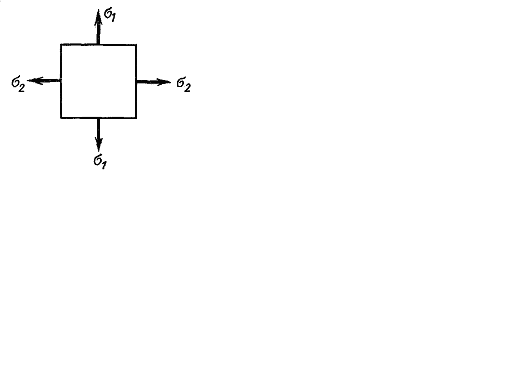
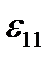 unit strain in the vertical direction under the action of the
unit strain in the vertical direction under the action of the 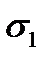 stress in equal to
stress in equal to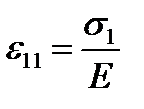 . (2.15)
. (2.15)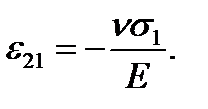 (2.16)
(2.16) alone we have the elongation
alone we have the elongation 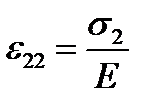 in the horizontal direction and the contraction
in the horizontal direction and the contraction 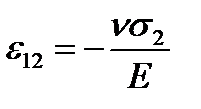 in the vertical direction (n - Poisson’s ratio).
in the vertical direction (n - Poisson’s ratio).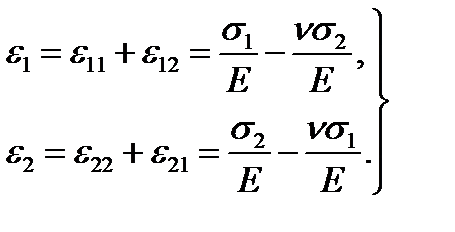 (2.17)
(2.17)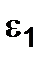 and
and 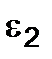 deformations are known, solving the equation (2.17) then we get the following formulas:
deformations are known, solving the equation (2.17) then we get the following formulas: (2.18)
(2.18)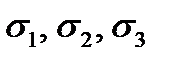 principal stresses are not equal to zero) we get
principal stresses are not equal to zero) we get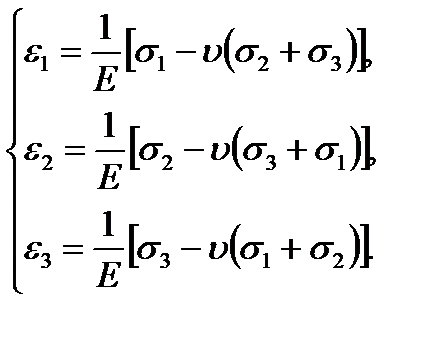 (2.19)
(2.19)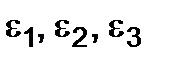 are known. Take a cube with the
are known. Take a cube with the 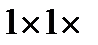 1 cm dimensions. Its volume before deforming equals
1 cm dimensions. Its volume before deforming equals  =1 сm3. The volume after deforming is equal to
=1 сm3. The volume after deforming is equal to 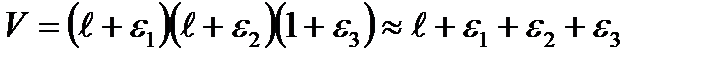 (the
(the 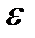 products are ignored since they are small compared with
products are ignored since they are small compared with 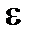 ).
).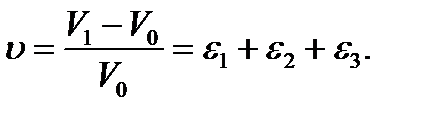 (2.20)
(2.20)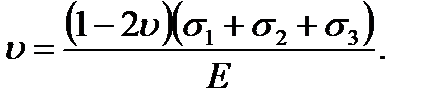 (2.21)
(2.21)


